一、项目效果

学校宿舍今天搬家,累麻了,突然发现展示处理的也很粗糙,就这样吧嘿嘿~~~
二、核心流程
1、openCV读取视频流、在每一帧图片上画一个矩形。
2、使用mediapipe获取手指关键点坐标。
3、根据手指坐标位置和矩形的坐标位置,判断手指点是否在矩形上,如果在则矩形跟随手指移动。
三、代码流程
环境准备:
python: 3.8.8
opencv: 4.2.0.32
mediapipe: 0.8.10.1
注:
1、opencv版本过高或过低可能出现一些如摄像头打不开、闪退等问题,python版本影响opencv可选择的版本。
2、pip install mediapipe 后可能导致openCV无法正常使用,卸了重新下载,习惯了就好。
1. 读取摄像头视频,画矩形
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
import cv2 import time import numpy as np
# 调用摄像头 0 默认摄像头 cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 初始方块数据 x = 100 y = 100 w = 100 h = 100
# 读取一帧帧照片 while True: # 返回frame图片 rec,frame = cap.read()
# 镜像 frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
# 画矩形 cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 0, 255), -1)
# 显示画面 cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# 退出条件 if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): break
cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
这是很基础的一步操作,此时我们运行这段代码,摄像头打开,我们会惊讶地看到自己英俊的脸庞,且左上角有个100*100的紫色矩形。
2. 导入mediapipe处理手指坐标
|
1 |
pip install mediapipe |
此时可能出现一些问题,比如openCV突然用不了了,没关系,卸载了重新下。
mediapipe详细信息:Hands - mediapipe (google.github.io)
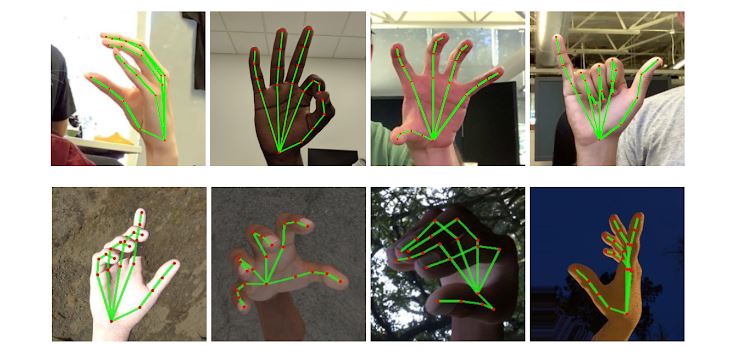
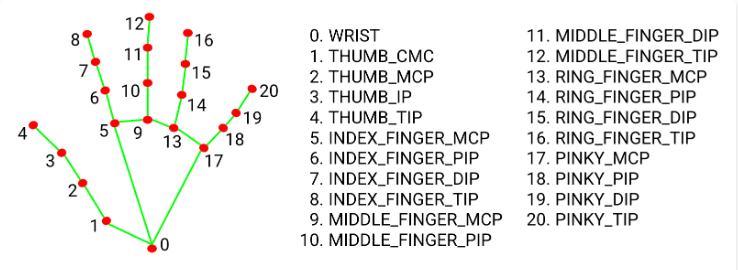
简单来说,它会返回给我们21个手指关键点的坐标,即它在视频画面的位置比例( 0~1 ),我们乘以对应画面的宽高,就能得到手指对应的坐标了。
本次用到食指和中指指尖,也就是8号和12号。
2.1 配置一些基础信息
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
import cv2 import time import numpy as np import mediapipe as mp
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
hands = mp_hands.Hands( static_image_mode=True, max_num_hands=2, min_detection_confidence=0.5) |
2.2 在处理每一帧图像时,加入
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
frame.flags.writeable = False frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 返回结果 results = hands.process(frame)
frame.flags.writeable = True frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) |
当我们在视频流中读取每一帧图片时,将其从BGR转为RGB供给mediapipe生成的hands对象读取,它会返回这张图片中手指关键点的信息,我们只需要继续对其作画,画在每一帧图片上。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
# 如果结果不为空 if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 遍历双手(根据读取顺序,一只只手遍历、画画) for hand_landmarks in results.multi_hand_landmarks: mp_drawing.draw_landmarks( frame, hand_landmarks, mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS, mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_landmarks_style(), mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style()) |
2.3 至此步骤完整代码
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 |
import cv2 import time import numpy as np import mediapipe as mp
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
hands = mp_hands.Hands( static_image_mode=True, max_num_hands=2, min_detection_confidence=0.5)
# 调用摄像头 0 默认摄像头 cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 方块初始数组 x = 100 y = 100 w = 100 h = 100
# 读取一帧帧照片 while True: # 返回frame图片 rec,frame = cap.read()
# 镜像 frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
frame.flags.writeable = False frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 返回结果 results = hands.process(frame)
frame.flags.writeable = True frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# 如果结果不为空 if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 遍历双手(根据读取顺序,一只只手遍历、画画) # results.multi_hand_landmarks n双手 # hand_landmarks 每只手上21个点信息 for hand_landmarks in results.multi_hand_landmarks: mp_drawing.draw_landmarks( frame, hand_landmarks, mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS, mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_landmarks_style(), mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style())
# 画矩形 cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 0, 255), -1)
# 显示画面 cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# 退出条件 if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): break
cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
此时我们运行看一下还挺有意思的:

