一,概念
1,排序
排序,就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或某些关键字的大小,递增或递减的排列起来的操作。 平时的上下文中,如果提到排序,通常指的是排升序(非降序)。 通常意义上的排序,都是指的原地排序(in place sort)。
2,稳定性
两个相等的数据,如果经过排序后,排序算法能保证其相对位置不发生变化,则我们称该算法是具备稳定性的排序算法。
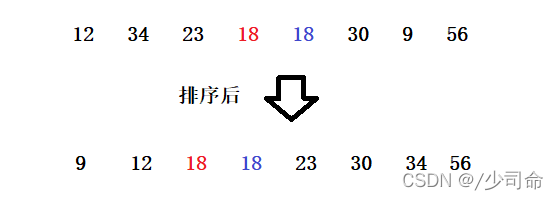
或者我们说没有跳跃的排序也是稳定的排序

二,排序详解
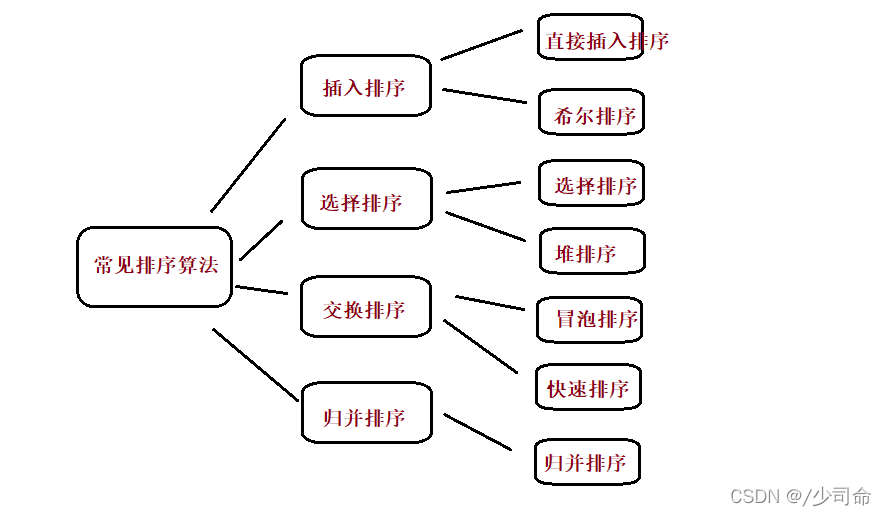
1,插入排序
①直接插入排序
整个区间被分为
1. 有序区间
2. 无序区间
每次选择无序区间的第一个元素,在有序区间内选择合适的位置插入
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
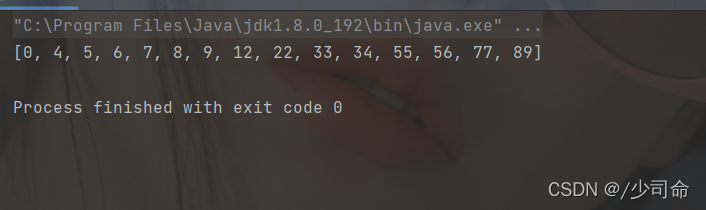
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
insertSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
/**
* 时间复杂度:
* 最好:O(N) -> 数据是有序的
* 最坏:O(N^2) -> 无序的数据
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:稳定排序
* @param array
*/
public static void insertSort(int[] array) {
for(int i = 1;i < array.length;i++) {//n-1
int tmp = array[i];
int j = i-1;
for(; j >= 0;j--) {//n-1
if(array[j] > tmp) {
array[j+1] = array[j];
}else{
//array[j+1] = tmp;
break;
}
}
array[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
|
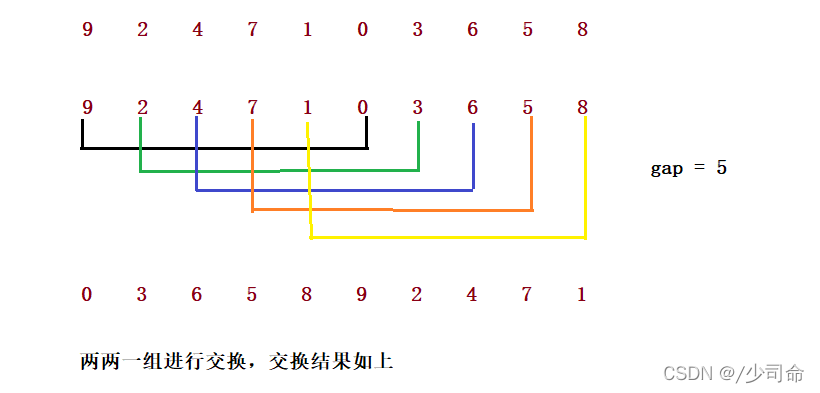
②希尔排序
希尔排序法又称缩小增量法。希尔排序法的基本思想是:先选定一个整数,把待排序文件中所有记录分成个组,所有 距离为的记录分在同一组内,并对每一组内的记录进行排序。然后,取,重复上述分组和排序的工作。当到达=1时, 所有记录在统一组内排好序。
1. 希尔排序是对直接插入排序的优化。
2. 当gap > 1时都是预排序,目的是让数组更接近于有序。当gap == 1时,数组已经接近有序的了,这样就会很 快。这样整体而言,可以达到优化的效果。我们实现后可以进行性能测试的对比。

