1. 需求
开发中我们经常遇到异步接口需要执行一些耗时的操作,并且接口要有返回结果。
使用场景:用户绑定邮箱、手机号,将邮箱、手机号保存入库后发送邮件或短信通知
接口要求:数据入库后给前台返回成功通知,后台异步执行发邮件、短信通知操作
一般的话在企业中会借用消息队列来实现发送,业务量大的话有一个统一消费、管理的地方。但有时项目中没有引用mq相关组件,这时为了实现一个功能去引用、维护一个消息组件有点大材小用,下面介绍几种不引用消息队列情况下的解决方式
定义线程池:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; /** * @description: 公共配置 * @author: yh * @date: 2022/8/26 */ @EnableAsync @Configuration public class CommonConfig { @Bean public TaskExecutor taskExecutor() { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 设置核心线程数 executor.setCorePoolSize(50); // 设置最大线程数 executor.setMaxPoolSize(200); // 设置队列容量 executor.setQueueCapacity(200); // 设置线程活跃时间(秒) executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(800); // 设置默认线程名称 executor.setThreadNamePrefix("task-"); // 设置拒绝策略 executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); // 等待所有任务结束后再关闭线程池 executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true); return executor; } } |
2. 解决方案
2.1 @Async
定义异步任务,如发送邮件、短信等
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
@Service public class ExampleServiceImpl implements ExampleService { @Async("taskExecutor") @Override public void sendMail(String email) { try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("异步任务执行完成, " + email + " 当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } |
Controller
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
@RequestMapping(value = "/api") @RestController public class ExampleController { @Resource private ExampleService exampleService;
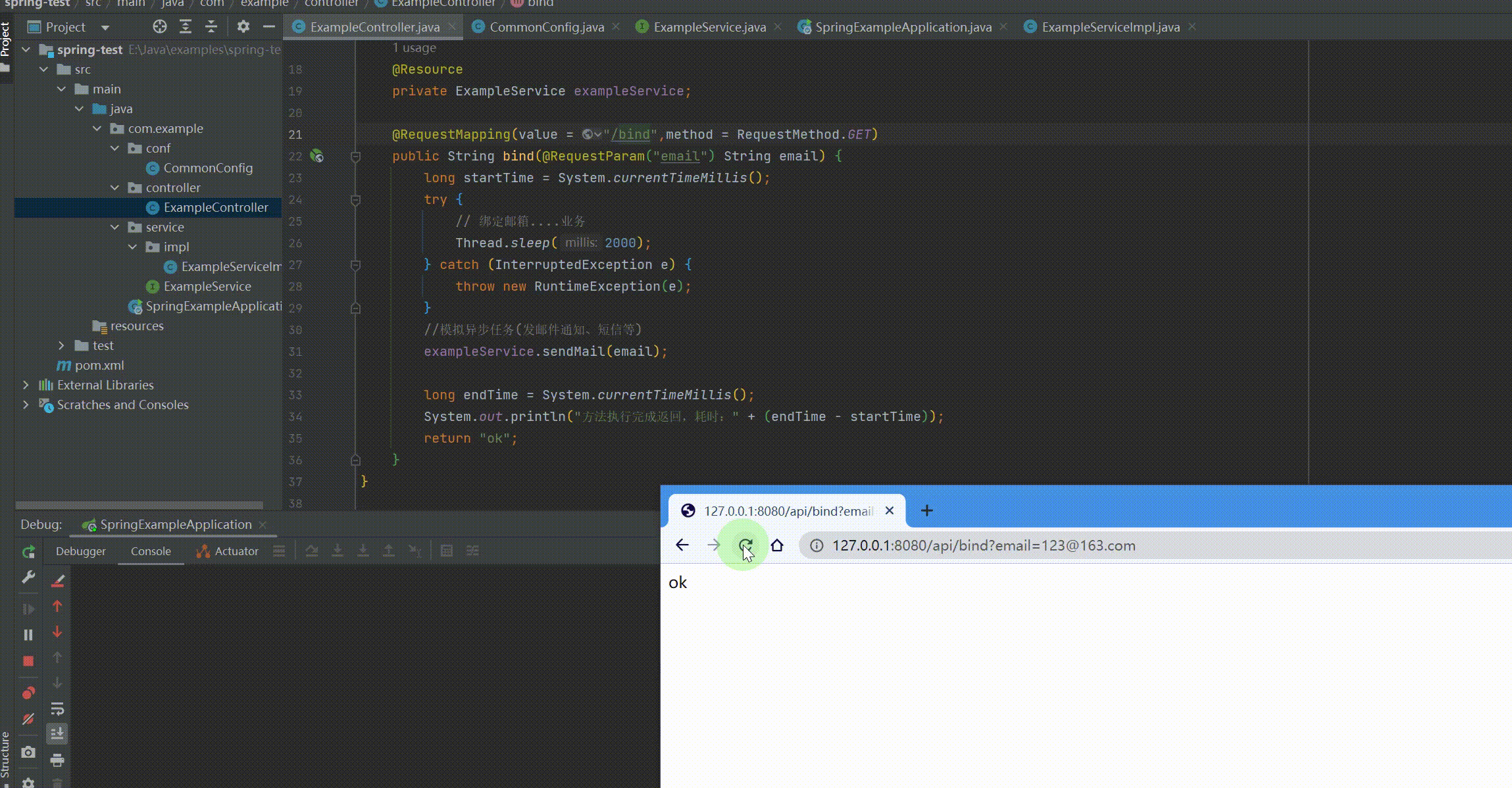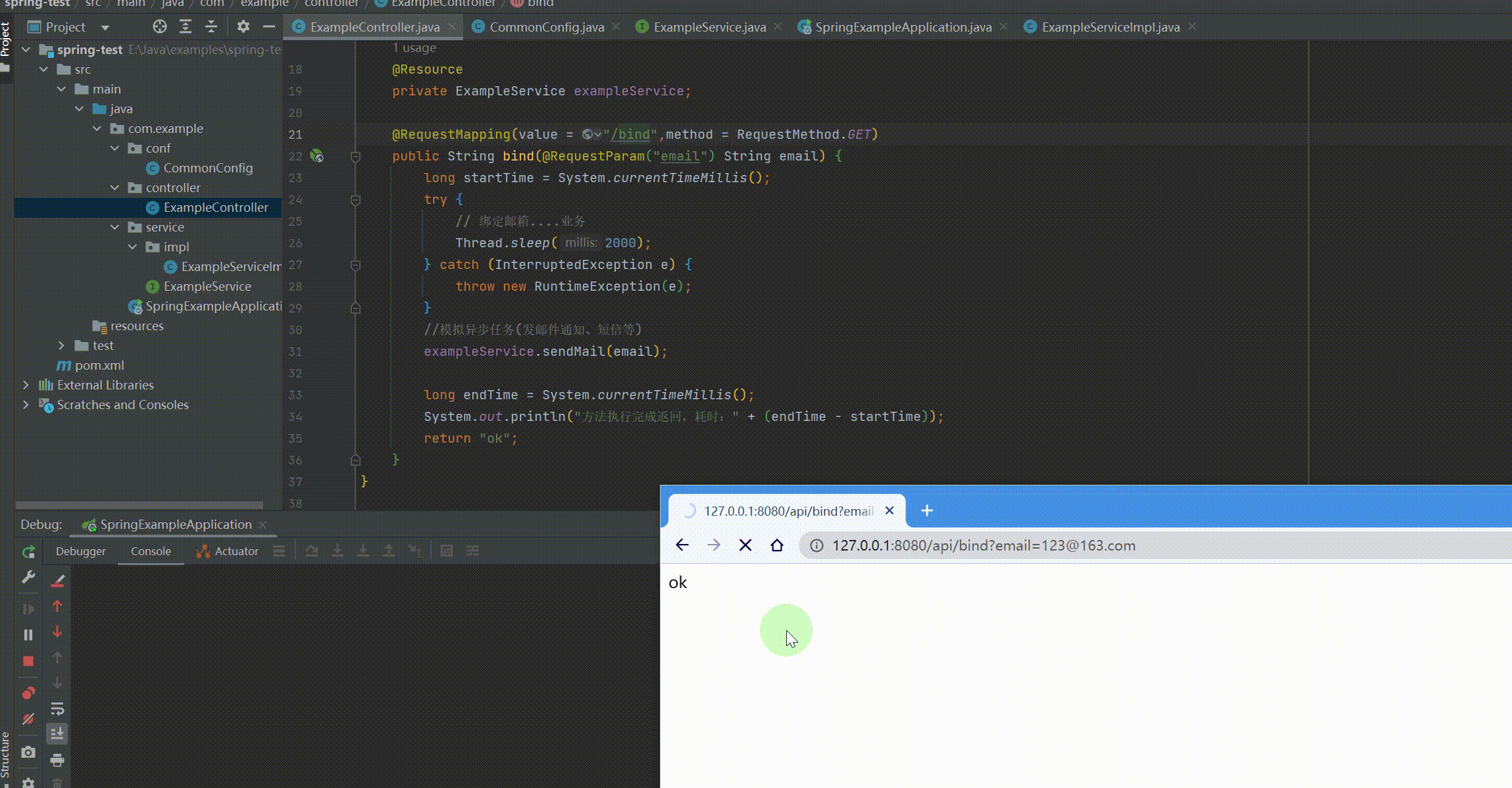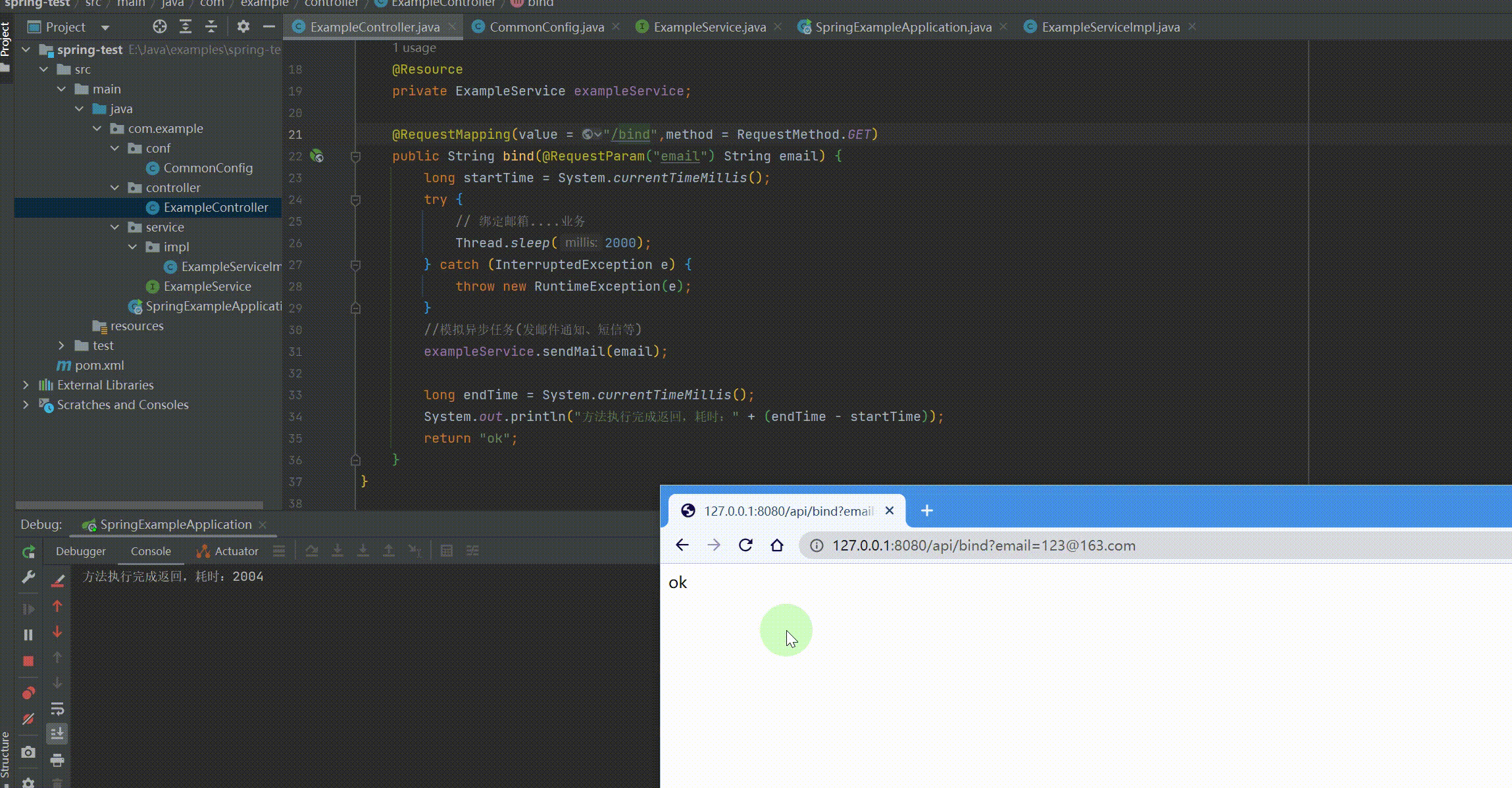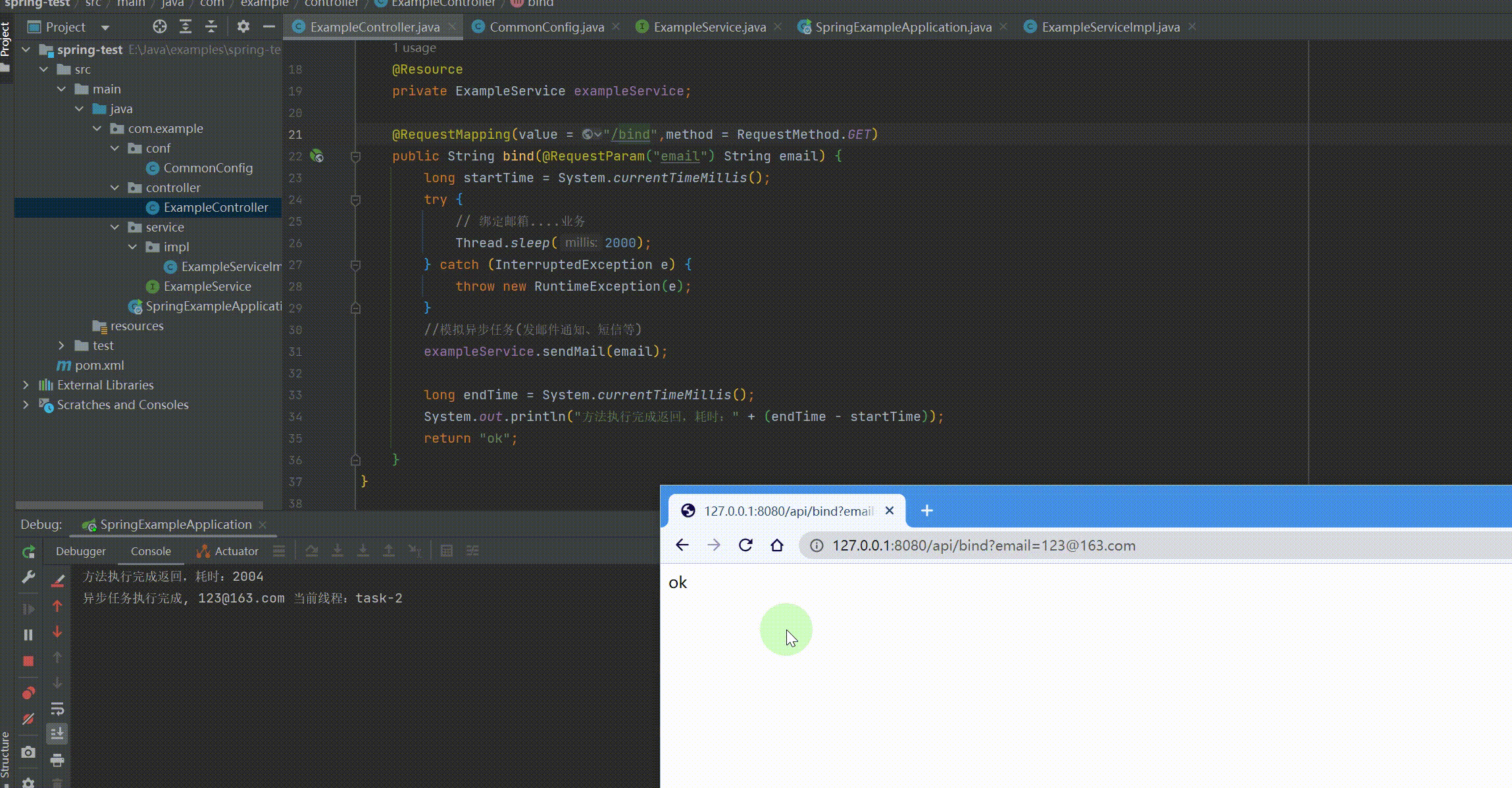
