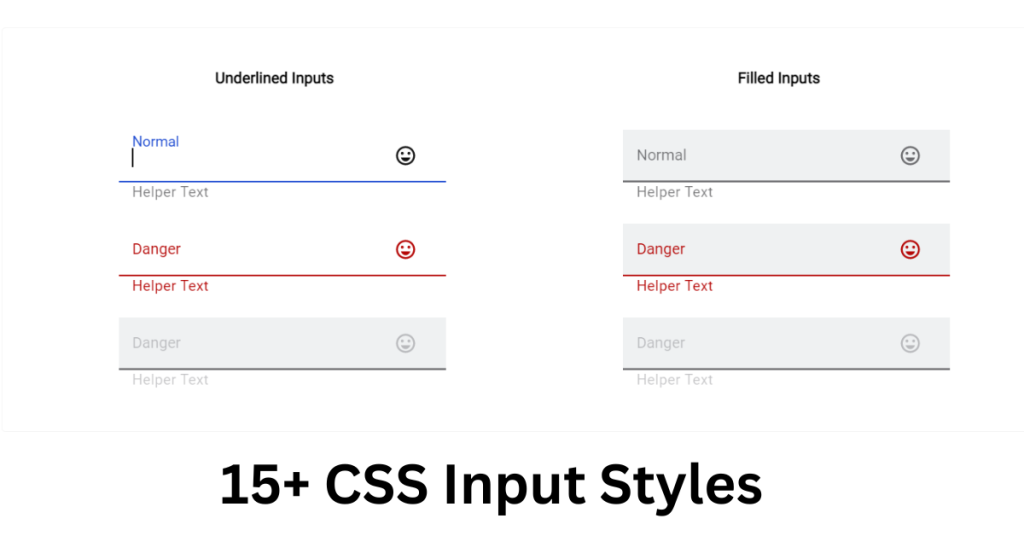
使用CSS3进行增强
滑过文字渐变
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
/* 这段代码实现了当鼠标滑过链接时的渐变效果 */ a { color: #007c21; transition: color .4s ease; } a:hover { color: #00bf32; } |
为元素创建圆角
使用CSS3可以在不引入额外的标记或图像的情况下,为大多数元素(包括表单元素、图像,甚至段落文本)创建圆角。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>Rounded Corners</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/rounded-corners.css" /> </head> <body> <div class="all-corners"></div> <div class="one-corner"></div> <div class="elliptical-corners"></div> <div class="circle"></div> </body> </html> |
使用CSS圆角的四个例子,包含了必要的厂商前缀以支持旧版的Android、Mobile Safari和Safari浏览器。对于.circle,使用75px与50%的效果是一样的,因为该元素的大小为150像素*150像素。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
div { background: #999; float: left; height: 150px; margin: 10px; width: 150px; } .all-corners { -webkit-border-radius: 20px; border-radius: 20px; } .one-corner { -webkit-border-top-left-radius: 75px; border-top-left-radius: 75px; } .elliptical-corners { -webkit-border-radius: 50px / 20px; border-radius: 50px / 20px; } .circle { -webkit-border-radius: 50%; border-radius: 50%; } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
div { background: #ff9; border: 5px solid #326795; float: left; height: 150px; margin: 10px; width: 150px; } .example-1 { /* Makes the radius of the top-left and bottom-right corners 10px and the top-right and bottom-left corners 20px */ border-radius: 10px 20px; } .example-2 { /* Makes the radius of the top-left corner 20px, and all other corners 0 */ border-radius: 20px 0 0; } .example-3 { /* Makes the radius of the top-left corner 10px, the top-right corner 20px, the bottom-right corner 0, and the bottom-left corner 30px */ border-radius: 10px 20px 0 30px; } |
为元素创建四个相同的圆角
- 这一步是可选的,输入-webkit-border-radius: r,这里的r是圆角的半径大小,表示为长度(带单位)。
- 输入border-radius: r,这里的r是圆角的半径大小,使用与第一步中相同的值。这是该属性的标准短形式语法。
为元素创建一个圆角
- 这一步是可选的,输入-webkit-border-top-left-radius: r,这里的r是左上方圆角的半径大小,表示为长度(带单位)。
- 输入border-top-left-radius: r,这里的r使用与第一步中相同的值。这是该属性的标准长形式语法。
- 创建右上方圆角使用top-right;创建右下方圆角使用bottom-right;创建左下方圆角使用bottom-left。
创建椭圆形圆角
- 这一步是可选的,输入-webkit-border-radius: x/y,其中x是圆角在水平方向上的半径大小,y是圆角在垂直方向上的半径大小,均表示为长度(带单位)。
- 输入border-radius: x/y,其中x和y跟第一步中的值相等。
使用border-radius(属性不是继承的)创建图形
- 输入-webkit-border-radius: r这里的r是元素的半径大小(带长度单位)。要创建圆形,可以使用短形式的语法,r的值应该等于元素高度或宽度的一半。
- 输入border-radius: r这里的r是元素的半径大小(带长度单位),跟第一步中的r相等。这是标准的无前缀语法。
注:不支持border-radius的旧的浏览器仅会以方角呈现元素。border-radius仅影响施加该样式的元素的角,不会影响其子元素的角。因此如果一个子元素有背景,该背景就有可能显示在一个或多个父元素的角的位置,从而影响圆角样式。有时元素的背景(这里讲的不是子元素的背景)会透过其圆角。为了避免这种情况,可以在元素的border-radius声明后面增加一条样式规则:background-clip: padding-box;。
为文本添加阴影
使用text-shadow可以在不使用图像表示文本的情况下,为段落、标题等元素中的文本添加动态的阴影效果。
为元素的文本添加阴影
- 输入text-shadow:。
- 分别输入表示x-offset(水平偏移量)、y-offset(垂直偏移量)、blur-radius(模糊半径)和color的值(前三个值带长度单位,四个值之间不用逗号分隔),例如 -2px 3px 7px #999。
为元素的文本添加多重阴影
- 输入text-shadow:。
