前言:
前面文章分析了单向链表,并给出了python和C++实现:单链表从原理到实现,python和C++两个版本
本文介绍的双向链表是在单向链表基础上的一个改进,每个节点指向其直接前驱和直接后继节点。因此,从双向链表的任意位置开始,都能访问所有的节点。
一、双向链表优缺点
双向链表的缺点:
从节点的结构上可以看出,双向链表的所需的存储空间大于单向链表。同时,对于插入和删除等操作来说,双向链表的节点操作更加复杂,涉及到节点的前后两个节点。
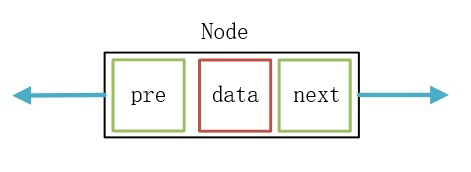
双向链表的节点:
对于双向链表来说,它的每个节点要指向“直接前驱”和“直接后继”,所以节点类需要含有两个指针域。指向直接前驱的指针使用pre表示,指向后继的指针使用next表示。
二、C++实现分析
(1)节点类
双向链表的节点含有两个指针域,即直接前驱pre和直接后继next。节点类采用的是模板实现,这样其所存储的数据就不再依赖于特定类型。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
template<class T> class Node { public: Node() {} Node *pre; Node *next; // 由于data属性是私有的 // 所以采用get和set对data进行处理 void setData(T data) { this->data = data; } T getData() { return this->data; } private: T data; }; |
(2)链表类分析
链表类应该包含基本的增、改、删、查等操作,由于其各种功能的实现是很相似的,
所以下面给出了需要实现的典型函数:
- 构造函数:
- isEmpty()判断是否为空;
- size()返回链表长度;
- insert()头插、尾插、中间插入节点;
- delete()删除节点;
- getNode()获取节点;
- traversal()遍历链表;
链表类的定义如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
template<class P> class DoubleLinkedList { public: DoubleLinkedList(); bool isEmpty(); Node<P> *getNode(int index); int size(); void insert(int data, int index); void traversal(); void remove(int index);
private: Node<P> *head; }; |
(3)链表类构造函数
初始化时需要创建头节点,作为头指针:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
template<class P> DoubleLinkedList<P>::DoubleLinkedList() { // 创建头结点 head = new Node<P>(); head->pre = NULL; head->next = NULL; head->setData(666); } |
(4)isEmpty()判断是否为空
对于双向链表来说,判断是否为空只需要判断头指针是否指向其他Node节点:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
template<class P> bool DoubleLinkedList<P>::isEmpty() { if (head->next == NULL) { return true; } else { return false; } } |
(5)size()获取链表长度
获取链表长度时需要判断链表是否为空,从而确定是否采用遍历的方式计算链表的长度。
由于采用的不是循环链表,所以循环的结束条件是判断是否指向空节点:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
template<class P> int DoubleLinkedList<P>::size() { if (isEmpty()) { return 0; } else { int count = 0; Node<P> *current = head->next; // 循环结束条件 while (current!=NULL) { current = current->next; count++; } return count; } } |
(6)getNode()获取节点
在插入和删除等操作中,需要频繁的进行节点获取操作。
所以应该封装为单独的函数用于节点获取,如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
template<class P> Node<P> *DoubleLinkedList<P>::getNode(int index) { Node<P> *current = head; int currentCount = 0; // 循环结束条件 while (currentCount<=index) { current = current->next; currentCount++; } return current; } |
(7)insert()插入节点
插入节点依旧包含头插法,尾插法和任意位置的插入。插入操作与单向链表的最大区别在于节点的指针移动较为复杂,需要将插入位置前后两个节点与新节点均建立联系:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
template<class P> void DoubleLinkedList<P>::insert(int data, int index) { Node<P> *node = new Node<P>(); node->setData(data); // 1、列表为空时 if (isEmpty()) { head->next = node; node->pre = head; return; } // 2、头插法 if (index == 0) { node->next = head->next; head->next->pre = node; node->pre = head; head->next = node; } // 3、尾插法 else if (index >= this->size() - 1) { // printf("index %d, size %d \n", index, this->size()); Node<P> *temp = this->getNode(this->size()-1); temp->next = node; node->pre = temp; } // 4、任意位置插入 else { Node<P> *pre = this->getNode(index); Node<P> *next = pre->next; node->next = pre->next; node->pre = pre; pre->next = node; node->next->pre = node; } } |
(8)、remove()删除节点
前面已经定义了用于获取节点的getNode()函数,所以remove()函数只需要进行指针移动操作。
将所要删除的节点的直接前驱节点和直接后继节点相连:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
template<class P> void DoubleLinkedList<P>::remove(int index) { // 保证索引有意义 if ((index < (this->size()-1)) && (index>0)) { Node<P> *node = this->getNode(index); Node<P> *pre = node->pre; Node<P> *next = node->next; pre->next = next; next->pre = pre; } } |
(9)traversal()遍历链表函数
虽然可以从双向链表的任一个节点开始遍历整个链表,但是下面的实现依旧是从头结点开始的,循环的结束依旧是指向空指针:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
template<class P> void DoubleLinkedList<P>::traversal() { if (!isEmpty()) { Node<P> *current = head; while (current) { cout << current->getData() << endl; current = current->next; } } } |