在Linux系统中,有多种方法可以查看当前系统的IP地址。以下是几种常见的方法:
方法一:使用 ifconfig 命令
ifconfig 是一个常用的网络配置工具,可以显示网络接口的详细信息,包括IP地址。
安装 ifconfig(如果未安装):
在Debian/Ubuntu系统上:
|
1 2 |
sudo apt update sudo apt install net-tools |
在Red Hat/CentOS系统上:
|
1 |
sudo yum install net-tools |
查看IP地址:
|
1 |
ifconfig |
你会看到类似以下的输出:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.1.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255 inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb9:1234 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 00:0c:29:b9:12:34 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 123456 bytes 123456789 (117.7 MiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 123456 bytes 123456789 (117.7 MiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host> loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback) RX packets 1234 bytes 123456 (120.5 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 1234 bytes 123456 (120.5 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 |
在上面的输出中,eth0 接口的IP地址是 192.168.1.100。
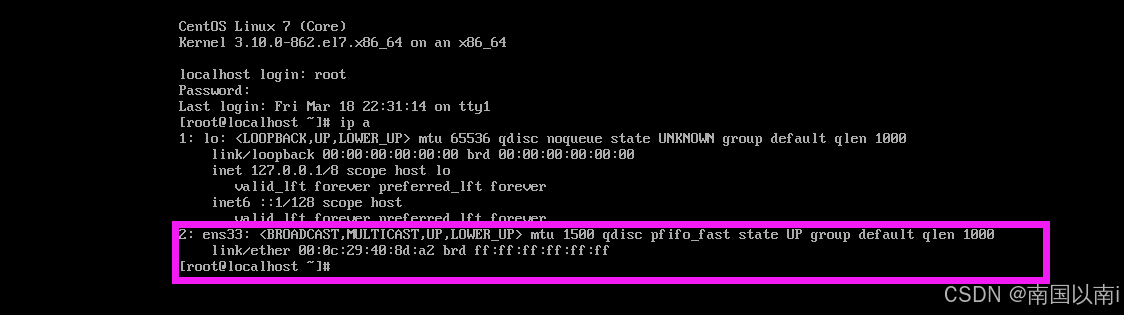
方法二:使用 ip 命令
ip 命令是一个更现代和灵活的网络配置工具,推荐使用。
查看IP地址:
|
1 |
ip addr show |
或者简写为:
|
1 |
ip a |
你会看到类似以下的输出:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:b9:12:34 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.100/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute eth0 valid_lft 86399sec preferred_lft 86399sec inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb9:1234/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever |
在上面的输出中,eth0 接口的IP地址是 192.168.1.100。
方法三:使用 hostname 命令
hostname 命令可以显示或设置系统的主机名,并且可以结合选项来显示IP地址。
查看IP地址:
|
1 |
hostname -I |
你会看到类似以下的输出:
方法四:使用 nmcli 命令
nmcli 是NetworkManager的命令行工具,可以方便地管理网络连接。
查看IP地址:
|
1 |
nmcli device show |
或者简写为:
|
1 |
nmcli d show |
你会看到类似以下的输出:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
GENERAL.DEVICE: eth0 GENERAL.TYPE: ethernet GENERAL.HWADDR: 00:0C:29:B9:12:34 GENERAL.MTU: 1500 GENERAL.STATE: 100 (connected) GENERAL.CONNECTION: Wired connection 1 IP4.ADDRESS[1]: 192.168.1.100/24 IP4.GATEWAY: 192.168.1.1 IP4.DNS[1]: 8.8.8.8 IP4.DNS[2]: 8.8.4.4 IP6.ADDRESS[1]: fe80::20c:29ff:feb9:1234/64 IP6.GATEWAY: -- |
在上面的输出中,eth0 接口的IP地址是 192.168.1.100。
方法五:使用 nmtui 工具
nmtui 是一个基于文本的用户界面工具,可以方便地管理网络连接。
启动 nmtui:
|
1 |
sudo nmtui |
选择 Show active connections:
在 nmtui 界面中,选择 Show active connections,然后按 Enter。
你会看到类似以下的输出:
|
1 2 3 |
Type Device State Connection -------------------------------------------------- Ethernet eth0 connected Wired connection 1 |
选择连接并查看详细信息:
选择 Wired connection 1,然后按 Enter。
你会看到类似以下的输出:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Connection: Wired connection 1 Type: Ethernet Interface: eth0 State: connected IPv4 Address: 192.168.1.100 IPv4 Gateway: 192.168.1.1 IPv4 DNS: 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4 IPv6 Address: fe80::20c:29ff:feb9:1234/64 |
在上面的输出中,eth0 接口的IP地址是 192.168.1.100。
总结
通过以上几种方法,你可以轻松地在Linux系统中查看当前的IP地址。推荐使用 ip 命令或 nmcli 命令,因为它们是现代Linux系统中最常用和强大的工具。