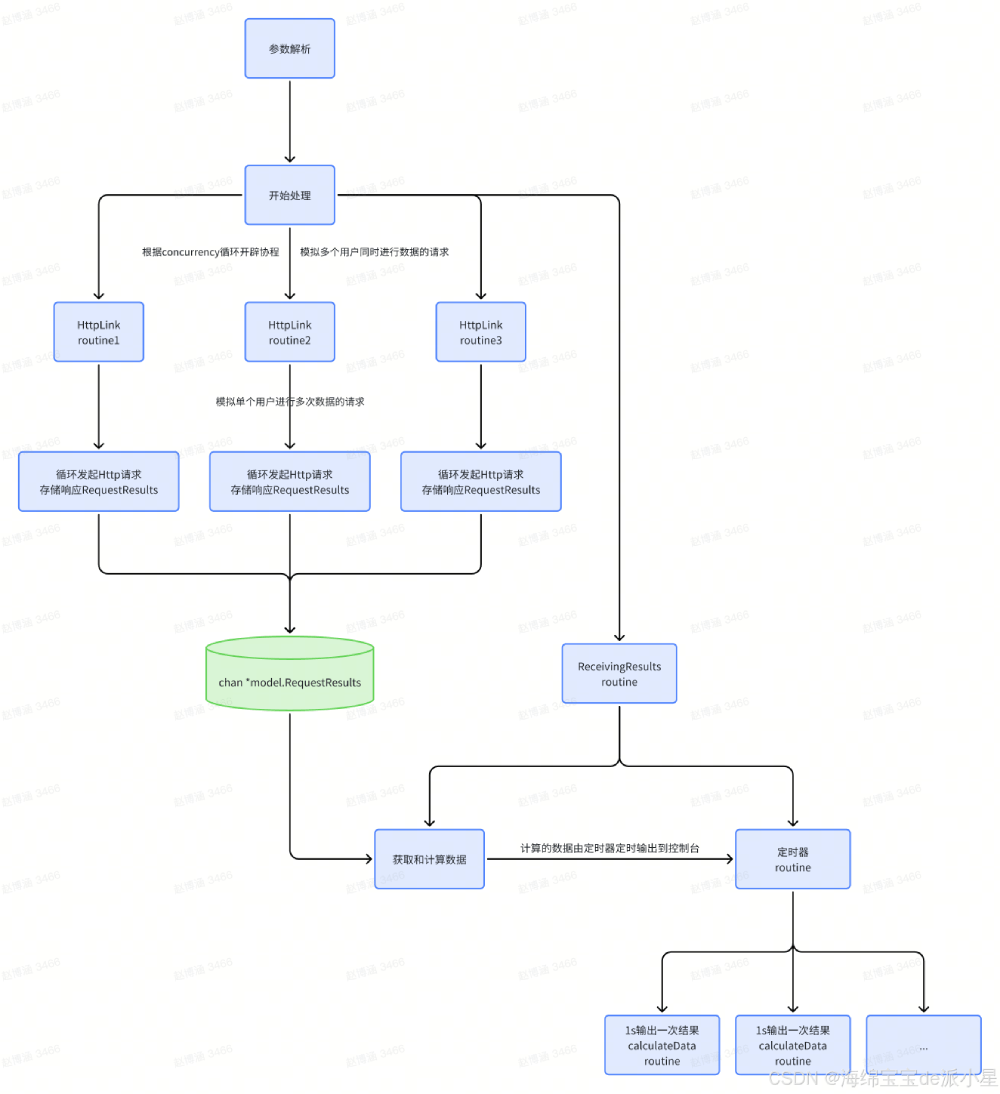
基本介绍
- 反射可以在运行时动态获取变量的各种信息,比如变量的类型,类别
- 如果是结构体变量,还可以获取到结构体本身的信息
- 通过反射,可以修改变量的值,可以调用关联的方法
- 使用反射,需要import("reflect")
示意图
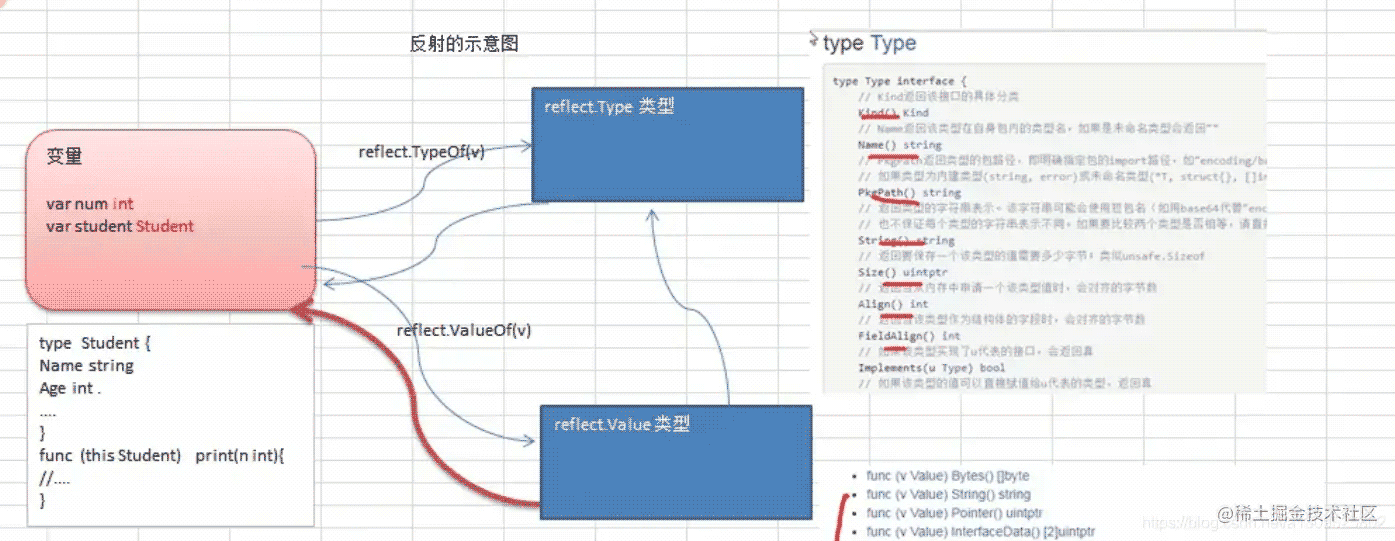
反射中常见函数和概念
reflect.TypeOf(变量名)
获取变量的类型,返回reflect.Type类型
reflect.ValueOf(变量名)
获取变量的值,返回reflect.Value类型reflect.Value是一个结构体类型,通过reflect.Value,可以获取到关于该变量的很多信息
变量.interface{}和reflect.Value是可以相互转换的

基本使用
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
package main import ( "fmt" "reflect" ) /* 1.编写案例,对基本数据类型,interface{},reflect.Value进行反射 2.编写案例,对结构体,interface{},reflect.Value进行反射 */ func reflectTest(b interface{}){ //打印出传参的type,kind,value fmt.Printf("b的类型为%v,b的kind为%v,value为%v\n",reflect.TypeOf(b),reflect.ValueOf(b).Kind(),reflect.ValueOf(b)) //b的类型为int,b的kind为int,value为100 //reflect.TypeOf(),reflect.ValueOf()返回的类型 fmt.Printf("reflect.TypeOf()返回类型为%T,reflect.ValueOf()返回类型为%T\n",reflect.TypeOf(b),reflect.ValueOf(b)) //reflect.TypeOf()返回类型为*reflect.rtype,reflect.ValueOf()返回类型为reflect.Value } type Student struct { Name string age int } func reflectTest2(b interface{}){ rTyp:=reflect.TypeOf(b) fmt.Println(rTyp) //main.Student rVal:=reflect.ValueOf(b) //将rVal转换成interface{} iV:=rVal.Interface() fmt.Printf("iv=%v type=%T\n",iV,iV) //iv={张三 18} type=main.Student //因为Go语言是静态语言,所以不能直接获取结构体中指定的值,所以我需要将其断言成需要的类型 stu,ok:=iV.(Student) if ok{ fmt.Printf(stu.Name,stu.age) //张三%!(EXTRA int=18) } } func main() { //1.编写案例,对基本数据类型,interface{},reflect.Value进行反射 var num int =100 reflectTest(num) //2.编写案例,对结构体,interface{},reflect.Value进行反射 stu:=Student{ Name: "张三", age: 18, } reflectTest2(stu) } |
反射注意事项
- reflect.ValueKind,获取的变量的类别,返回的是一个常量
- Type是类型,Kind是类别,Type和Kind可能是相同的,也可能是不同的,例如结构体
- 通过反射可以在让变量在interface{}和reflect.Value之间相互转换
- 通过反射的方式获取变量的值(并返回对应的类型),要求数据类型匹配,比如x是int,那么就应该使用reflect.Value(x).Int(),而不能使用其他的,否则报panic
- 通过反射来修改变量,注意当使用Setxxx方法来设置需要通过对应的指针类型来完成,这样才能改变传入变量的值,同时需要使用到reflect.Value.Elem()方法
反射的最佳实践
使用反射来遍历结构体的字段,调用结构体的方法,并获取结构体标签的值
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 |
package main import ( "fmt" "reflect" ) //定义了一个Monster结构体 type Monster struct { Name string `json:"name"` Age int `json:"monster_age"` Score float32 `json:"成绩"` Sex string } //方法,返回两个数的和 func (s Monster) GetSum(n1, n2 int) int { return n1 + n2 } //方法, 接收四个值,给s赋值 func (s Monster) Set(name string, age int, score float32, sex string) { s.Name = name s.Age = age s.Score = score s.Sex = sex } //方法,显示s的值 func (s Monster) Print() { fmt.Println("---start~----") fmt.Println(s) fmt.Println("---end~----") } func TestStruct(a interface{}) { //获取reflect.Type 类型 typ := reflect.TypeOf(a) //获取reflect.Value 类型 val := reflect.ValueOf(a) //获取到a对应的类别 kd := val.Kind() //如果传入的不是struct,就退出 if kd != reflect.Struct { fmt.Println("expect struct") return } //获取到该结构体有几个字段 num := val.NumField() fmt.Printf("struct has %d fields\n", num) //4 //变量结构体的所有字段 for i := 0; i < num; i++ { fmt.Printf("Field %d: 值为=%v\n", i, val.Field(i)) //获取到struct标签, 注意需要通过reflect.Type来获取tag标签的值 tagVal := typ.Field(i).Tag.Get("json") //如果该字段于tag标签就显示,否则就不显示 if tagVal != "" { fmt.Printf("Field %d: tag为=%v\n", i, tagVal) } } //获取到该结构体有多少个方法 numOfMethod := val.NumMethod() fmt.Printf("struct has %d methods\n", numOfMethod) //var params []reflect.Value //方法的排序默认是按照 函数名的排序(ASCII码) val.Method(1).Call(nil) //获取到第二个方法。调用它 //调用结构体的第1个方法Method(0) var params []reflect.Value //声明了 []reflect.Value params = append(params, reflect.ValueOf(10)) params = append(params, reflect.ValueOf(40)) res := val.Method(0).Call(params) //传入的参数是 []reflect.Value, 返回[]reflect.Value fmt.Println("res=", res[0].Int()) //返回结果, 返回的结果是 []reflect.Value*/ } func main() { //创建了一个Monster实例 var a Monster = Monster{ Name: "黄鼠狼精", Age: 400, Score: 30.8, } //将Monster实例传递给TestStruct函数 TestStruct(a) } |