前言
YOLOV5模型从发布到现在都是炙手可热的目标检测模型,被广泛运用于各大场景之中。因此,我们不光要知道如何进行yolov5模型的训练,而且还要知道怎么进行部署应用。在本篇博客中,我将利用yolov5模型简单的实现从摄像头端到web端的部署应用demo,为读者提供一些部署思路。
一、YOLOV5的强大之处
你与目标检测高手之差一个YOLOV5模型。YOLOV5可以说是现目前几乎将所有目标检测tricks运用于一身的模型了。在它身上能找到很多目前主流的数据增强、模型训练、模型后处理的方法,下面我们就简单总结一下yolov5所使用到的方法:
yolov5增加的功能:
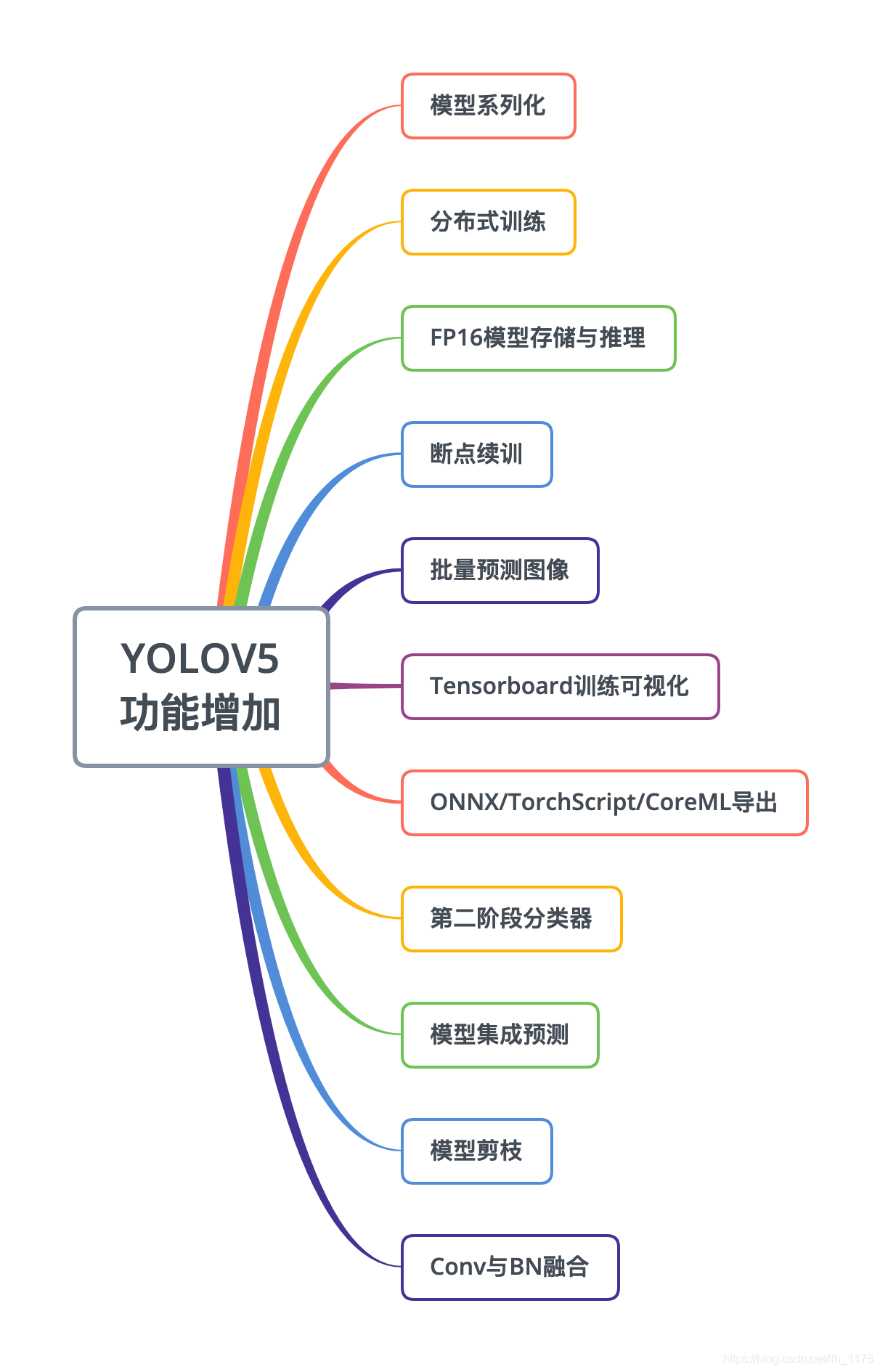
yolov5训练和预测的tricks:
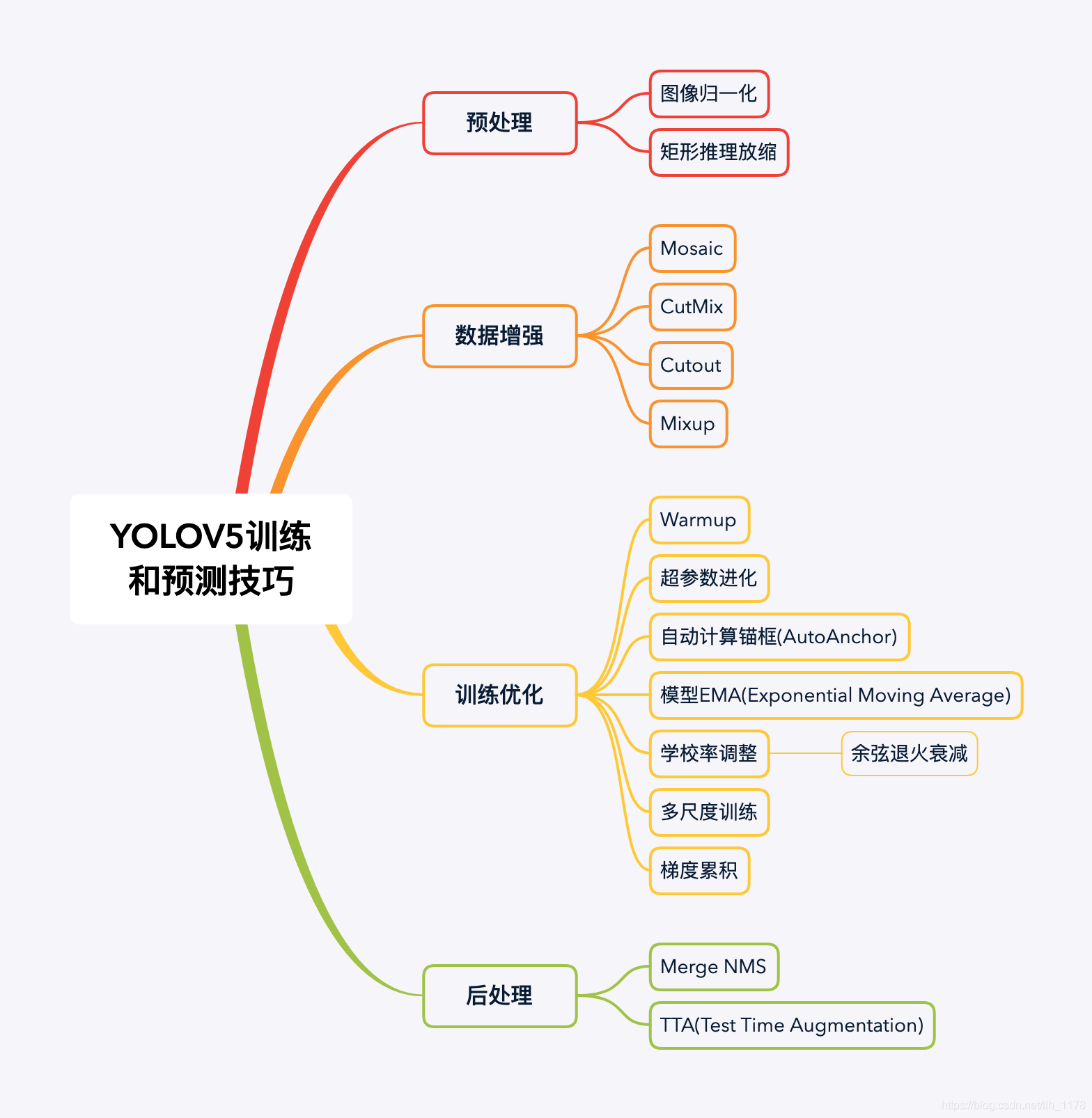
二、YOLOV5部署多路摄像头的web应用
1.多路摄像头读取
在此篇博客中,采用了yolov5源码的datasets.py代码中的LoadStreams类进行多路摄像头视频流的读取。因为,我们只会用到datasets.py中视频流读取的部分代码,所以,将其提取出来,新建一个camera.py文件,下面则是camera.py文件的代码部分:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 |
# coding:utf-8 import os import cv2 import glob import time import numpy as np from pathlib import Path from utils.datasets import letterbox from threading import Thread from utils.general import clean_str
img_formats = ['bmp', 'jpg', 'jpeg', 'png', 'tif', 'tiff', 'dng', 'webp'] # acceptable image suffixes vid_formats = ['mov', 'avi', 'mp4', 'mpg', 'mpeg', 'm4v', 'wmv', 'mkv'] # acceptable video suffixes
class LoadImages: # for inference def __init__(self, path, img_size=640, stride=32): p = str(Path(path).absolute()) # os-agnostic absolute path if '*' in p: files = sorted(glob.glob(p, recursive=True)) # glob elif os.path.isdir(p): files = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(p, '*.*'))) # dir elif os.path.isfile(p): files = [p] # files else: raise Exception(f'ERROR: {p} does not exist')
images = [x for x in files if x.split('.')[-1].lower() in img_formats] videos = [x for x in files if x.split('.')[-1].lower() in vid_formats] ni, nv = len(images), len(videos)
self.img_size = img_size self.stride = stride self.files = images + videos self.nf = ni + nv # number of files self.video_flag = [False] * ni + [True] * nv self.mode = 'image' if any(videos): self.new_video(videos[0]) # new video else: self.cap = None assert self.nf > 0, f'No images or videos found in {p}. ' \ f'Supported formats are:\nimages: {img_formats}\nvideos: {vid_formats}'
def __iter__(self): self.count = 0 return self
def __next__(self): if self.count == self.nf: raise StopIteration path = self.files[self.count]
if self.video_flag[self.count]: # Read video self.mode = 'video' ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read() if not ret_val: self.count += 1 self.cap.release() if self.count == self.nf: # last video raise StopIteration else: path = self.files[self.count] self.new_video(path) ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
self.frame += 1 print(f'video {self.count + 1}/{self.nf} ({self.frame}/{self.nframes}) {path}: ', end='')