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
/**
* 时间复杂度:不好算 n^1.3 - n^1.5 之间
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定的排序
* 技巧:如果在比较的过程当中 没有发生跳跃式的交换 那么就是稳定的
* @param array
*
*
* @param array 排序的数组
* @param gap 每组的间隔 -》 组数
*/
public static void shell(int[] array,int gap) {
for (int i = gap; i < array.length; i++) {
int tmp = array[i];
int j = i-gap;
for (; j >= 0; j -= gap) {
if(array[j] > tmp) {
array[j+gap] = array[j];
}else {
break;
}
}
array[j+gap] = tmp;
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
shell(array,5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
|

2,选择排序
①直接选择排序
每一次从无序区间选出最大(或最小)的一个元素,存放在无序区间的最后(或最前),直到全部待排序的数据元素排完 。

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
selectSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/**
* 时间复杂度:
* 最好:O(N^2)
* 最坏:O(N^2)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定的
* @param array
*/
public static void selectSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < array.length; j++) {
if(array[j] < array[i]) {
int tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
|
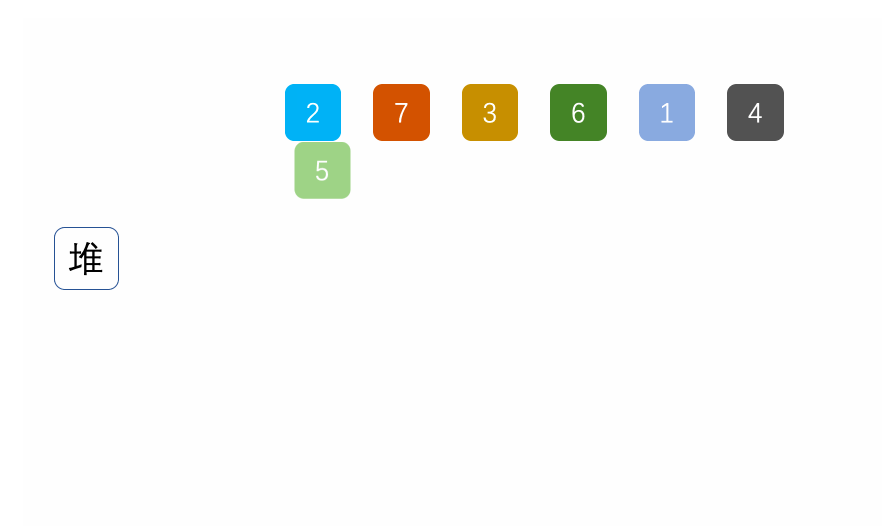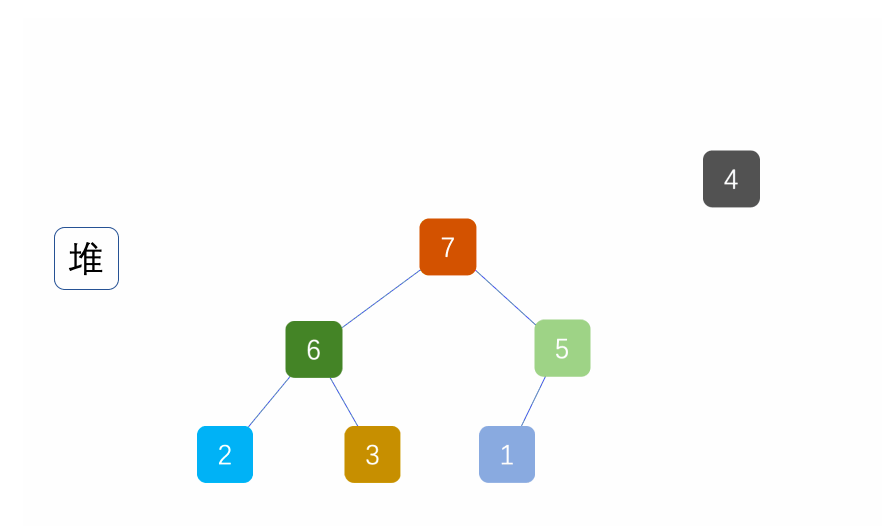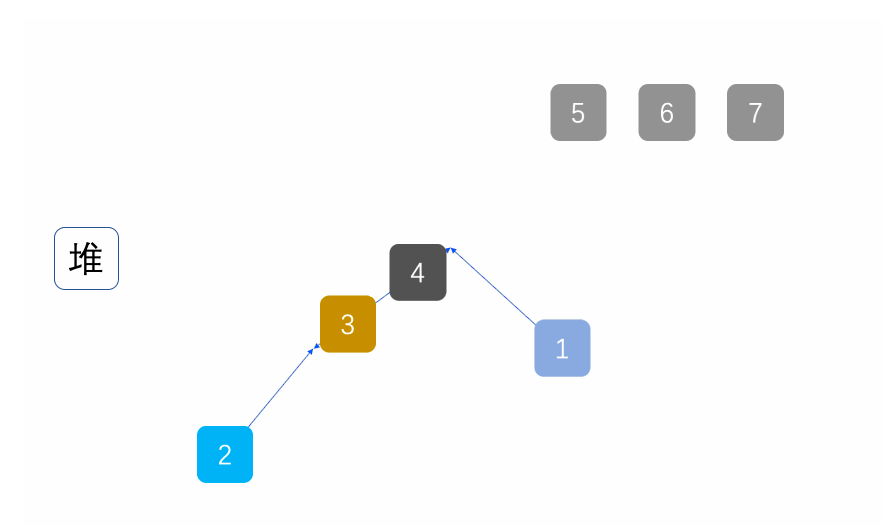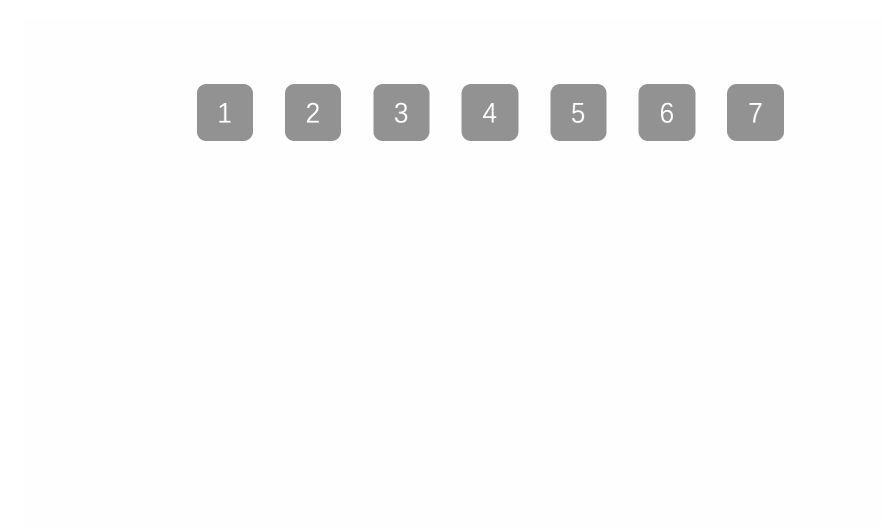
②堆排序