3. 位置计算
我们这个实验要求拖动方块,那肯定也有不拖动的时候,因此不妨根据上一步获取食指(8)和中指(12)指尖的位置,如果这俩离得近,我们就在他与方块重合的时候,根据手指的位置改变方块的坐标。

完整代码

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 |
import cv2 import time import math import numpy as np import mediapipe as mp
# mediapipe配置 mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands hands = mp_hands.Hands( static_image_mode=True, max_num_hands=2, min_detection_confidence=0.5)
# 调用摄像头 0 默认摄像头 cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# cv2.namedWindow("frame", 0) # cv2.resizeWindow("frame", 960, 640)
# 获取画面宽度、高度 width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)) height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# 方块初始数组 x = 100 y = 100 w = 100 h = 100
L1 = 0 L2 = 0
on_square = False square_color = (0, 255, 0)
# 读取一帧帧照片 while True: # 返回frame图片 rec,frame = cap.read()
# 镜像 frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
frame.flags.writeable = False frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 返回结果 results = hands.process(frame)
frame.flags.writeable = True frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# 如果结果不为空 if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 遍历双手(根据读取顺序,一只只手遍历、画画) # results.multi_hand_landmarks n双手 # hand_landmarks 每只手上21个点信息 for hand_landmarks in results.multi_hand_landmarks: mp_drawing.draw_landmarks( frame, hand_landmarks, mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS, mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_landmarks_style(), mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style())
# 记录手指每个点的x y 坐标 x_list = [] y_list = [] for landmark in hand_landmarks.landmark: x_list.append(landmark.x) y_list.append(landmark.y)
# 获取食指指尖 index_finger_x, index_finger_y = int(x_list[8] * width),int(y_list[8] * height)
# 获取中指 middle_finger_x,middle_finger_y = int(x_list[12] * width), int(y_list[12] * height)
# 计算两指尖距离 finger_distance = math.hypot((middle_finger_x - index_finger_x), (middle_finger_y - index_finger_y))
# 如果双指合并(两之间距离近) if finger_distance < 60:
# X坐标范围 Y坐标范围 if (index_finger_x > x and index_finger_x < (x + w)) and ( index_finger_y > y and index_finger_y < (y + h)):
if on_square == False: L1 = index_finger_x - x L2 = index_finger_y - y square_color = (255, 0, 255) on_square = True
else: # 双指不合并/分开 on_square = False square_color = (0, 255, 0)
# 更新坐标 if on_square: x = index_finger_x - L1 y = index_finger_y - L2
# 图像融合 使方块不遮挡视频图片 overlay = frame.copy() cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), square_color, -1) frame = cv2.addWeighted(overlay, 0.5, frame, 1 - 0.5, 0)
# 显示画面 cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# 退出条件 if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): break
cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() |