1、replace替换
replace就是最简单的字符串替换,当一串字符串中有可能会出现的敏感词时,我们直接使用相应的replace方法用*替换出敏感词即可。
缺点:
文本和敏感词少的时候还可以,多的时候效率就比较差了。
示例代码:
|
1 2 3 |
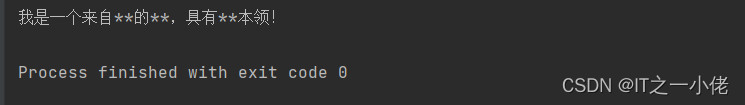
text = '我是一个来自星星的超人,具有超人本领!' text = text.replace("超人", '*' * len("超人")).replace("星星", '*' * len("星星")) print(text) # 我是一个来自***的***,具有***本领! |
运行结果:
如果是多个敏感词可以用列表进行逐一替换。
示例代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
text = '我是一个来自星星的超人,具有超人本领!' words = ['超人', '星星']
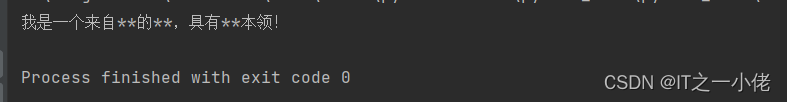
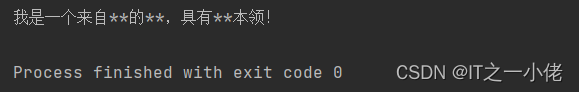
for word in words: text = text.replace(word, '*' * len(word)) print(text) # 我是一个来自***的***,具有***本领! |
运行效果:
2、正则表达式
使用正则表达式是一种简单而有效的方法,可以快速地匹配敏感词并进行过滤。在这里我们主要是使用“|”来进行匹配,“|”的意思是从多个目标字符串中选择一个进行匹配。
示例代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
import re
def filter_words(text, words): pattern = '|'.join(words) return re.sub(pattern, '***', text)
if __name__ == '__main__': text = '我是一个来自星星的超人,具有超人本领!' words = ['超人', '星星'] res = filter_words(text, words) print(res) # 我是一个来自***的***,具有***本领! |
运行结果:
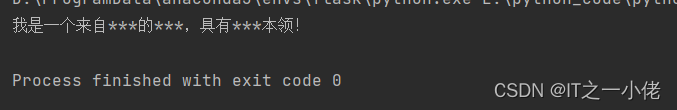
3、使用ahocorasick第三方库
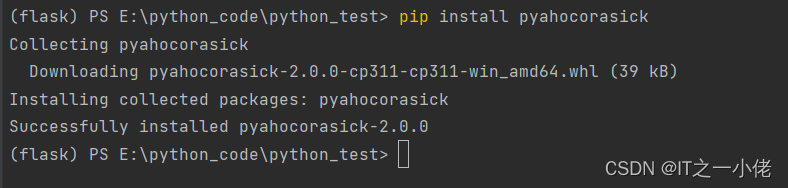
ahocorasick库安装:
|
1 |
pip install pyahocorasick |
示例代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
import ahocorasick
def filter_words(text, words): A = ahocorasick.Automaton() for index, word in enumerate(words): A.add_word(word, (index, word)) A.make_automaton()
result = [] for end_index, (insert_order, original_value) in A.iter(text): start_index = end_index - len(original_value) + 1 result.append((start_index, end_index))
for start_index, end_index in result[::-1]: text = text[:start_index] + '*' * (end_index - start_index + 1) + text[end_index + 1:] return text
if __name__ == '__main__': text = '我是一个来自星星的超人,具有超人本领!' words = ['超人', '星星'] res = filter_words(text, words) print(res) # 我是一个来自***的***,具有***本领! |
运行结果:
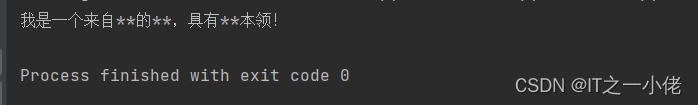
4、字典树
使用字典树是一种高效的方法,可以快速地匹配敏感词并进行过滤。
示例代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 |
class TreeNode: def __init__(self): self.children = {} self.is_end = False
class Tree: def __init__(self): self.root = TreeNode()
def insert(self, word): node = self.root for char in word: if char not in node.children: node.children[char] = TreeNode() node = node.children[char] node.is_end = True
def search(self, word): node = self.root for char in word: if char not in node.children: return False node = node.children[char] return node.is_end
def filter_words(text, words): tree = Tree() for word in words: tree.insert(word)
result = [] for i in range(len(text)): node = tree.root for j in range(i, len(text)): if text[j] not in node.children: break node = node.children[text[j]] if node.is_end: result.append((i, j)) for start_index, end_index in result[::-1]: text = text[:start_index] + '*' * (end_index - start_index + 1) + text[end_index + 1:] return text
if __name__ == '__main__': text = '我是一个来自星星的超人,具有超人本领!' words = ['超人', '星星'] res = filter_words(text, words) print(res) # 我是一个来自***的***,具有***本领! |
运行结果:
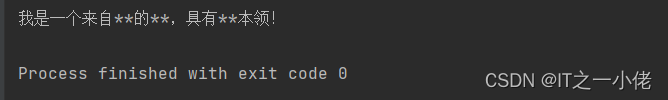
5、DFA算法
使用DFA算法是一种高效的方法,可以快速地匹配敏感词并进行过滤。DFA的算法,即Deterministic Finite Automaton算法,翻译成中文就是确定有穷自动机算法。它的基本思想是基于状态转移来检索敏感词,只需要扫描一次待检测文本,就能对所有敏感词进行检测。
示例代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 |
class DFA: def __init__(self, words): self.words = words self.build()
def build(self): self.transitions = {} self.fails = {} self.outputs = {} state = 0 for word in self.words: current_state = 0 for char in word: next_state = self.transitions.get((current_state, char), None) if next_state is None: state += 1 self.transitions[(current_state, char)] = state current_state = state else: current_state = next_state self.outputs[current_state] = word queue = [] for (start_state, char), next_state in self.transitions.items(): if start_state == 0: queue.append(next_state) self.fails[next_state] = 0 while queue: r_state = queue.pop(0) for (state, char), next_state in self.transitions.items(): if state == r_state: queue.append(next_state) fail_state = self.fails[state] while (fail_state, char) not in self.transitions and fail_state != 0: fail_state = self.fails[fail_state] self.fails[next_state] = self.transitions.get((fail_state, char), 0) if self.fails[next_state] in self.outputs: self.outputs[next_state] += ', ' + self.outputs[self.fails[next_state]]
def search(self, text): state = 0 result = [] for i, char in enumerate(text): while (state, char) not in self.transitions and state != 0: state = self.fails[state] state = self.transitions.get((state, char), 0) if state in self.outputs: result.append((i - len(self.outputs[state]) + 1, i)) return result
def filter_words(text, words): dfa = DFA(words) result = [] for start_index, end_index in dfa.search(text): result.append((start_index, end_index)) for start_index, end_index in result[::-1]: text = text[:start_index] + '*' * (end_index - start_index + 1) + text[end_index + 1:] return text
if __name__ == '__main__': text = '我是一个来自星星的超人,具有超人本领!' words = ['超人', '星星'] res = filter_words(text, words) print(res) # 我是一个来自***的***,具有***本领! |
运行结果: