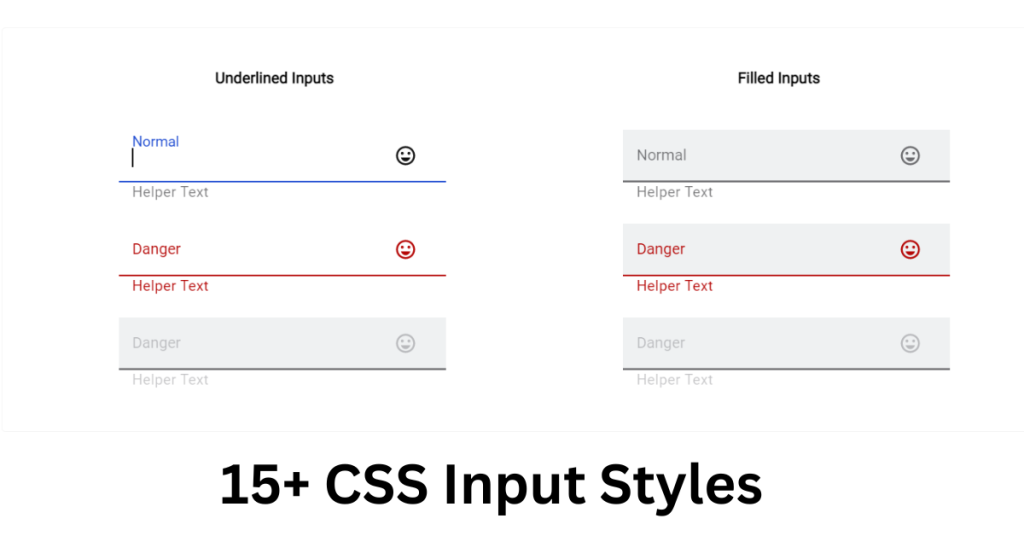
伪元素与伪类两者都是通过在选择器后附加一个特定的关键字来定义,遵循相似的语法规则,并在 CSS 规则块中设置相应的样式。伪元素 能够通过 content 属性添加或替换内容。例如,:before 和 :after 可以插入文本、图像或其他生成的内容。伪类 仅影响元素的样式,而不添加或修改内容。它们基于用户的交互、文档结构或其他逻辑条件来改变元素的表现。主要区别如下:
作用对象:
- 伪类选择器(Pseudo-classes)作用于实际存在的元素,用于描述元素的某种特定状态或关系,如链接的访问状态(:visited)、鼠标悬停状态(:hover)、是否为文档中的第一个子元素(:first-child)等。它们不直接改变元素的结构,而是影响元素在特定条件下的表现样式。
- 伪元素选择器(Pseudo-elements)则用于创建并选择元素内的某个特定部分或是在元素前后生成新的、虚拟的内容节点。例如,:before 和 :after 可以用来插入额外内容,:first-line 和 :first-letter 分别选择元素首行文本和首字母,:marker 控制列表项标记样式等。这些伪元素并不对应于HTML文档中的实际元素,但可以对其应用样式,如同它们是真实存在的部分一样。
语法标识:
- 伪类 通常使用一个冒号(:)进行标识,如 :hover、:focus。
- 伪元素 在 CSS3 中使用两个连续的冒号(::)进行标识,以区分于旧版 CSS 中的伪类。尽管大多数现代浏览器仍接受单冒号表示伪元素(如 :before),但为了符合 W3C 标准和保持最佳实践,建议使用双冒号形式,如 ::before、::after。
可复用性:
- 伪类 可以在同一选择器中组合使用,如 a:hover:focus 表示同时处于悬停和聚焦状态的链接。
- 伪元素 由于代表了元素内部的特定部分或生成的新内容,一般不能在同一选择器中重复出现。一个元素在同一时刻只能有一个:before或:after伪元素生效。
一、CSS3 伪元素选择器详解与应用实例
CSS3 伪元素是一种特殊的 CSS 选择器,它们允许开发者在不修改 HTML 结构的前提下,通过 CSS 为元素添加或修改特定部分的样式,或者在元素内部或外部生成并控制虚拟内容。以下是对几种常见 CSS3 伪元素的详解以及应用实例:
1、:before 和 :after
:before 和 :after 伪元素分别在所选元素的内容区域之后创建一个新的、无内容的、不可见的“子元素”。然后,通过给这个伪元素设置样式(如内容、尺寸、颜色、背景等),使其变为可见,并在视觉上表现为紧随原元素内容之后的部分。这些内容由 content 属性定义,并且可以应用其他样式。
语法:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
selector:before { content: "..." /* 或其他值 */; /* 其他样式声明 */ } selector:after { content: "..." /* 或其他值 */; /* 其他样式声明 */ } |
其中,content 属性是定义伪元素生成内容的关键。它可以接受以下几种值:
- 字符串:直接指定要显示的文字。
- 引号包围的HTML实体:如 content: "—";(破折号)。
- URL:插入图片资源,如 content: url(image.png);。
- 生成内容关键字:如 content: counter(name);(计数器)或 content: attr(attribute-name);(获取元素属性值)。
应用实例:
1.1. 添加装饰性内容
添加引号、图标或其他装饰性元素。
添加引号:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
blockquote:before { content: open-quote; font-size: larger; color: #666; } blockquote:after { content: close-quote; } |
在列表项前/后添加自定义图标:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
li:before { content: url(icon-checkmark.svg); margin-right: 0.5em; } li.completed:after { content: "\2713"; /* Unicode 字符:对勾 */ color: green; font-size: 1.5em; vertical-align: super; } |
1.2. 清除浮动
:after 常用于创建一个空的块级元素,配合 clear:both 来清除浮动对后续元素的影响,避免“高度塌陷”问题。
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