else: # Read image self.count += 1 img0 = cv2.imread(path) # BGR assert img0 is not None, 'Image Not Found ' + path print(f'image {self.count}/{self.nf} {path}: ', end='')
# Padded resize img = letterbox(img0, self.img_size, stride=self.stride)[0]
# Convert img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416 img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return path, img, img0, self.cap
def new_video(self, path): self.frame = 0 self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(path) self.nframes = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
def __len__(self): return self.nf # number of files
class LoadWebcam: # for inference def __init__(self, pipe='0', img_size=640, stride=32): self.img_size = img_size self.stride = stride
if pipe.isnumeric(): pipe = eval(pipe) # local camera # pipe = 'rtsp://192.168.1.64/1' # IP camera # pipe = 'rtsp://username:password@192.168.1.64/1' # IP camera with login # pipe = 'http://wmccpinetop.axiscam.net/mjpg/video.mjpg' # IP golf camera
self.pipe = pipe self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(pipe) # video capture object self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_BUFFERSIZE, 3) # set buffer size
def __iter__(self): self.count = -1 return self
def __next__(self): self.count += 1 if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit self.cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() raise StopIteration
# Read frame if self.pipe == 0: # local camera ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read() img0 = cv2.flip(img0, 1) # flip left-right else: # IP camera n = 0 while True: n += 1 self.cap.grab() if n % 30 == 0: # skip frames ret_val, img0 = self.cap.retrieve() if ret_val: break
assert ret_val, f'Camera Error {self.pipe}' img_path = 'webcam.jpg' print(f'webcam {self.count}: ', end='')
# Padded resize img = letterbox(img0, self.img_size, stride=self.stride)[0]
# Convert img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416 img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return img_path, img, img0, None
def __len__(self): return 0
class LoadStreams: # multiple IP or RTSP cameras def __init__(self, sources='streams.txt', img_size=640, stride=32): self.mode = 'stream' self.img_size = img_size self.stride = stride
if os.path.isfile(sources): with open(sources, 'r') as f: sources = [x.strip() for x in f.read().strip().splitlines() if len(x.strip())] else: sources = [sources]