基本原理也是选择排序,只是不在使用遍历的方式查找无序区间的最大的数,而是通过堆来选择无序区间的最大的数。
注意: 排升序要建大堆;排降序要建小堆。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
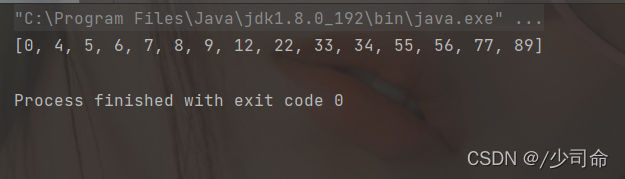
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
heapSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
public static void siftDown(int[] array,int root,int len) {
int parent = root;
int child = 2*parent+1;
while (child < len) {
if(child+1 < len && array[child] < array[child+1]) {
child++;
}
//child的下标就是左右孩子的最大值下标
if(array[child] > array[parent]) {
int tmp = array[child];
array[child] = array[parent];
array[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public static void createHeap(int[] array) {
//从小到大排序 -》 大根堆
for (int i = (array.length-1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0 ; i--) {
siftDown(array,i,array.length);
}
}
/**
* 时间复杂度:O(N*logN) 都是这个时间复杂度
* 复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定的排序
* @param array
*/
public static void heapSort(int[] array) {
createHeap(array);//O(n)
int end = array.length-1;
while (end > 0) {//O(N*logN)
int tmp = array[end];
array[end] = array[0];
array[0] = tmp;
siftDown(array,0,end);
end--;
}
}
|

3,交换排序
①冒泡排序
在无序区间,通过相邻数的比较,将最大的数冒泡到无序区间的最后,持续这个过程,直到数组整体有序
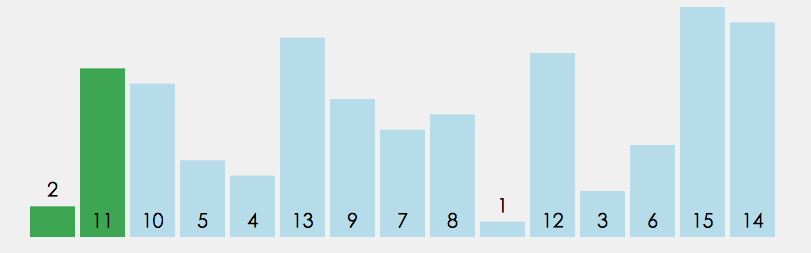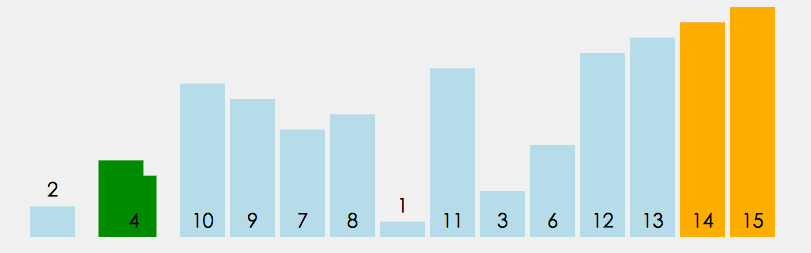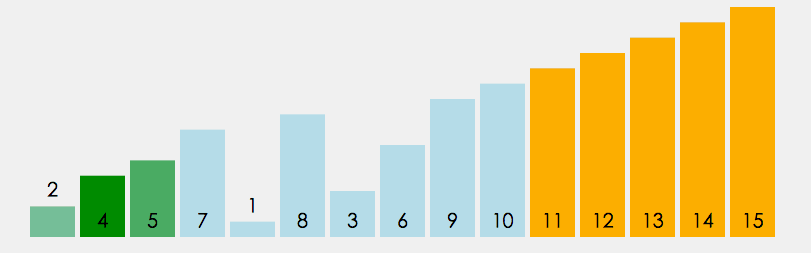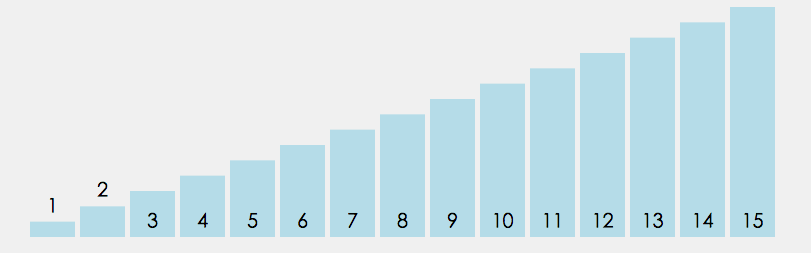