.clearfix:after { content: ""; display: table; clear: both; } |
将 .clearfix 类应用于需要清除内部浮动的容器元素。
1.3. 替代或扩展HTML内容
利用 attr() 函数,可以从元素的属性中提取值作为 :after 的内容,实现动态文本展示。
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
abbr[title]:after { content: " (" attr(title) ")"; font-size: smaller; color: gray; } |
此例中,当鼠标悬停在带有 title 属性的 abbr 元素上时,会显示一个包含 title 属性值的小字号灰色括注内容。
1.4. 实现复杂形状与动画
结合 content、background、border 等属性以及CSS3的 transform、transition 或 animation,可以使用 :after 创建复杂的形状和动画效果。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
.button:after { content: ""; display: inline-block; width: 0; height: 0; border-top: ?em solid transparent; border-right: ?em solid transparent; border-bottom: ?em solid #007BFF; border-left: ?em solid transparent; margin-left: 0.½em; } .button:hover:after { transform: translateY(-0.1em); transition: transform 0.2s ease-in-out; } |
上述代码在.button元素后创建了一个三角形下拉箭头,并在鼠标悬停时实现平滑的下移动画。
注意事项
- :after 伪元素必须与 content 属性一起使用,否则不会产生任何效果。
- 由于 :after 是创建的虚拟元素,无法通过JavaScript进行DOM操作。
- 虽然 :after 生成的内容可以参与布局,但它不计入DOM,不影响语义,也不影响键盘导航等辅助功能。
总结而言,CSS3 伪元素选择器通过在元素内容后插入自定义内容,极大地丰富了网页设计的表现力,且无需改动HTML结构。熟练运用伪元素与其他CSS技巧,可以帮助开发者构建更加美观、响应迅速且易于维护的网页界面。
2、:first-line 和 :first-letter
:first-line 伪元素选择器用于设置元素内首行文本的样式,而 :first-letter 伪元素则用于设置元素内首字母的样式。
语法:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
selector:first-line { /* 样式声明 */ } selector:first-letter { /* 样式声明 */ } |
应用实例:
首行缩进:
|
1 2 3 |
article p:first-line { text-indent: 2em; } |
首字母大写与装饰:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
article h2:first-letter { font-size: 2em; float: left; margin-right: 0.5em; line-height: 0.8; color: #8A2BE2; background-color: #F8F8FF; padding: 0.?em 0.?em; border-radius: 0.5em; } |
二、CSS3 伪类选择器详解与实践示例
CSS3 伪类选择器是一种强大的工具,它允许开发者基于元素状态而非其在文档树中的位置或类、ID等固有属性来精确地定位并施加样式。这些选择器以特殊的语法结构描述元素的不同条件状态,如用户交互、位置关系、内容特性等,从而实现动态、响应式的网页设计。以下是CSS3伪类选择器的详细解释及其实际应用示例。
1、静态伪类选择器
:link与:visited
:link: 用于选择尚未被用户访问过的超链接(<a>元素)。通常用于设置未访问链接的基本样式。
|
1 2 3 4 |
a:link { color: blue; text-decoration: none; } |
:visited: 选择用户已经访问过的链接。用于设置已访问链接的区分样式。
|
1 2 3 |
a:visited { color: purple; } |
2、用户交互伪类选择器 :hover, :focus, :active
:hover: 当鼠标指针悬浮在元素上时,匹配该元素。
|
1 2 3 4 |