n = len(sources) self.imgs = [None] * n self.sources = [clean_str(x) for x in sources] # clean source names for later for i, s in enumerate(sources): # Start the thread to read frames from the video stream print(f'{i + 1}/{n}: {s}... ', end='') cap = cv2.VideoCapture(eval(s) if s.isnumeric() else s) assert cap.isOpened(), f'Failed to open {s}' w = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)) h = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)) fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) % 100 _, self.imgs[i] = cap.read() # guarantee first frame thread = Thread(target=self.update, args=([i, cap]), daemon=True) print(f' success ({w}x{h} at {fps:.2f} FPS).') thread.start() print('') # newline
# check for common shapes s = np.stack([letterbox(x, self.img_size, stride=self.stride)[0].shape for x in self.imgs], 0) # shapes self.rect = np.unique(s, axis=0).shape[0] == 1 # rect inference if all shapes equal if not self.rect: print('WARNING: Different stream shapes detected. For optimal performance supply similarly-shaped streams.')
def update(self, index, cap): # Read next stream frame in a daemon thread n = 0 while cap.isOpened(): n += 1 # _, self.imgs[index] = cap.read() cap.grab() if n == 4: # read every 4th frame success, im = cap.retrieve() self.imgs[index] = im if success else self.imgs[index] * 0 n = 0 time.sleep(0.01) # wait time
def __iter__(self): self.count = -1 return self
def __next__(self): self.count += 1 img0 = self.imgs.copy() if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit cv2.destroyAllWindows() raise StopIteration
# Letterbox img = [letterbox(x, self.img_size, auto=self.rect, stride=self.stride)[0] for x in img0]
# Stack img = np.stack(img, 0)
# Convert img = img[:, :, :, ::-1].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2) # BGR to RGB, to bsx3x416x416 img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return self.sources, img, img0, None
def __len__(self): return 0 # 1E12 frames = 32 streams at 30 FPS for 30 years |
2.模型封装
接下来,我们借助detect.py文件对yolov5模型进行接口封装,使其提供模型推理能力。新建一个yolov5.py文件,构建一个名为darknet的类,使用函数detect,提供目标检测能力。其代码如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 |
# coding:utf-8 import cv2 import json import time import torch import numpy as np from camera import LoadStreams, LoadImages from utils.torch_utils import select_device from models.experimental import attempt_load from utils.general import non_max_suppression, scale_coords, letterbox, check_imshow
class Darknet(object): """docstring for Darknet""" def __init__(self, opt): self.opt = opt self.device = select_device(self.opt["device"]) self.half = self.device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA self.model = attempt_load(self.opt["weights"], map_location=self.device) self.stride = int(self.model.stride.max()) self.model.to(self.device).eval() self.names = self.model.module.names if hasattr(self.model, 'module') else self.model.names if self.half: self.model.half() self.source = self.opt["source"] self.webcam = self.source.isnumeric() or self.source.endswith('.txt') or self.source.lower().startswith( ('rtsp://', 'rtmp://', 'http://'))
def preprocess(self, img): img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(self.device) img = img.half() if self.half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32 img /= 255.0 # 图像归一化 if img.ndimension() == 3: img = img.unsqueeze(0) return img
def detect(self, dataset): view_img = check_imshow() t0 = time.time() for path, img, img0s, vid_cap in dataset: img = self.preprocess(img)
t1 = time.time() pred = self.model(img, augment=self.opt["augment"])[0] # 0.22s pred = pred.float() pred = non_max_suppression(pred, self.opt["conf_thres"], self.opt["iou_thres"]) t2 = time.time()
pred_boxes = [] for i, det in enumerate(pred): if self.webcam: # batch_size >= 1 p, s, im0, frame = path[i], '%g: ' % i, img0s[i].copy(), dataset.count else: p, s, im0, frame = path, '', img0s, getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0) s += '%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:] # print string gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh if det is not None and len(det): det[:, :4] = scale_coords( img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results for c in det[:, -1].unique(): n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class s += f"{n} {self.names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, " # add to string
for *xyxy, conf, cls_id in det: lbl = self.names[int(cls_id)] xyxy = torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4).view(-1).tolist() score = round(conf.tolist(), 3) label = "{}: {}".format(lbl, score) x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(xyxy[0]), int(xyxy[1]), int(xyxy[2]), int(xyxy[3]) pred_boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2, lbl, score)) if view_img: self.plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, color=(255, 0, 0), label=label)
# Print time (inference + NMS) # print(pred_boxes) print(f'{s}Done. ({t2 - t1:.3f}s)')
if view_img: print(str(p)) cv2.imshow(str(p), cv2.resize(im0, (800, 600))) if self.webcam: if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): break else: cv2.waitKey(0)