- 分别输入x-offset(水平偏移量)、y-offset(垂直偏移量)、blur-radius(模糊半径)和color的值(前三个值带长度单位,四个值之间不用逗号分隔)。
- blur-radius的值是可选的。
- 输入,(逗号)。
- 对四种属性使用不同的值重复第二步。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>Text Shadow</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/text-shadow.css" /> </head> <body> <p class="basic">Basic Shadow</p> <p class="basic-negative">Basic Shadow</p> <p class="blur">Blur Radius</p> <p class="blur-inversed">Blur Radius</p> <p class="multiple">Multiple Text Shadows</p> </body> </html> |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
body { background: #fff; color: #222; font: 100%/1.05 helvetica, sans-serif; padding-top: 20px; } p { color: #222; /* nearly black */ font-size: 4.5em; font-weight: bold; margin: 0 0 45px; } p:last-child { margin: 0; } .basic { text-shadow: 3px 3px #aaa; } /* uses negative offsets--you can mix positive and negative ones, too. */ .basic-negative { text-shadow: -4px -2px #ccc; /* a little lighter grey than #aaa */ } .blur { text-shadow: 2px 2px 10px grey; } .blur-inversed { color: white; text-shadow: 2px 2px 10px #000; /* black */ } /* this example has two shadows, but you can include more by separating each with a comma */ .multiple { text-shadow: 2px 2px white, 6px 6px rgba(50,50,50,.25); } |
这些类演示了几种text-shadow的效果。第一个、第二个和第五个都省略了模糊半径的值。.multiple类告诉我们,可以为单个元素添加多个阴影样式,每组属性之间用逗号分隔。这样,通过结合使用多个阴影样式,可以创建出特殊而有趣的效果。
将text-shadow(属性是继承的)改回默认值
即输入text-shadow: none;,这个属性不需要输入使用厂商前缀。
text-shadow属性接受四个值:带长度单位的x-offset、带长度单位的y-offset、可选的带长度单位的blur-radius以及color值。如不指定blur-radius,将假定其值为0。x-offset和y-offset值可以是正整数也可以是负整数,也就是说1px和-1px都是有效的。blur-radius值必须是正整数。这三个值都可以为0。尽管text-shadow的语法与边框和背景属性的语法是类似的,但它不能像边框和背景那样单独的指定四个属性值。如果不指定text-shadow,它就会使用初始值none。
为其他元素添加阴影
使用text-shadow属性可以为元素的文本添加阴影,使用box-shadow属性则可以为元素本身添加阴影。他们的基础属性集是相同的,不过box-shadow还允许使用使用两个可选的属性:inset关键字属性和spread属性(用于扩张或收缩阴影)。
box-shadow属性接受六个值:带长度单位的x-offset和y-offset、可选的带长度单位的blur-radius、可选的inset关键字、可选的带长度单位的spread值及color值。如果不指定blur-radius和spread的值,则设为0。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>Box Shadow</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/box-shadow.css" /> </head> <body> <div class="shadow"> <p>Shadow with Blur</p> </div> <div class="shadow-negative"> <p>Shadow with Negative Offsets and Blur</p> </div> <div class="shadow-spread"> <p>Shadow with Blur and Spread</p> </div> <div class="shadow-offsets-0"> <p>Shadow with Offsets Zero, Blur, and Spread</p> </div> <div class="inset-shadow"> <p>Inset Shadow</p> </div> <div class="multiple"> <p>Multiple Shadows</p> </div> <div class="shadow-negative-spread"> <p>Shadow with Blur and Negative Spread</p> </div> </body> </html> |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
