1、什么是Action泛型委托
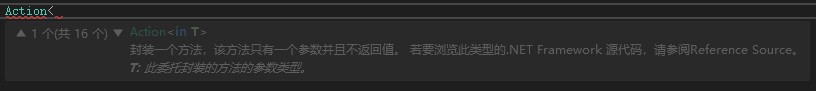
Action<T>是.NET Framework内置的泛型委托,可以使用Action<T>委托以参数形式传递方法,而不用显示声明自定义的委托。封装的方法必须与此委托定义的方法签名相对应。也就是说,封装的方法必须具有一个通过值传递给它的参数,并且不能有返回值。
2、Action委托定义
查看Action的定义:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
namespace System { // // 摘要: // 封装一个方法,该方法不具有参数且不返回值。 [TypeForwardedFrom("System.Core, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=Neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089")] public delegate void Action(); } |
你会发现,Action其实就是没有返回值的delegate。
3、示例
Action委托至少0个参数,至多16个参数,无返回值。
Action 表示无参,无返回值的委托。
Action<int,string> 表示有传入参数int,string无返回值的委托。
Action<int,string,bool> 表示有传入参数int,string,bool无返回值的委托。
Action<int,int,int,int> 表示有传入4个int型参数,无返回值的委托。
代码示例如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 |
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ActionDemo { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 无参数无返回值的委托 Action action1 = new Action(ActionWithNoParaNoReturn); action1(); Console.WriteLine("----------------------------"); // 使用delegate Action action2 = delegate { Console.WriteLine("这里是使用delegate"); }; // 执行 action2(); Console.WriteLine("----------------------------"); // 使用匿名委托 Action action3 = () => { Console.WriteLine("这里是匿名委托"); }; action3(); Console.WriteLine("----------------------------"); // 有参数无返回值的委托 Action<int> action4 = new Action<int>(ActionWithPara); action4(23); Console.WriteLine("----------------------------"); // 使用delegate Action<int> action5 = delegate (int i) { Console.WriteLine($"这里是使用delegate的委托,参数值是:{i}"); }; action5(45); Console.WriteLine("----------------------------"); // 使用匿名委托 Action<string> action6 = (string s) => { Console.WriteLine($"这里是使用匿名委托,参数值是:{s}"); }; action6("345"); Console.WriteLine("----------------------------"); // 多个参数无返回值的委托 Action<int, string> action7 = new Action<int, string>(ActionWithMulitPara); action7(7, "abc"); Console.WriteLine("----------------------------"); // 使用delegate Action<int, int, string> action8 = delegate (int i1, int i2, string s) { Console.WriteLine($"这里是三个参数的Action委托,参数1的值是:{i1},参数2的值是:{i2},参数3的值是:{s}"); }; action8(12, 34, "abc"); Console.WriteLine("----------------------------"); Action<int,int,string, string> action9 = (int i1,int i2, string s1,string s2) => { Console.WriteLine($"这里是使用四个参数的委托,参数1的值是:{i1},参数2的值是:{i2},参数3的值是:{s1},参数4的值是:{s2}"); }; // 执行委托 action9(34,56, "abc","def"); Console.ReadKey(); }
static void ActionWithNoParaNoReturn() { Console.WriteLine("这是无参数无返回值的Action委托"); }
static void ActionWithPara(int i) { Console.WriteLine($"这里是有参数无返回值的委托,参数值是:{i}"); }
static void ActionWithMulitPara(int i,string s) { Console.WriteLine($"这里是有两个参数无返回值的委托,参数1的值是:{i},参数2的值是:{s}"); } } } |
运行结果:
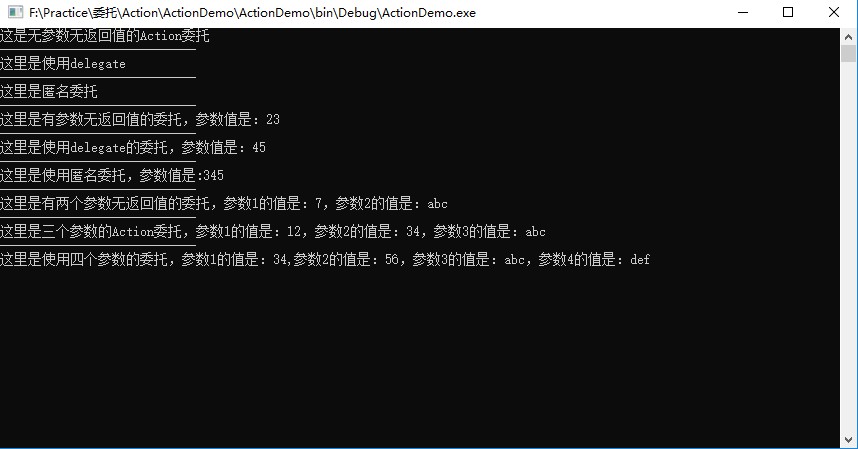
4、真实示例
先看下面一张截图:
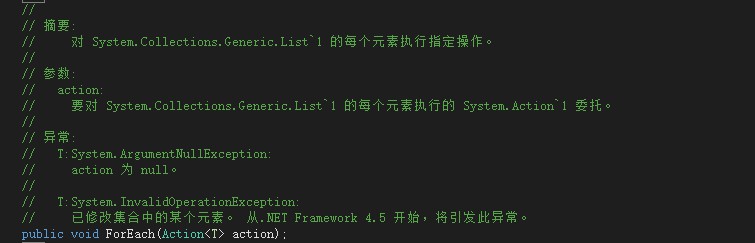
从截图中可以看出:ForEach()方法的参数是一个参数类型是T的无返回值的Action委托,下面的示例中利用Action委托作为参数传递给ForEach()方法。
1、定义Student实体类
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ActionDemo { public class Student { public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public int Sex { get; set; } } } |
2、利用ForEach()方法输出集合内容
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks;
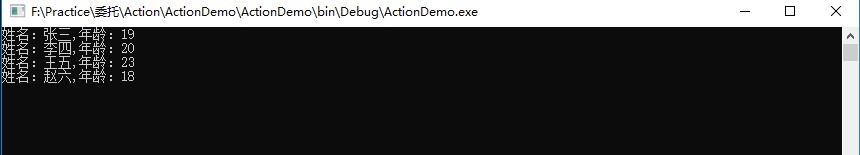
namespace ActionDemo { public class ActionTest { public static void Test() { List<Student> list = new List<Student>() { new Student(){Id=1,Name="张三",Age=19,Sex=1}, new Student(){Id=2,Name="李四",Age=20,Sex=2}, new Student(){Id=3,Name="王五",Age=23,Sex=1}, new Student(){Id=4,Name="赵六",Age=18,Sex=1} };
// Action<Student>委托作为参数传递给ForEach()方法 list.ForEach(student => { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{student.Name},年龄:{student.Age}"); }); } } } |
3、在Main()方法中调用
|
1 |
ActionTest.Test(); |
4、结果