print(f'Done. ({time.time() - t0:.3f}s)') # print('[INFO] Inference time: {:.2f}s'.format(t3-t2)) # return pred_boxes
# Plotting functions def plot_one_box(self, x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=None): # Plots one bounding box on image img tl = line_thickness or round(0.001 * max(img.shape[0:2])) + 1 # line thickness color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3])) cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl) if label: tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0] c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3 cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1) # filled cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [0, 0, 0], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if __name__ == "__main__": with open('yolov5_config.json', 'r', encoding='utf8') as fp: opt = json.load(fp) print('[INFO] YOLOv5 Config:', opt) darknet = Darknet(opt) if darknet.webcam: # cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference dataset = LoadStreams(darknet.source, img_size=opt["imgsz"], stride=darknet.stride) else: dataset = LoadImages(darknet.source, img_size=opt["imgsz"], stride=darknet.stride) darknet.detect(dataset) cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
此外,还需要提供一个模型配置文件,我们使用json文件进行保存。新建一个yolov5_config.json文件,内容如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
{ "source": "streams.txt", # 为视频图像文件地址 "weights": "runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt", # 自己的模型地址 "device": "cpu", # 使用的device类别,如是GPU,可填"0" "imgsz": 640, # 输入图像的大小 "stride": 32, # 步长 "conf_thres": 0.35, # 置信值阈值 "iou_thres": 0.45, # iou阈值 "augment": false # 是否使用图像增强 } |
视频图像文件可以是单独的一张图像,如:"…/images/demo.jpg",也可以是一个视频文件,如:"…/videos/demo.mp4",也可以是一个视频流地址,如:“rtsp://wowzaec2demo.streamlock.net/vod/mp4:BigBuckBunny_115k.mov”,还可以是一个txt文件,里面包含多个视频流地址,如:
|
1 2 |
rtsp://wowzaec2demo.streamlock.net/vod/mp4:BigBuckBunny_115k.mov rtsp://wowzaec2demo.streamlock.net/vod/mp4:BigBuckBunny_115k.mov |
- 有了如此配置信息,通过运行yolov5.py代码,我们能实现对视频文件(mp4、avi等)、视频流地址(http、rtsp、rtmp等)、图片(jpg、png)等视频图像文件进行目标检测推理的效果。
3.Flask后端处理
有了对模型封装的代码,我们就可以利用flask框架实时向前端推送算法处理之后的图像了。新建一个web_main.py文件:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 |