body { background: #000; color: #fff; } h1 { font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 2.25em; line-height: 1.1; text-align: center; } /* NOTE: The background-image URLs are different below than in the example shown in the book, because I've placed the images in a sub-folder (called "img"), as is typical when organizing a site. Also, I thought it would be helpful for you to see how to construct your background-image URLs under these circumstances. Note that the URLs are relative to where the style sheet lives, NOT the HTML page that is displaying the image. */ .night-sky { background-color: navy; /* fallback color */ background-image: url(../img/ufo.png), url(../img/stars.png), url(../img/stars.png), url(../img/sky.png); background-position: 50% 102%, 100% -150px, 0 -150px, 50% 100%; background-repeat: no-repeat, no-repeat, no-repeat, repeat-x; height: 300px; margin: 25px auto 0; /* slightly different than book */ padding-top: 36px; width: 75%; } |
上面程序用于演示使用box-shadow添加一个或多个阴影的效果。前五个类各自应用了一个彼此不同的阴影样式。最后一个类应用了两个阴影(还可以应用更多个阴影)。不理解box-shadow的浏览器会直接忽略这些CSS样式规则,呈现没有阴影的页面。
为元素添加阴影
- 输入-webkit-box-shadow:。
- 分别输入表示x-offset、y-offset、blur-radius、spread和color的值(前四个值均带长度单位),例如 2px 2px 5px #333。
- 输入box-shadow:,再重复第二步。
创建内阴影
- 输入-webkit-box-shadow:。
- 分别输入表示表示x-offset、y-offset、blur-radius、spread和color的值(前四个值均带长度单位),例如 2px 2px 5px #333。
- 在冒号后输入inset,再输入一个空格(也可以在第二步之前输入inset和一个空格)。
- 输入box-shadow:,再重复第二步和第三步。
为元素应用多重阴影
- 输入-webkit-box-shadow:。
- 分别输入表示表示x-offset、y-offset、blur-radius、spread和color的值(前四个值均带长度单位),例如 2px 2px 5px #333。
- 如果有必要,将inset关键字包含在内。
- 输入逗号。对每种属性使用不同的值重复第二步。
- 输入box-shadow:,再重复第二步至第四步。
将box-shadow(属性是不继承的)改回默认值
- 输入-webkit-box-shadow: none;。
- 输入box-shadow: none;。
注:x-offset、y-offset和spread值可以是正整数,也可以是负整数。blur-radius值必须是正整数。这三个值都可以为零。inset关键字可以让阴影位于元素内部。
应用多重背景
多重背景几乎可以应用于任何元素。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>Multiple Backgrounds</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/multiple-backgrounds.css" /> </head> <body> <div class="night-sky"> <h1>In the night sky...</h1> </div> </body> </html> |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
... .night-sky { background-color: navy; /* fallback color */ background-image: url(../img/ufo.png), url(../img/stars.png), url(../img/stars.png), url(../img/sky.png); background-position: 50% 102%, 100% -150px, 0 -150px, 50% 100%; background-repeat: no-repeat, no-repeat, no-repeat, repeat-x; height: 300px; margin: 25px auto 0; /* slightly different than book */ padding-top: 36px; width: 75%; } |
为单个元素应用多重背景图像(不需要使用厂商前缀)
- 输入background-color: b,这里的b是希望为元素应用的备用背景颜色。
- 输入background-image: u,这里的u是绝对或相对路径引用的url列表(用逗号分隔。支持多重背景的浏览器,图像是分层次相互重叠在一起的,用逗号分隔的列表中的第一个图像位于顶部。)
- 输入background-position: p,这里的p是成对的x-offset和y-offset(可以是正的,也可以是负的;带长度单位或者关键字,如center top)的集合,用逗号分隔。对于第二步中指定的每个url,都应有一组x-offset和y-offset。
- 输入background-repeat: r,这里的r是repeat-x、repeat-y或no-repeat值,用逗号分隔,第二步中指定的每个url对应一个值。
对于多重背景图像,可以使用标准的短形式语法,即使用逗号分隔每组背景参数。这种表示方法的好处是开发者既可以指定备用背景颜色,也可以为旧的浏览器指定图像。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