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
/**
* 时间复杂度:
* 最好最坏都是O(n^2)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:稳定的排序
* 冒泡 直接插入
* @param array
*/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++) {
if(array[j] > array[j+1]) {
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
|

②快速排序
1. 从待排序区间选择一个数,作为基准值(pivot);
2. Partition: 遍历整个待排序区间,将比基准值小的(可以包含相等的)放到基准值的左边,将比基准值大的(可 以包含相等的)放到基准值的右边;
3. 采用分治思想,对左右两个小区间按照同样的方式处理,直到小区间的长度 == 1,代表已经有序,或者小区间 的长度 == 0,代表没有数据。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
quickSort1(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
public static int partition(int[] array,int low,int high) {
int tmp = array[low];
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && array[high] >= tmp) {
high--;
}
array[low] = array[high];
while (low < high && array[low] <= tmp) {
low++;
}
array[high] = array[low];
}
array[low] = tmp;
return low;
}
public static void quick(int[] array,int start,int end) {
if(start >= end) {
return;
}
int mid = (start+end)/2;
int pivot = partition(array,start,end);
quick(array,start,pivot-1);
quick(array,pivot+1,end);
}
/**
* 时间复杂度:
* 最好:O(n*logn) 均匀的分割下
* 最坏:o(n^2) 数据有序的时候
* 空间复杂度:
* 最好:logn
* 最坏:O(n)