# import the necessary packages from yolov5 import Darknet from camera import LoadStreams, LoadImages from utils.general import non_max_suppression, scale_coords, letterbox, check_imshow from flask import Response from flask import Flask from flask import render_template import time import torch import json import cv2 import os
# initialize a flask object app = Flask(__name__)
# initialize the video stream and allow the camera sensor to warmup with open('yolov5_config.json', 'r', encoding='utf8') as fp: opt = json.load(fp) print('[INFO] YOLOv5 Config:', opt)
darknet = Darknet(opt) if darknet.webcam: # cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference dataset = LoadStreams(darknet.source, img_size=opt["imgsz"], stride=darknet.stride) else: dataset = LoadImages(darknet.source, img_size=opt["imgsz"], stride=darknet.stride) time.sleep(2.0)
@app.route("/") def index(): # return the rendered template return render_template("index.html")
def detect_gen(dataset, feed_type): view_img = check_imshow() t0 = time.time() for path, img, img0s, vid_cap in dataset: img = darknet.preprocess(img)
t1 = time.time() pred = darknet.model(img, augment=darknet.opt["augment"])[0] # 0.22s pred = pred.float() pred = non_max_suppression(pred, darknet.opt["conf_thres"], darknet.opt["iou_thres"]) t2 = time.time()
pred_boxes = [] for i, det in enumerate(pred): if darknet.webcam: # batch_size >= 1 feed_type_curr, p, s, im0, frame = "Camera_%s" % str(i), path[i], '%g: ' % i, img0s[i].copy(), dataset.count else: feed_type_curr, p, s, im0, frame = "Camera", path, '', img0s, getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0)
s += '%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:] # print string gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh if det is not None and len(det): det[:, :4] = scale_coords( img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results for c in det[:, -1].unique(): n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class s += f"{n} {darknet.names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, " # add to string
for *xyxy, conf, cls_id in det: lbl = darknet.names[int(cls_id)] xyxy = torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4).view(-1).tolist() score = round(conf.tolist(), 3) label = "{}: {}".format(lbl, score) x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(xyxy[0]), int(xyxy[1]), int(xyxy[2]), int(xyxy[3]) pred_boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2, lbl, score)) if view_img: darknet.plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, color=(255, 0, 0), label=label)
# Print time (inference + NMS) # print(pred_boxes) print(f'{s}Done. ({t2 - t1:.3f}s)') if feed_type_curr == feed_type: frame = cv2.imencode('.jpg', im0)[1].tobytes() yield (b'--frame\r\n' b'Content-Type: image/jpeg\r\n\r\n' + frame + b'\r\n')
@app.route('/video_feed/<feed_type>') def video_feed(feed_type): """Video streaming route. Put this in the src attribute of an img tag.""" if feed_type == 'Camera_0': return Response(detect_gen(dataset=dataset, feed_type=feed_type), mimetype='multipart/x-mixed-replace; boundary=frame')