.night-sky { /* fallback with both a color and image */ background: navy url(../img/ufo.png) no-repeat center bottom; /* for supporting browsers */ background: url(../img/ufo.png) no-repeat 50% 102%, url(../img/stars.png) no-repeat 100% -150px, url(../img/stars.png) no-repeat 0 -150px, url(../img/sky.png) repeat-x 50% 100%; height: 300px; margin: 25px auto 0; padding-top: 36px; width: 75%; } |
使用渐变背景
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>Gradient Backgrounds</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/gradients.css" /> </head> <body> <div class="vertical-down"><p>default</p></div> <div class="vertical-up"><p>to top</p></div> <div class="horizontal-rt"><p>to right</p></div> <div class="horizontal-lt"><p>to left</p></div> <div class="angle-bot-rt"><p>to <br />bottom right</p></div> <div class="angle-bot-lt"><p>to <br />bottom left</p></div> <div class="angle-top-rt"><p>to top right</p></div> <div class="angle-top-lt"><p>to top left</p></div> <div class="angle-120deg"><p>120deg</p></div> <div class="angle-290deg"><p>290deg</p></div> <section class="radial"> <div class="radial-center"><p>default</p></div> <div class="radial-top"><p>at top</p></div> <div class="radial-size-1"><p>100px, 50px</p></div> <div class="radial-size-2"><p>70% 90% at <br />bottom left</p></div> <div class="radial-various-1"><p>various 1</p></div> <div class="radial-various-2"><p>various 2</p></div> </section> <section class="color-stops"> <div class="color-stops-1"><p>yellow 10%, green</p></div> <div class="color-stops-2"><p>to top right, yellow, <br>green 70%, <br>blue</p></div> </section> </body> </html> |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 |
body { padding: 1.25em; /* 20px/16px, so 20px on each side */ font-size: 100%; } div { float: left; height: 150px; margin: 10px; width: 150px; } p { color: #fff; font: bold 1.25em/1 sans-serif; /* 20px/16px */ padding-top: 1.65em; /* 33px/16px */ text-align: center; } /* NOTE: The gradients below are in the standard CSS3 syntax. The browsers that support them are Chrome 26+, Firefox 16+, IE 10+, and Opera 12.10+. See gradients-with-browser-prefixes.css for the same gradient effects, but with the vendor prefix code also included so the gradients will work on several older browsers.A background with a "fallback" comment is the color that will show in browsers that don't support the gradient syntax. You can use a backgroundimage as a fallback as well (either on its own or in combination with a color).For example, background: red url(gradient-image.jpg) no-repeat;. */ /* LINEAR GRADIENTS ------------------------------------------ */ /* :::: Vertical :::: */ .vertical-down { background: silver; /* fallback */ /* default gradient, so you don't need to specify "to bottom" before the colors */ background: linear-gradient(silver, black); } .vertical-up { background: silver; background: linear-gradient(to top, silver, black); } /* :::: Horizontal :::: */ .horizontal-rt { background: silver; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(to right, silver, black); } .horizontal-lt { background: silver; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(to left, silver, black); } /* :::: Diagonal Angles :::: */ /* Note: The figures on page 377 show aqua as the fallback color, but I've switched it to navy below because the white text will be easier to read on a navy background. */ .angle-bot-rt { background: navy; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(to bottom right, aqua, navy); } .angle-bot-lt { background: navy; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(to bottom left, aqua, navy); } .angle-top-rt { background: navy; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(to top right, aqua, navy); } .angle-top-lt { background: navy; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(to top left, aqua, navy); } /* :::: Angles via Degrees :::: */ .angle-120deg { background: navy; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(120deg, aqua, navy); } .angle-290deg { background: navy; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(290deg, aqua, navy); } /* RADIAL GRADIENTS ------------------------------------------ */ /* :::: Radial :::: */ .radial p { text-shadow: 0 0 3px #000; } .radial-center { background: red; /* fallback */ background: radial-gradient(yellow, red); /* default */ } .radial-top { background: red; /* fallback */ background: radial-gradient(at top, yellow, red); } .radial-size-1 { background: red; /* fallback */ background: radial-gradient(100px 50px, yellow, red); } .radial-size-2 { background: red; /* fallback */ background: radial-gradient(70% 90% at bottom left, yellow, red); } .radial-various-1 { background: red; /* fallback */ background: radial-gradient(closest-side at 70px 60px, yellow, lime, red); } .radial-various-2 { background: red; /* fallback */ background: radial-gradient(30px 30px at 65% 70%, yellow, lime, red); } /* LINEAR GRADIENTS WITH COLOR STOPS ------------------------------------------ */ .color-stops div { margin-bottom: 30px; } .color-stops p { padding-top: 25px; text-shadow: 0 0 3px #000; } .color-stops-2 p { font-size: 18px; line-height: 1.05; } .color-stops-1 { background: green; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(yellow 10%, green); } .color-stops-2 { background: green; /* fallback */ background: linear-gradient(to top right, yellow, green 70%, blue); } |
创建备用背景颜色
输入background: color或者background-color: color,这里的color可以是十六进制数、RGB值以及其他任何支持的颜色名称,另外也可以使用图像。最好不要将RGBA、HSL或HSLA值作为备用背景颜色(如果你不打算支持IE则不必在意),因为IE8及以前的版本不支持。
定义线性渐变
- 输入background: linear-gradient(。
- 如果希望渐变方向是从上向下(默认方向),则可以跳过这一步。
- 输入方向后面加一个逗号,方向指to top、to right、to bottom right、to top right等这样的值。
- 或者输入方向后面加一个逗号,这里的方向指的是角度值(如45deg、107deg等)。根据后面讲到的“指定颜色”等,定义渐变颜色。
- 输入);完成渐变。
定义径向渐变
- 输入background: radial-gradient(。
- 指定渐变的形状。希望指定尺寸则可根据第三步中指定的尺寸自行确定。
- 否则输入circle或ellipse。
