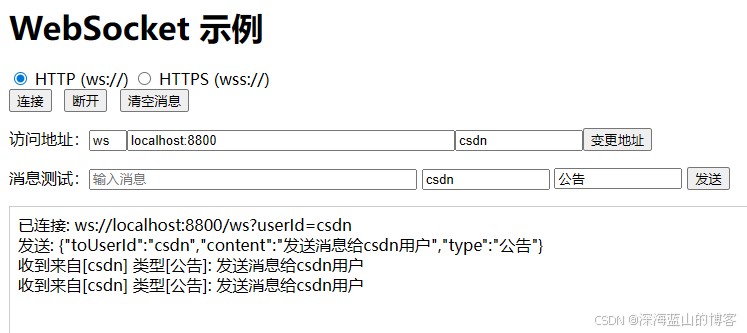
多态参数
就像我们现实生活中电脑的usb接口,我们既可以接受手机对象,又可以接受相机对象,等等,体现了接口的多态,查看以下代码
接口:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
package InterfaceM;
public interface Interface { public void join(); public void stop(); } |
手机类:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
package InterfaceM;
public class Phone implements Interface{
@Override public void join() { System.out.println(this.toString()+"接入了电脑"); }
@Override public void stop() { System.out.println(this.toString()+"离开了电脑"); } } |
相机类;
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
package InterfaceM;
public class Camera implements Interface { @Override public void join() { System.out.println(this.toString()+"接入了电脑"); }
@Override public void stop() { System.out.println(this.toString()+"离开了电脑"); } } |
电脑类:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
package InterfaceM;
public class Computer { public void work(Interface interF){ interF.join(); interF.stop(); }
public static void main(String[] args) { Camera camera=new Camera(); Phone phone=new Phone(); //将相机接入电脑 Computer computer=new Computer(); computer.work(camera); computer.work(phone); } } |
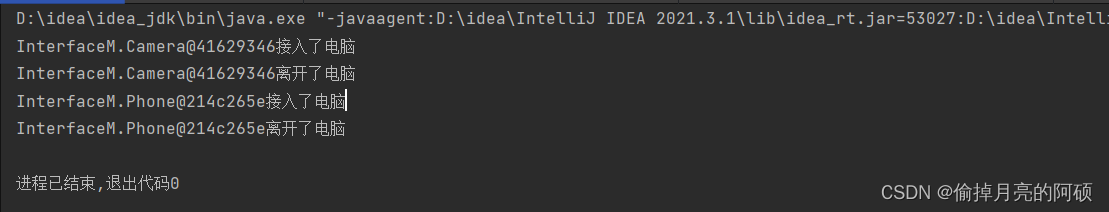
多态数组
在computer类型的数组中,我们即可以存放多种对象类型的数组。而且对应不同的数组对象,我们可以做出不同的事件。
在刚才的上述代码中我们在phone类中加入call功能,要求有插入phone时,调用call函数
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
package InterfaceM;
public class Computer { public void work(Interface interF){ interF.join(); interF.stop(); }
public static void main(String[] args) { Camera camera=new Camera(); Phone phone=new Phone(); //将相机接入电脑 Interface []interf=new Interface[2]; interf[0]=camera; interf[1]=phone; Computer computer=new Computer(); for (int i=0;i<interf.length;i++){ computer.work(interf[i]); if (interf[i]instanceof Phone){ phone.call(); } } } } |
接口的多态传递现象
如果我们运行以下代码,由于ih并没有被teacher继承,会发生报错,但是当我们用ig继承ih之后,我们可以发现这样就不会报错。这样体现出了多态的继承传递现象。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { IG ig=new Teacher(); IH ih=new Teacher(); } } interface IH{} interface IG{} class Teacher implements IG{
} |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { IG ig=new Teacher(); IH ih=new Teacher(); } } interface IH{} interface IG extends IH{} class Teacher implements IG{
} |