elif feed_type == 'Camera_1': return Response(detect_gen(dataset=dataset, feed_type=feed_type), mimetype='multipart/x-mixed-replace; boundary=frame')
if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port="5000", threaded=True) |
通过detect_gen函数将多个视频流地址推理后的图像按照feed_type类型,通过video_feed视频流路由进行传送到前端。
4.前端展示
最后,我们写一个简单的前端代码。首先新建一个templates文件夹,再在此文件夹中新建一个index.html文件,将下面h5代码写入其中:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
<html> <head> <style> * { box-sizing: border-box; text-align: center; }
.img-container { float: left; width: 30%; padding: 5px; }
.clearfix::after { content: ""; clear: both; display: table; } .clearfix{ margin-left: 500px; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Multi-camera with YOLOv5</h1> <div class="clearfix"> <div class="img-container" align="center"> <p align="center">Live stream 1</p> <img src="{{ url_for('video_feed', feed_type='Camera_0') }}" class="center" style="border:1px solid black;width:100%" alt="Live Stream 1"> </div> <div class="img-container" align="center"> <p align="center">Live stream 2</p> <img src="{{ url_for('video_feed', feed_type='Camera_1') }}" class="center" style="border:1px solid black;width:100%" alt="Live Stream 2"> </div> </div> </body> </html> |
至此,我们利用YOLOv5模型实现多路摄像头实时推理代码就写完了,下面我们开始运行:
- 在终端中进行跟目录下,直接运行:
|
1 |
python web_main.py |
然后,会在终端中出现如下信息:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
[INFO] YOLOv5 Config: {'source': 'streams.txt', 'weights': 'runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt', 'device': 'cpu', 'imgsz': 640, 'stride': 32, 'conf_thres': 0.35, 'iou_thres': 0.45, 'augment': False} Fusing layers... 1/2: rtsp://wowzaec2demo.streamlock.net/vod/mp4:BigBuckBunny_115k.mov... success (240x160 at 24.00 FPS). 2/2: rtsp://wowzaec2demo.streamlock.net/vod/mp4:BigBuckBunny_115k.mov... success (240x160 at 24.00 FPS).
* Serving Flask app "web_main" (lazy loading) * Environment: production WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment. Use a production WSGI server instead. * Debug mode: off * Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit) |
* 接着打开浏览器,输入localhost:5000后,终端没有报任何错误,则就会出现如下页面:
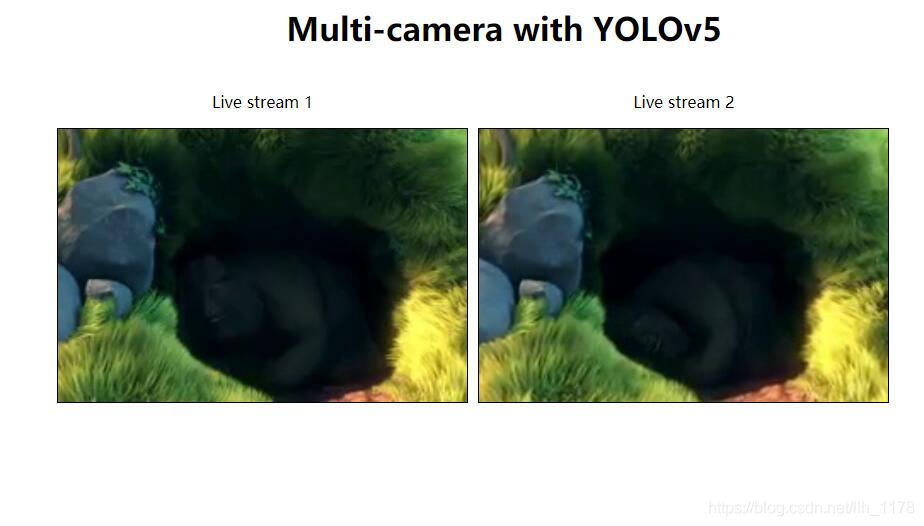
总结
1. 由于没有额外的视频流rtmp/rtsp文件地址,所以就找了一个公开的视频流地址,但是没有办法看到检测效果;
2. 部署的时候,只能使用视频流地址进行推理,且可以为多个视频流地址,保存为stream.txt,用yolov5_config.json导入;
3. 此demo版本为简易版的端到端模型部署方案,还可以根据场景需要添加更多功能。