* 稳定性:不稳定的排序
*
* k*n*logn
* 2
* 1.2
* @param array
*/
public static void quickSort1(int[] array) {
quick(array,0,array.length-1);
}
|

4,归并排序
归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子 序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
mergeSort1(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
public static void merge(int[] array,int low,int mid,int high) {
int s1 = low;
int e1 = mid;
int s2 = mid+1;
int e2 = high;
int[] tmp = new int[high-low+1];
int k = 0;//代表tmp数组的下标
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2) {
if(array[s1] <= array[s2]) {
tmp[k++] = array[s1++];
}else {
tmp[k++] = array[s2++];
}
}
//有2种情况
while (s1 <= e1){
//说明第2个归并段没有了数据 把第1个归并段剩下的数据 全部拷贝过来
tmp[k++] = array[s1++];
}
while (s2 <= e2) {
//说明第1个归并段没有了数据 把第2个归并段剩下的数据 全部拷贝过来
tmp[k++] = array[s2++];
}
//tmp数组当中 存储的就是当前归并好的数据
for (int i = 0; i < tmp.length; i++) {
array[i+low] = tmp[i];
}
}
public static void mergeSortInternal(int[] array,int low,int high) {
if(low >= high) {
return;
}
int mid = (low+high) / 2;
mergeSortInternal(array,low,mid);
mergeSortInternal(array,mid+1,high);
//合并的过程
merge(array,low,mid,high);
}
/**
* 时间复杂度: O(N*log n)
* 空间复杂度:O(N)
* 稳定性:稳定的
* @param array
*/
public static void mergeSort1(int[] array) {
mergeSortInternal(array, 0,array.length-1);
}
|