button:hover { background-color: #f0f0f0; cursor: pointer; } |
:focus: 选择获得焦点的元素,常见于表单控件或可聚焦元素(如<input>, <textarea>, <button>等)。
|
1 2 3 4 |
input:focus { outline: 2px solid #007BFF; box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.2rem rgba(0, 123, 255, 0.25); } |
:active: 用于表示用户正在激活或按下某个元素(通常在鼠标点击或触摸屏上按压时)。
|
1 2 3 4 |
a:active { color: red; font-weight: bold; } |
3、结构化伪类选择器 :first-child, :last-child, :only-child, :nth-child(n)等
:first-child: 选择作为其父元素第一个子元素的元素。
|
1 2 3 |
li:first-child { list-style-type: square; } |
:last-child: 选择作为其父元素最后一个子元素的元素。
|
1 2 3 |
div > p:last-child { margin-bottom: 0; } |
:only-child: 选择没有兄弟元素的元素。
|
1 2 3 |
.message:only-child { border-width: 2px; } |
:nth-child(n): 选择其父元素的第n个子元素,其中n可以是数字、关键词(even, odd)或公式(如2n+1)。
|
1 2 3 |
li:nth-child(2n) { background-color: #f9f9f9; } |
4、内容相关伪类选择器
:empty, :target, :enabled, :disabled, :checked等
:empty: 选择没有任何内容(包括子元素、文本节点等)的元素。
|
1 2 3 |
div.empty:empty { display: none; } |
:target: 选择当前URL片段标识符(hash)与该元素ID相匹配的元素。
|
1 2 3 |
#content:target { background-color: lightyellow; } |
:enabled与:disabled: 分别选择启用状态与禁用状态的表单元素。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
input:enabled { background-color: white; } input:disabled { opacity: 0.6; cursor: not-allowed; } |
:checked: 用于复选框(<input type="checkbox">)、单选按钮(<input type="radio">)或<option>元素处于选中状态时。
|
1 2 3 |
input[type="checkbox"]:checked + label { text-decoration: line-through; } |
5、否定伪类选择器
:not(selector)
:not(): 选择不符合括号内指定选择器的元素。
|
1 2 3 4 |
/* 除了class为"exclude"的所有段落 */ p:not(.exclude) { color: green; } |
6、其他伪类选择器
:root, :nth-of-type(n), :nth-last-of-type(n), :first-of-type, :last-of-type, :only-of-type等
:root: 选择文档的根元素(HTML文档中通常是<html>元素)。
|
1 2 3 |
:root { --primary-color: #3498db; } |
:nth-of-type(n)与:nth-last-of-type(n): 类似于:nth-child(n),但仅针对同级元素中特定类型的子元素。
|
1 2 3 |
article:nth-of-type(even) { background-color: #f5f5f5; } |
:first-of-type, :last-of-type与:only-of-type: 分别选择同级元素中第一个、最后一个或唯一一个特定类型的子元素。
|
1 2 3 |
div > p:first-of-type { font-weight: bold; } |
通过熟练掌握以上CSS3伪类选择器及其应用场景,开发者能够编写出更高效、更具表现力和交互性的CSS代码,提升网站的用户体验和视觉效果。随着CSS标准的不断演进,还可能有更多新的伪类选择器加入到CSS3的行列中,为前端开发提供更为丰富和精细的控制手段。
无论是伪类还是伪元素,都是为了增强 CSS 选择器的功能,使开发者能够在不改动 HTML 结构的情况下,更精细地控制元素的样式和布局。