pathlib:面向对象的文件系统路径
pathlib官方介绍: Python3.4+内置的标准库,Object-oriented filesystem paths(面向对象的文件系统路径)
1. 使用示例
1.1 最常用:获取项目目录
os.path方法
|
1 2 3 4 |
import os project_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) print(project_dir) # /Users/root/Code/project print(type(project_dir)) # <class 'str'> |
pathlib方法
|
1 2 3 4 |
from pathlib import Path project_dir = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent print(project_dir) # /Users/root/Code/project print(type(project_dir)) # <class 'pathlib.PosixPath'> |
1.2 遍历一个目录下指定文件
os方法
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
file_list = [] for file in os.listdir(csv_dir): if not file.endswith('.csv'): continue file_list.append(file) |
pathlib方法
|
1 2 3 |
from pathlib import Path csv_dir = Path(csv_dir) file_list = csv_dir.glob('*.csv') |
1.3 递归目录下的所有文件
os方法
os.walk方法
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
file_list = [] for root, dirs, files in os.walk('/Users/root/Code/project'): for f in files: if f.endswith('.py'): file_list.append(os.path.join(root, f)) |
|
1 2 3 |
# glob方法 from glob import glob file_list = glob('/Users/root/Code/project/**/*.py', recursive=True) |
pathlib方法
|
1 |
file_list = csv_dir.rglob('*.csv') # 生成器对象 |
2. 优势对比
1、当需要获取多个层级目录时,os.path需要使用嵌套的写法,而pathlib则是正常的链式调用。pathlib的使用更加友好,使得路径对象更加明确。
2、os.path只用于基本的路径处理,如果需要其他操作如重命名/新建/复制文件等,需要用os下的其他模块。而pathlib可以用于处理路径相关操作,并且是一个轻量级的库。
3、os.path操作的路径时字符串,而pathlib操作的路径时对象。提供了对资源路径和资源命名结构的通用抽象。它把文件系统接口从os模块中隔离出来,打开了从应用层配置文件系统的大门。
换句话说,pathlib.Path这个接口代表的可以不仅是os的资源路径,还可以是HDFS的资源路径,RESTful API的资源路径。
3. 基本介绍
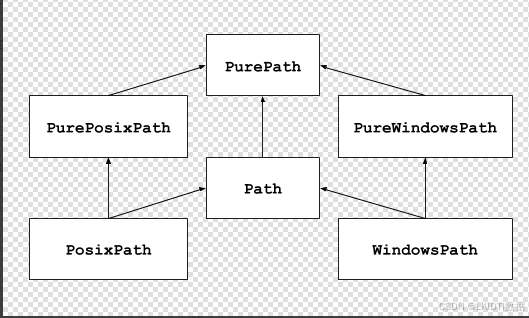
1、官网上给出的该模块提供表示文件系统路径的类,如下,其语义适用于不同的操作系统,路径类被分为提供纯计算操作而没有 I/O 的纯路径,以及从纯路径继承而来但提供 I/O 操作的具体路径。一般情况下,直接使用Path即可。
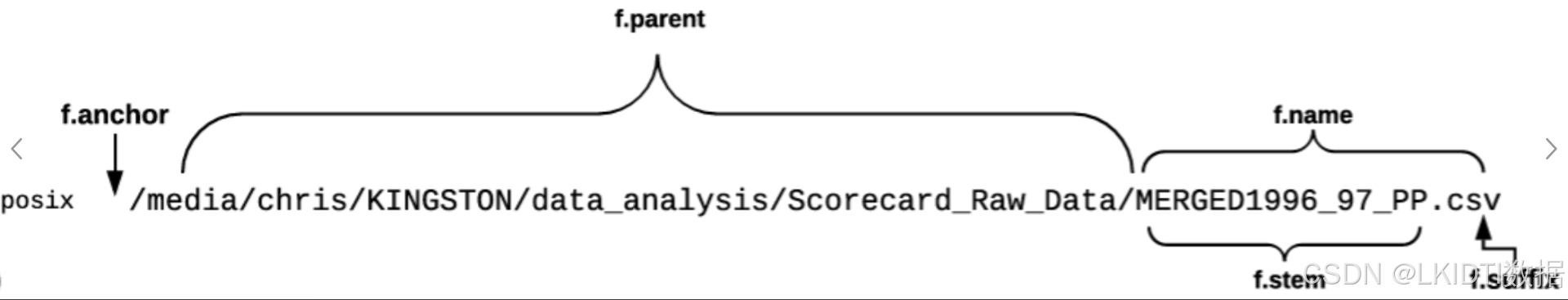
2、Path属性
4. 常见用法
获取当前文件绝对路径
|
1 2 3 4 |
from pathlib import Path path = Path(__file__).resolve() path >>> /Users/root/Code/project/conf/path_conf.py |
获取当前文件的上级目录
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
from pathlib import Path path = Path(__file__).resolve() path.parent >>> /Users/root/Code/project/conf path.parent.parent >>> /Users/root/Code/project |
获取文件名
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
from pathlib import Path path = Path(__file__).resolve() path.name >>> path_conf.py path.stem >>> path_conf path.suffix >>> .py |
修改文件名,修改后缀
|
1 2 3 4 |
from pathlib import Path file = Path('data.csv') new_file = file.with_name('result.csv') new_file = file.with_suffix('.txt') |
路径拼接
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
from pathlib import Path root = Path(__file__).resolve().parent # 方式1 conf_file = root / 'conf/path_conf.py' # 方式2 conf_file = root / Path('conf/path_conf.py') # 方式3 conf_file = root.joinpath('conf/path_conf.py') |
路径判断
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
from pathlib import Path path = Path(__file__).resolve() path.is_file() # 是否为文件 path.is_dir() # 是否为目录 path.exists() # 是否存在 |
文件操作
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
from pathlib import Path file = Path(__file__).resolve() file.touch() # 新建文件 file.replace('../data.csv') # 移动文件 file.unlink() # 删除文件 |
读取文件
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
file = Path('../data/1.csv') data = file.read_text() # 读取文件 data = file.write_text() # 写入文件 # 也可以作为普通路径使用 with open(file, 'r') as f: data = f.read() |
5. 参考资料
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/pathlib.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/heniu/p/12872604.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/87940289
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33524938
https://www.jianshu.com/p/a820038e65c3
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1640696