@RequestMapping(value = "/bind",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String bind(@RequestParam("email") String email) { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // 绑定邮箱....业务 Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } //模拟异步任务(发邮件通知、短信等) exampleService.sendMail(email);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("方法执行完成返回,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime)); return "ok"; } } |
运行结果:
2.2 TaskExecutor
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
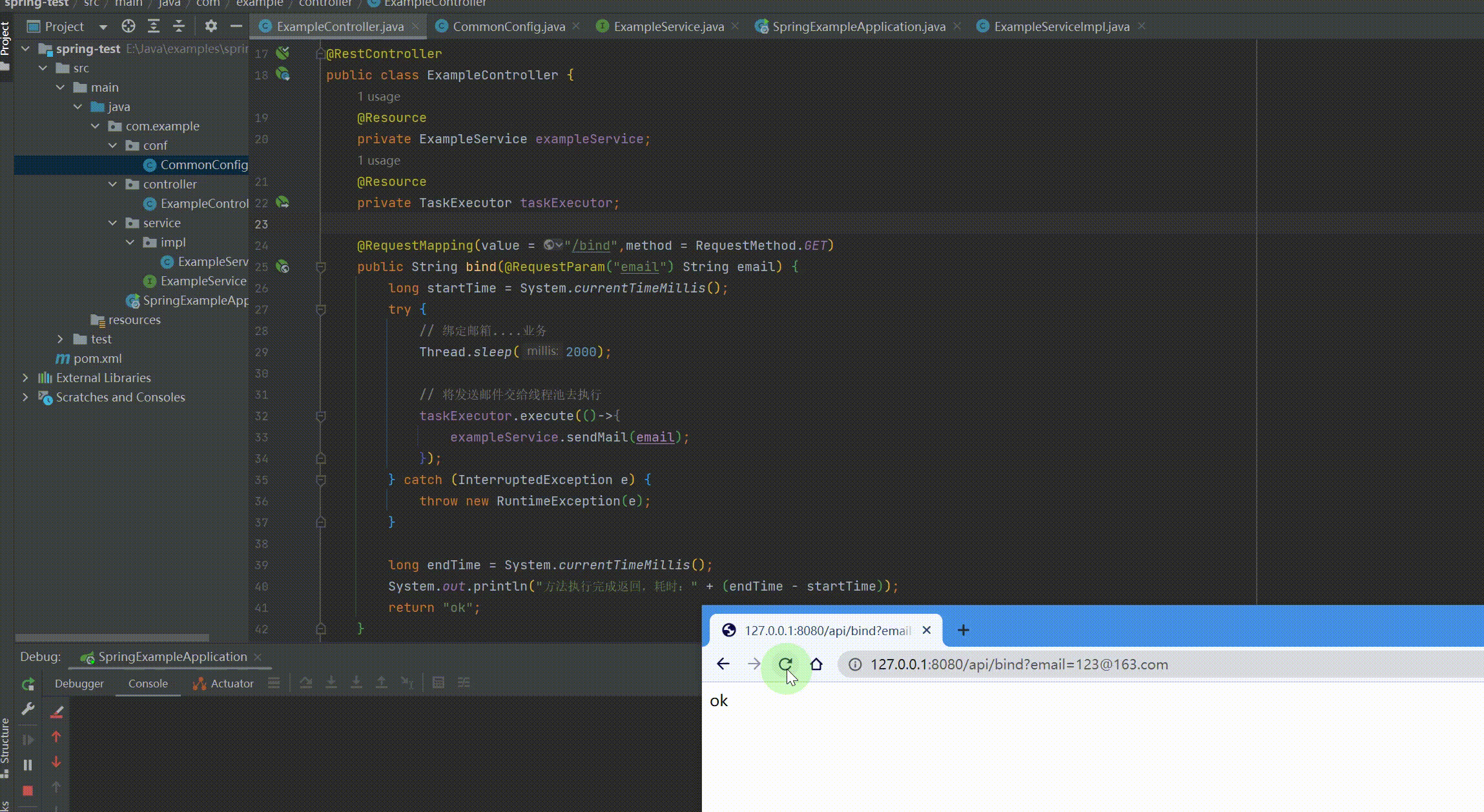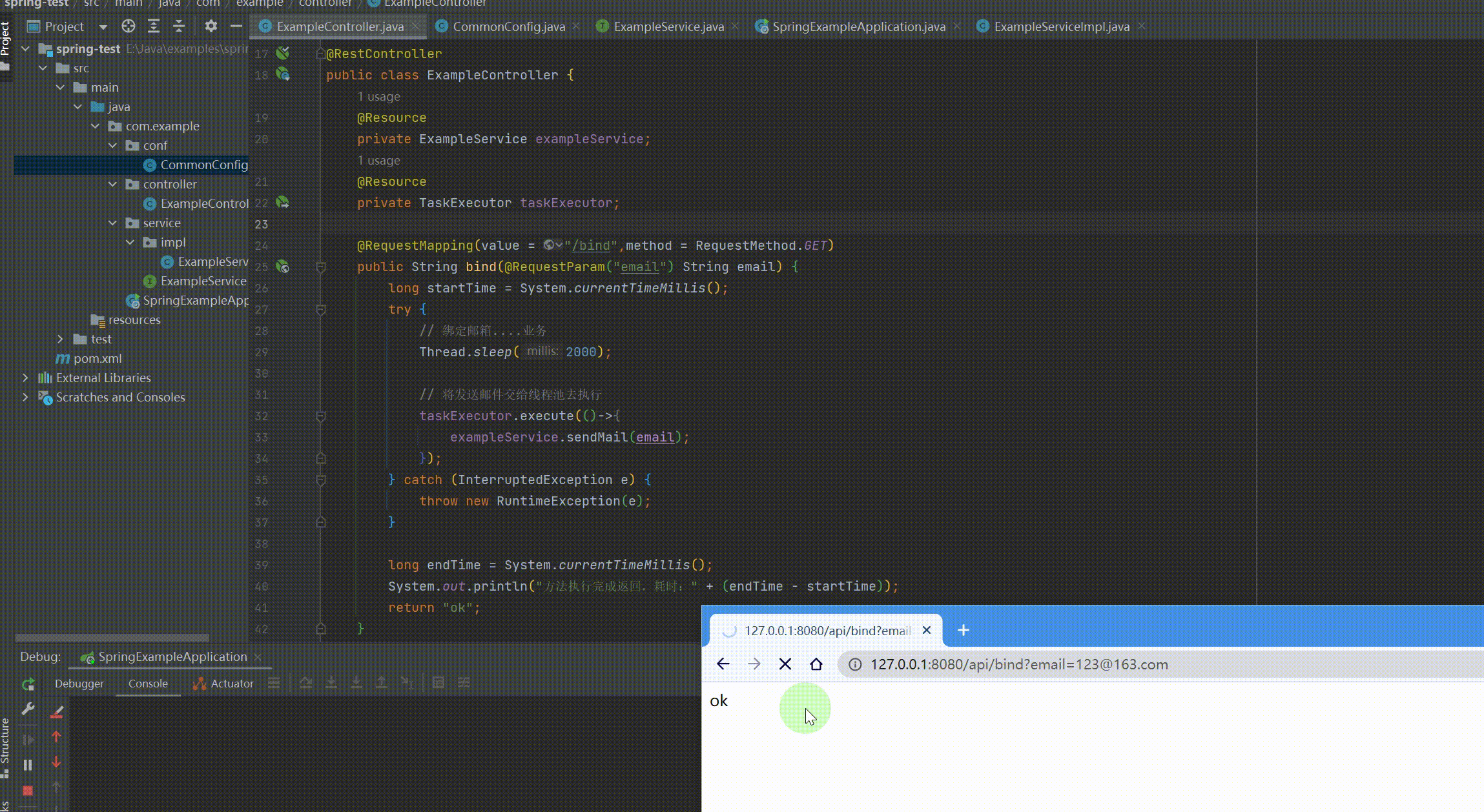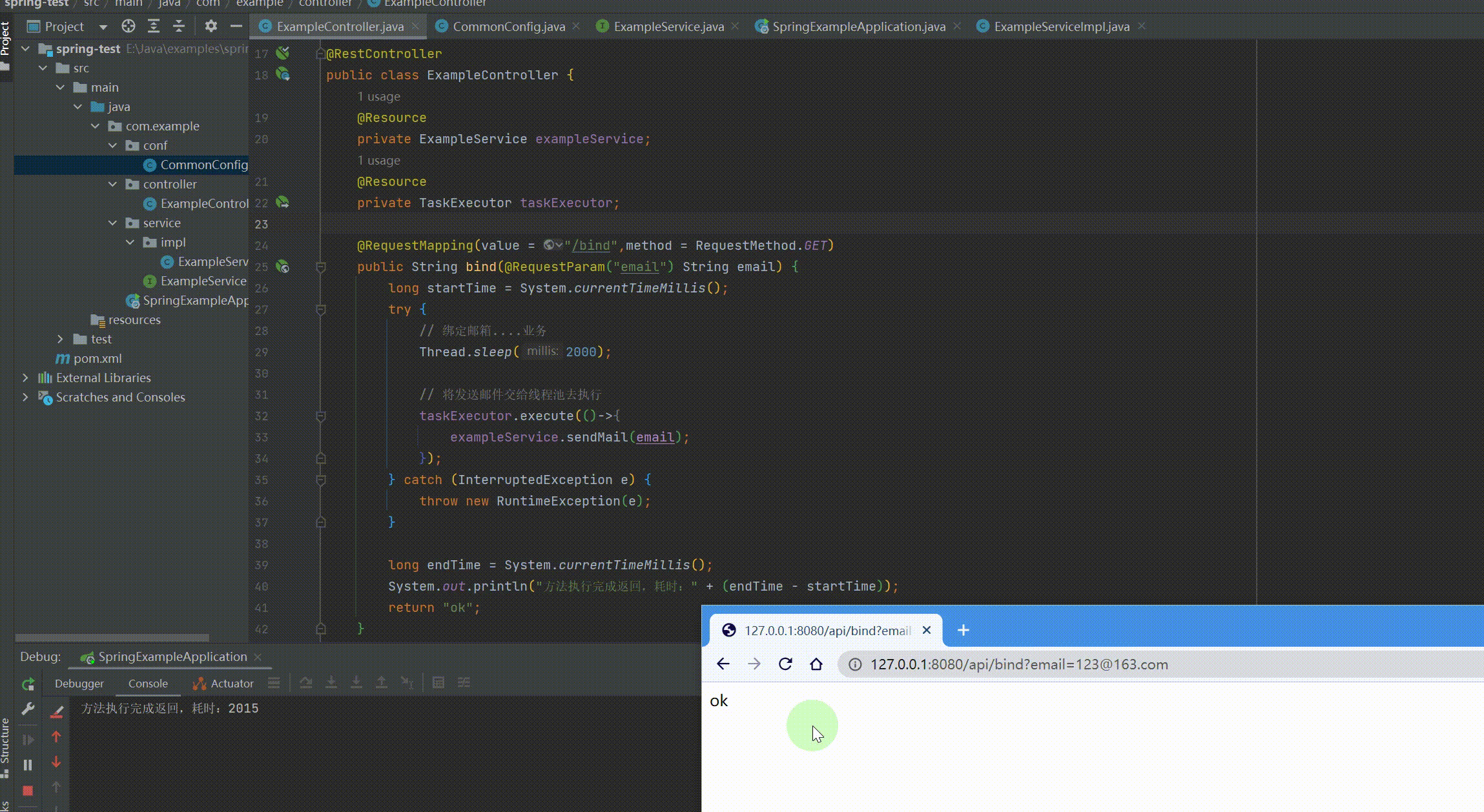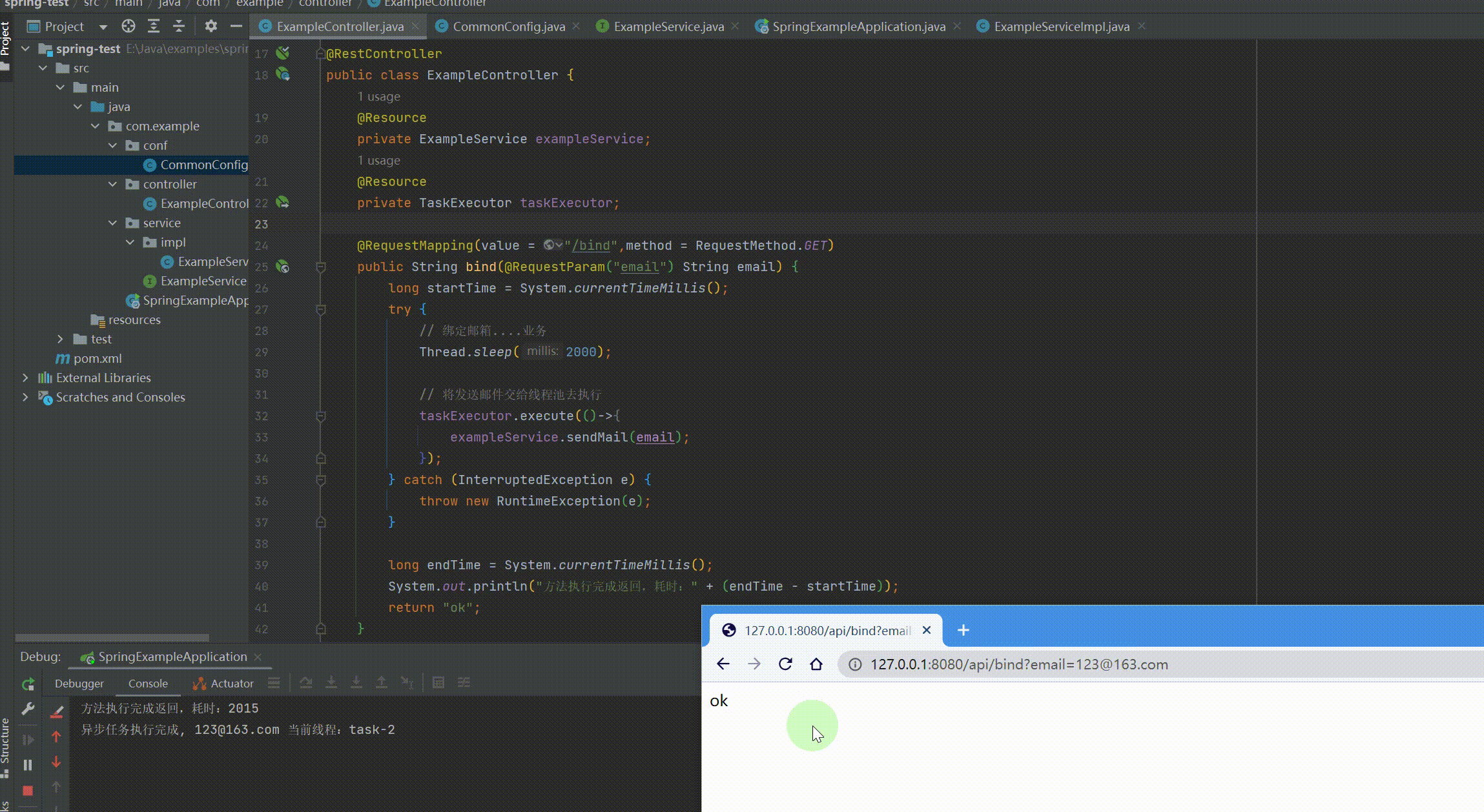
@RequestMapping(value = "/api") @RestController public class ExampleController { @Resource private ExampleService exampleService; @Resource private TaskExecutor taskExecutor;
@RequestMapping(value = "/bind", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String bind(@RequestParam("email") String email) { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // 绑定邮箱....业务 Thread.sleep(2000);
// 将发送邮件交给线程池去执行 taskExecutor.execute(() -> { exampleService.sendMail(email); }); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); }
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("方法执行完成返回,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime)); return "ok"; } } |
运行结果:
2.3 Future
首先去掉Service方法中的@Async("taskExecutor"),此时执行就会变成同步,总计需要5s才能完成接口返回。这次我们使用jdk1.8中的CompletableFuture来实现异步任务
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
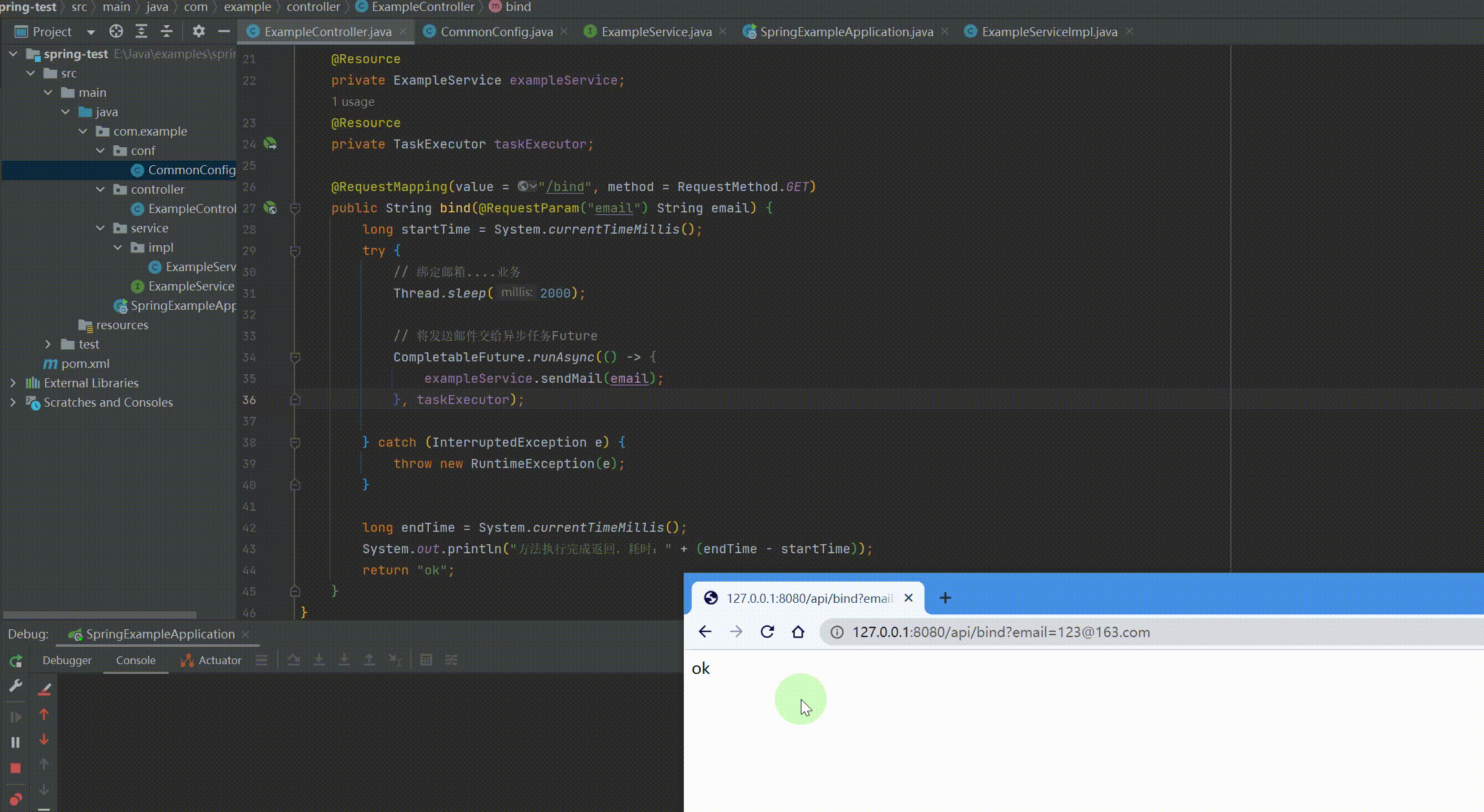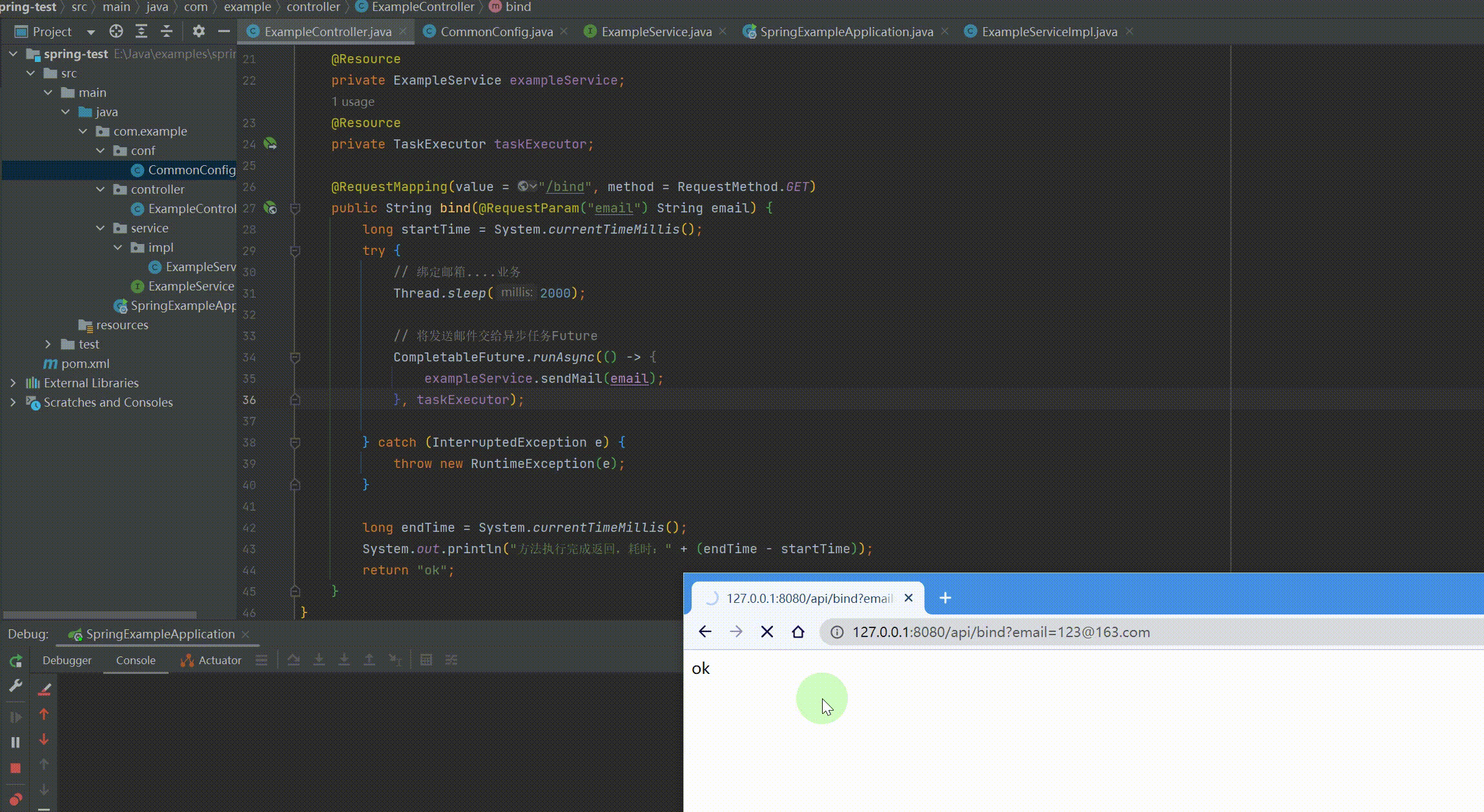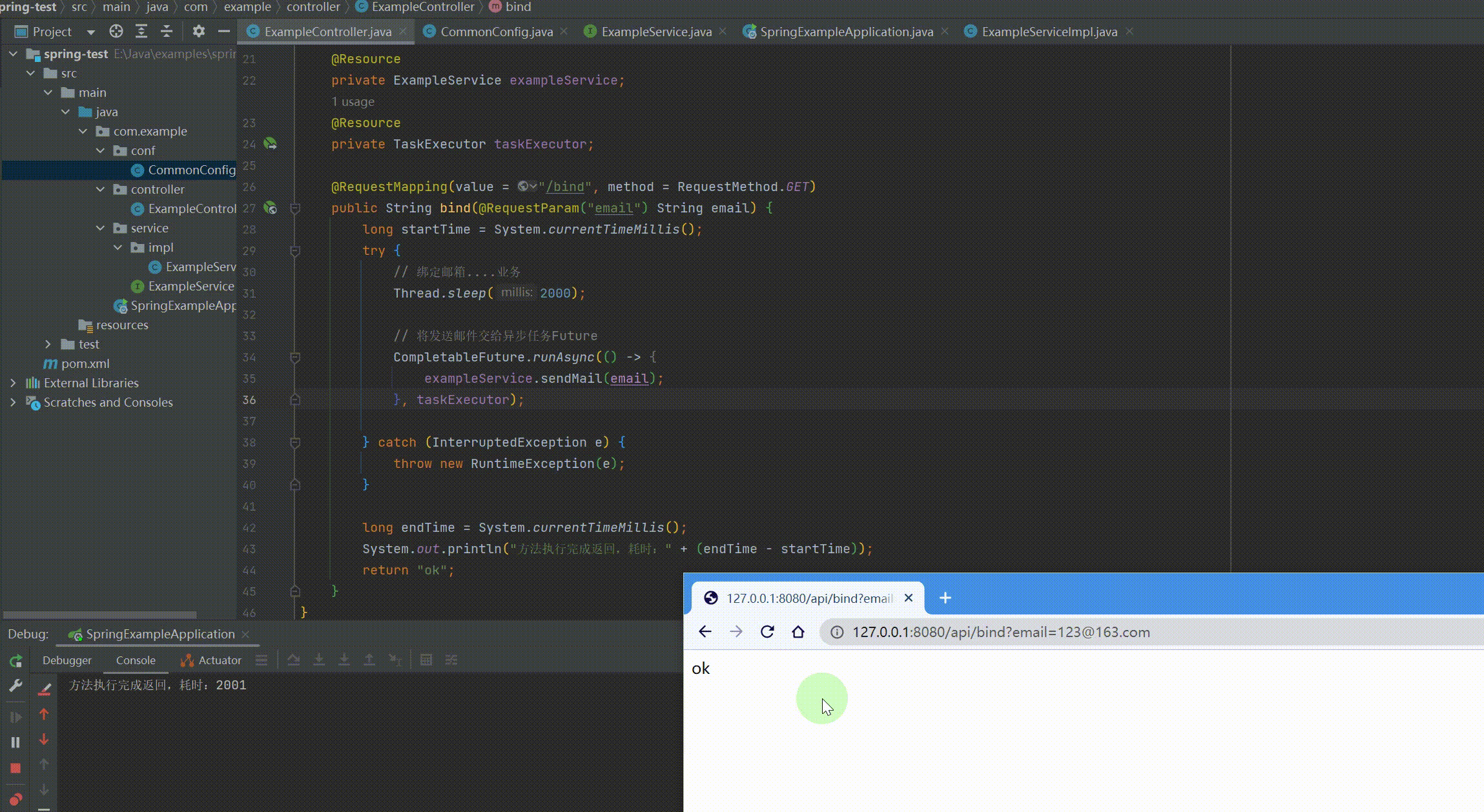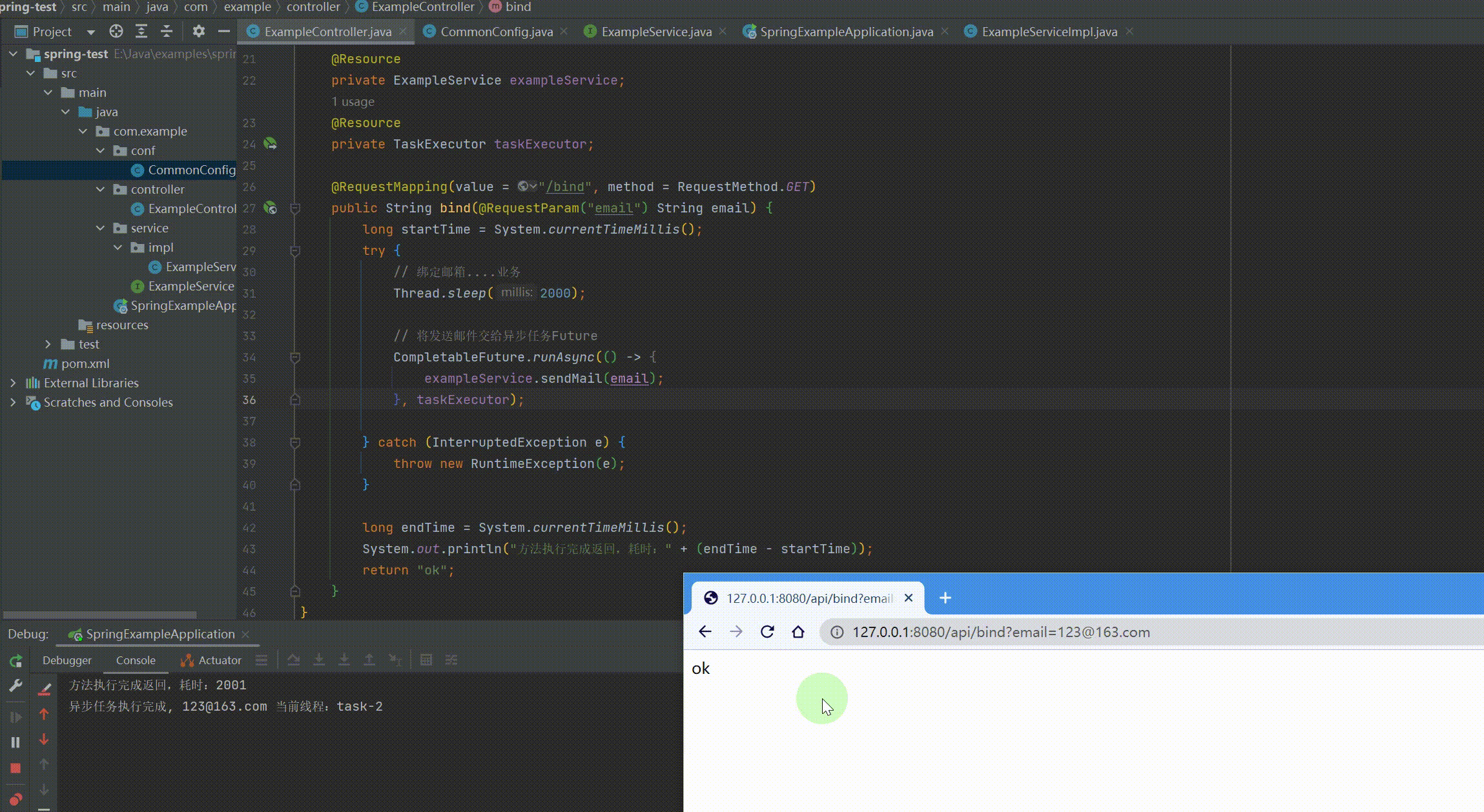
@RequestMapping(value = "/api") @RestController public class ExampleController { @Resource private ExampleService exampleService; @Resource private TaskExecutor taskExecutor;
@RequestMapping(value = "/bind", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String bind(@RequestParam("email") String email) { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // 绑定邮箱....业务 Thread.sleep(2000);
// 将发送邮件交给异步任务Future,需要记录返回值用supplyAsync CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { exampleService.sendMail(email); }, taskExecutor);
} catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); }
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("方法执行完成返回,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime)); return "ok"; } } |
运行结果:
2.4 @EventListener
Spring为我们提供的一个事件监听、订阅的实现,内部实现原理是观察者设计模式;为的就是业务系统逻辑的解耦,提高可扩展性以及可维护性。事件发布者并不需要考虑谁去监听,监听具体的实现内容是什么,发布者的工作只是为了发布事件而已。
2.4.1 定义event事件模型
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
public class NoticeEvent extends ApplicationEvent { private String email; private String phone; public NoticeEvent(Object source, String email, String phone) { super(source); this.email = email; this.phone = phone; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } } |
2.4.2 事件监听
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
@Component public class ComplaintEventListener {
/** * 只监听NoticeEvent事件 * @author: yh * @date: 2022/8/27 */ @Async @EventListener(value = NoticeEvent.class) // @Order(1) 指定事件执行顺序 public void sendEmail(NoticeEvent noticeEvent) { //发邮件 try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("发送邮件任务执行完成, " + noticeEvent.getEmail() + " 当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }
@Async @EventListener(value = NoticeEvent.class) // @Order(2) 指定事件执行顺序 public void sendMsg(NoticeEvent noticeEvent) { //发短信 try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("发送短信步任务执行完成, " + noticeEvent.getPhone() + " 当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } |
2.4.5 事件发布
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
@RequestMapping(value = "/api") @RestController public class ExampleController { /** * 用于事件推送 * @author: yh * @date: 2022/8/27 */ @Autowired private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
@RequestMapping(value = "/bind", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String bind(@RequestParam("email") String email) { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // 绑定邮箱....业务 Thread.sleep(2000);
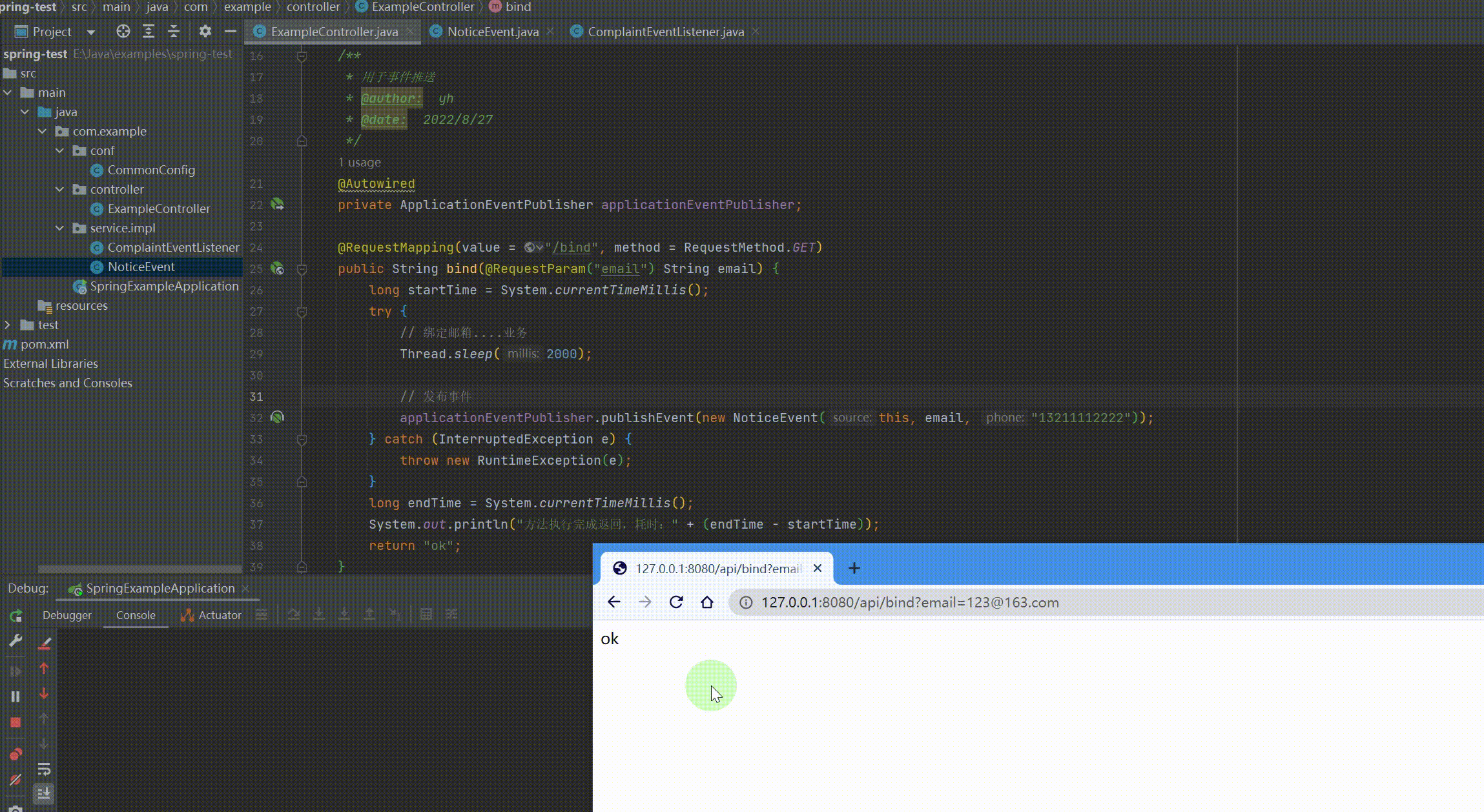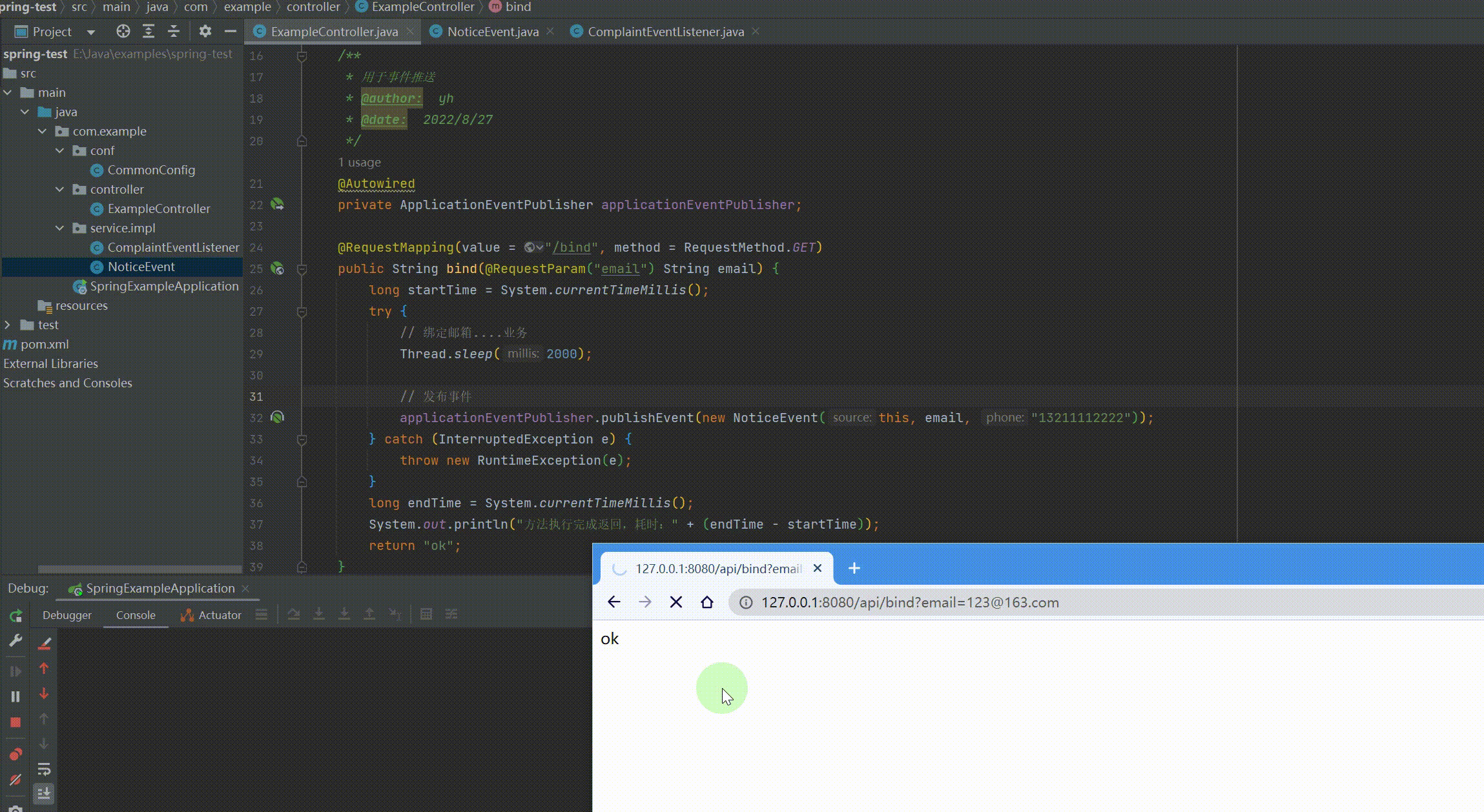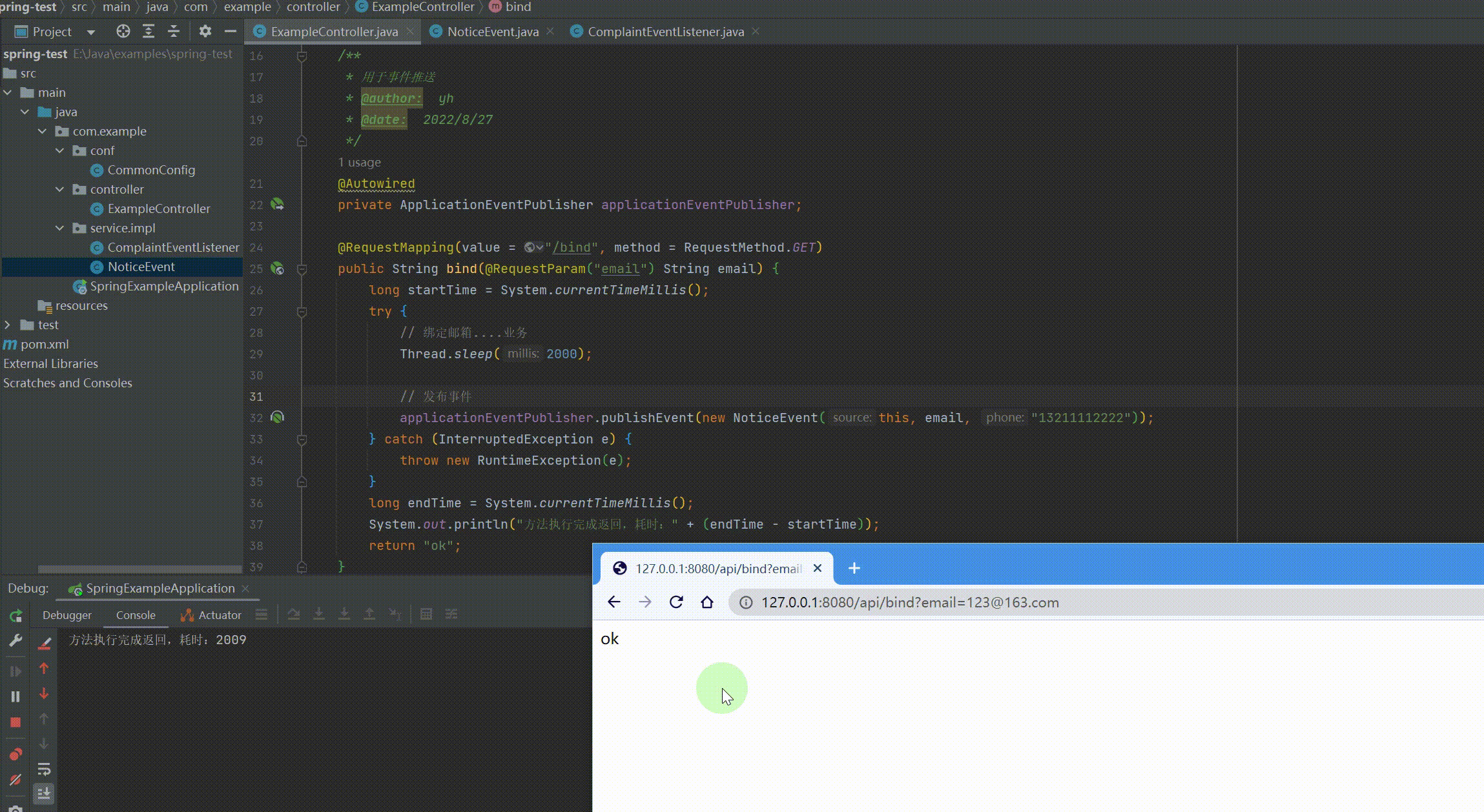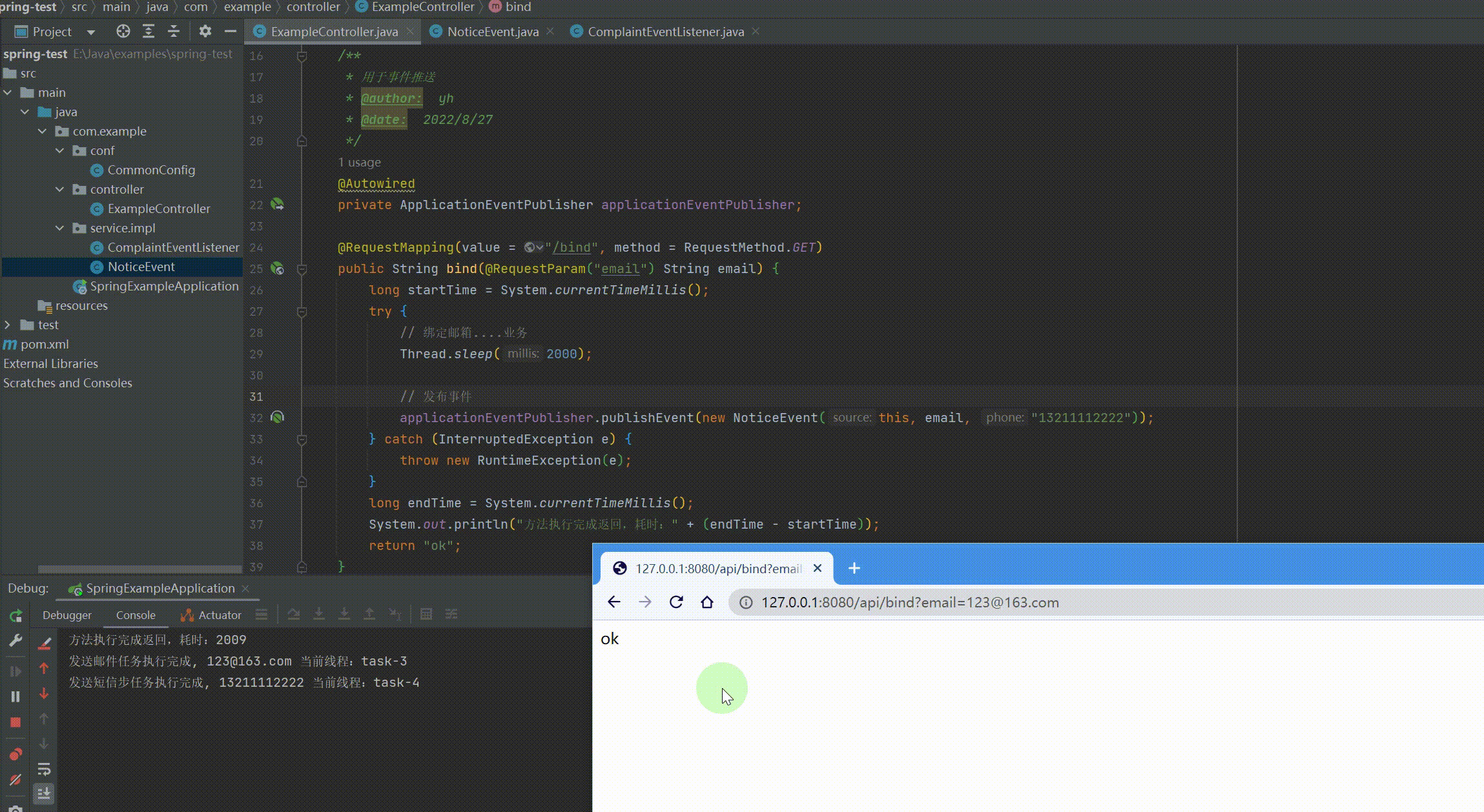
// 发布事件,这里偷个懒手机号写死 applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new NoticeEvent(this, email, "13211112222")); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("方法执行完成返回,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime)); return "ok"; } } |
运行结果:
3. 总结
通过@Async、子线程、Future异步任务、Spring自带ApplicationEvent事件监听都可以完成以上描述的需求。