- 指定渐变的尺寸。
- 如果希望尺寸为自动指定的值(默认值为·farthest-corner·,最远的角),则跳过这一步。
- 否则输入代表渐变宽度和高度的一个长度值(如200px或7em)或代表宽度和高度的一对值(390px 175px或60% 85%)。
- 注意,如果只使用一个值,则这个值不能是百分数。或者输入closest-side、farthest-side、closest-corner或farthest-corner。
- 这些关键字代表相对于渐变的中心,渐变可以伸展到多大的空间。
- 边界决定了渐变的尺寸。指定渐变的位置。希望渐变的位置从元素的中心开始(默认值)则可跳过这一步。
- 输入at top、at right、at bottom left、at top right等表示渐变中心位置的值。或者输入表示渐变中心位置的一对坐标,并以at开头,例如at 200px 43px、at 30% 40%、at 50% -10px等。定义渐变颜色。输入);完成渐变。
指定颜色
- 输入至少两种颜色,每种颜色之间用逗号分隔。
- 指定的第一个颜色出现在渐变的开始位置,最后一个出现的颜色出现在渐变的结束位置。
- 对于径向渐变,它们分别为最里边的颜色和最外边的颜色。
为元素设置不透明度(opacity属性不继承)
使用opacity属性可以修改元素的透明度。方法是输入opacity: x,这里的x表示元素元素的不透明程度(两位小数,不带单位)。
opacity的默认值为1(完全不透明),范围为0~1。
通过使用opacity属性和:hover伪属性,可以产生一些有趣且实用的效果。例如img { opacity: .75; }默认情况下可以将图片设置为75%的不透明度,img:hover { opacity: 1; }可导致用户鼠标停留在元素上时元素变为不透明。在将缩略图链接到全尺寸版本时经常看到这种效果。对于访问者来说,悬浮可增强图像的动感。
opacity属性与使用RGBA或HSLA设置的透明背景色是两个容易混淆的概念。opacity影响的是整个元素(包括其内容),而background-color: rgba(128,0,64,.6);这样的设置仅影响背景的透明度。
生成内容的效果
使用:before和:after伪元素可以很方便地为页面添加一些令人难以置信的设计效果。它们可以与content属性结合使用,从而创建所谓的生成内容。生成内容指的是通过CSS创建的内容而不是HTML生成的。
|
1 2 3 |
... <p>This area is one of the most tranquil spaces at the Villa. As I wandered around, enjoying shade provided by sycamore and laurel trees and serenaded by splashing water from two sculptural fountains, I couldn't help but think … <a href="victoria.html" class="more">Read More</a></p> ... |
|
1 2 3 4 |
/* The generated content */ .more:after { content: " »"; } |
通过上面代码,可以使带有class="more"的元素会在其后显示一个双箭头,以后如需变动,修改也只需要修改.more类即可,而不需要改动大量的HTML页面。
使用sprite拼合图像
浏览器中文本显示速度很快,但是图像往往会减慢页面的加载速度。为解决这一问题,可以将多个图像拼合成单个背景图像(sprite),再通过CSS控制具体显示图像的哪一部分,使用的就是background-position属性。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
.documents li { margin-top: .45em; } /* Each link in the HTML has this class */ .icon { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.1; font-size: .875em; min-height: 16px; /* set to height of icon so it isn't cut off at all */ padding-left: 23px; padding-top: 2px; /* allows positioning the icon absolutely relative to elements with class="icon" in the HTML */ position: relative; } .icon:before { background-image: url(../img/sprite.png); content: " "; display: block; height: 16px; /* icon height */ left: 0; /* default. change this if want the icon to appear in different spot */ position: absolute; width: 16px; /* icon width */ top: 0; /* default. change this if want the icon to appear in different spot */ } /* Shift position of sprite image for any document filename that ends with .xls */ a[href$=".xls"]:before { background-position: -17px 0; } /* Shift position of sprite image for any document filename that ends with .docx */ a[href$=".docx"]:before { background-position: -34px 0; } |
可以将sprite应用于任意数量的元素。在上面这个例子中,使用.icon:before来实现所需的效果。这样sprite就是通过content: " ";生成的空格的背景图像。将其设置为display: block;,从而就可以设置与图标大小匹配的高度和宽度。没有这三个属性,图像将不会显示。通过使用background-position,可以将正确的图标放入该位置。