代码示例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 |
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np import pytesseract from PIL import Image
img = cv.imread('test.jpg') rows, cols, _ = img.shape img = cv.resize(img, (int(cols/2), int(rows/2))) img = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) nrows, ncols = img.shape print(cols, ncols, rows, nrows) gray_blurred = cv.GaussianBlur(img, (5, 5), 0)
flag = 200
lines = [] while len(lines) != 4: # 使用Canny边缘检测 edges = cv.Canny(gray_blurred, 50, 150, apertureSize=3) lines = cv.HoughLines(edges, 1, np.pi / 180, flag) if lines is None: lines = [] if flag < 80: raise Exception('未找到合适的边缘处理参数') flag -= 5 print(flag) nlines = [] # 如果找到了直线,使用它们来计算仿射变换矩阵 if lines is not None: for rho, theta in lines[:, 0]: a = np.cos(theta) b = np.sin(theta) x0 = a * rho y0 = b * rho x1 = int(x0 + 1000 * (-b)) y1 = int(y0 + 1000 * (a)) x2 = int(x0 - 1000 * (-b)) y2 = int(y0 - 1000 * (a)) cv.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 2) nlines.append([(x1, y1), (x2, y2)]) points = [] for i in range(len(nlines) - 1): for j in range(i + 1, len(nlines)): line = nlines[i] x1, y1 = line[0] x2, y2 = line[1] line1 = nlines[j] x3, y3 = line1[0] x4, y4 = line1[1] try: u = ((x4-x3)*(y1-y3) - (y4-y3)*(x1-x3)) / ((y4-y3)*(x2-x1) - (x4-x3)*(y2-y1)) except Exception as e: continue x = x1 + u * (x2 - x1) y = y1 + u * (y2 - y1) if x > 0 and y > 0 and x < ncols and y < nrows: points.append((x, y)) pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r'D:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe' center = (int(ncols/2), int(nrows/2)) pstmap = {} for point in points: x, y = point cx, cy = center if x < cx and y < cy: pstmap['lt'] = point elif x > cx and y < cy: pstmap['rt'] = point elif x > cx and y > cy: pstmap['rb'] = point else: pstmap['lb'] = point
pst1 = np.float32([pstmap['lt'], pstmap['rt'], pstmap['rb'], pstmap['lb']]) pst2 = np.float32([[0, 0], [ncols, 0], [ncols, nrows], [0, nrows]]) M = cv.getPerspectiveTransform(pst1, pst2) dst = cv.warpPerspective(img, M, (ncols, nrows))
x1, y1 = 0, 0 def mouse_callback(event, x, y, flags, param): global x1, y1 if event == cv.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN: x1, y1 = x, y elif event == cv.EVENT_LBUTTONUP: x2, y2 = x, y wimg = dst[y1:y2, x1:x2] _, wimg = cv.threshold(wimg, 80, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY) wimg = cv.bitwise_not(wimg) cv.imwrite('test_dst.jpg', wimg) image = Image.open('test_dst.jpg') # 打印选定区域的坐标 print(f"({x1}, {y1}) -> ({x2}, {y2})") print(pytesseract.image_to_string(image, lang='chi_sim')) cv.namedWindow('dst') cv.setMouseCallback("dst", mouse_callback) cv.imshow('img', img) cv.imshow('dst', dst) print(dst[2]) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows() |
方法:
1. 首先读取图片, 因为我手机拍摄图片尺寸太大, 所以进行了缩放
2. 对图片进行高斯模糊, 方便进行边缘处理
3. 从高到低适配不同的阈值检测图片内容边缘
4. 通过反向霍夫变换获取确定边缘直线的四个点
5. 通过直线两两相交确定四个定点
6. 进行透视变换
7. 添加鼠标事件, 监测鼠标选定区域
8. 鼠标选定区域后, 裁剪图片, 对图片进行二值化处理, 我这里做了文字黑白反转
9. 利用pytesseract对裁剪后的图片进行文字识别
注意事项:
1. 选择的文字区域会影响识别成功率, 如果文字区域紧贴文字, 可能会失败, 盲猜影响了特征提取
2. 图片尺寸大小会影响边缘检测, 不缩放图片时, 阈值调整不当的话, 很容易生成N条边缘直线, 阈值怎么选定请了解霍夫变换的原理。
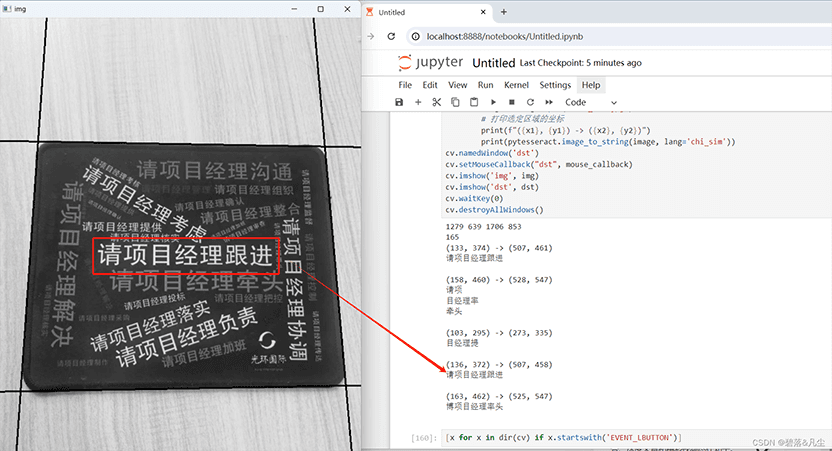
识别效果(加了二值化处理的准确度会很好):
补充:几个常用的OpenCV二值化代码示例
1. 全局阈值二值化:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
import cv2 img = cv2.imread('image.jpg', 0) _, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) cv2.imshow('image', img) cv2.imshow('threshold', thresh) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
2. 自适应阈值二值化:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
import cv2 img = cv2.imread('image.jpg', 0) thresh = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 2) cv2.imshow('image', img) cv2.imshow('adaptive threshold', thresh) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
3. Otsu二值化:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
import cv2 img = cv2.imread('image.jpg', 0) _, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU) cv2.imshow('image', img) cv2.imshow('Otsu threshold', thresh) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
这些示例代码可以根据需要进行修改和调整,以适应不同的图像处理任务。