本篇文章介绍java volatile关键字作用及使用场景
1. volatile关键字的作用:
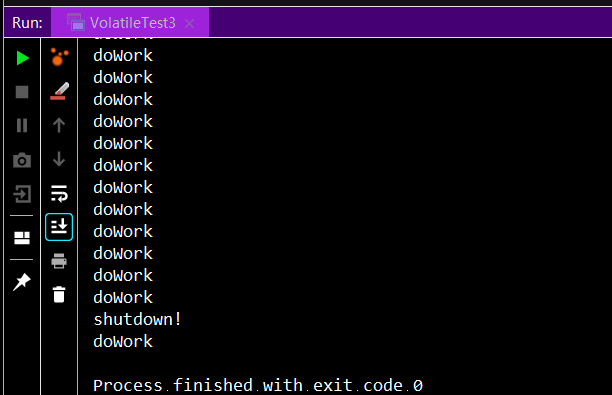
保证了变量的可见性(visibility)。被volatile关键字修饰的变量,如果值发生了变更,其他线程立马可见,避免出现脏读的现象。如以下代码片段,isShutDown被置为true后,doWork方法仍有执行。如用volatile修饰isShutDown变量,可避免此问题。
出现脏读时,运行结果如下:
2. 为什么会出现脏读?
Java内存模型规定所有的变量都是存在主存当中,每个线程都有自己的工作内存。线程对变量的所有操作都必须在工作内存中进行,而不能直接对主存进行操作。并且每个线程不能访问其他线程的工作内存。变量的值何时从线程的工作内存写回主存,无法确定。
3. happens-before规则的理解与勘误
在网上查volatile关键字相关信息时,多篇博客提到了happens-before原则,个人对此原则的理解是:当操作该volatile变量时,所有前序对该变量的操作都已完成(如不存在已变更,但未写回主存的情况),所有后续对该变量的操作,都未开始。仅此而已。
这里,我认为网上很常见的一个理论对此理解有误,如下图。此观点认为,由于volatile变量flag的happens-before原则,所以A线程2处对其的写操作一定先于B线程3处对其的读操作。其实这种观点是有逻辑缺陷的,如果存在一个C线程,先读取flag的值,后写入flag的值,那C线程的执行时机是什么呢?如果还有其他D、E线程呢。。。对于这段代码的正确理解是,只要3处拿到的flag是true,那么a的值一定是1,而不是0.因为volition修饰的变量,处理器不会对其进行重排序,所以1处对a的赋值,一定发生在2处对flag的赋值之前。
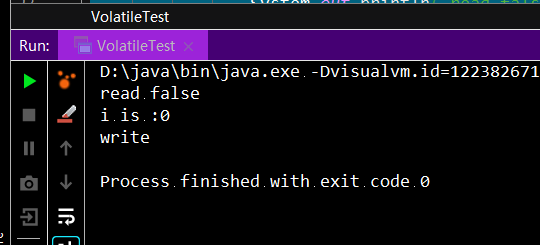
如果flag不是volatile变量,那么1处和2处代码的执行顺序是无法保证的(处理器的指令重排序),虽然大部分情况1会先于2执行。happens-before原则约束的并不是多线程对同一变量的读和写操作之间的顺序,而是保证读操作时,前序所有对该变量的写操作已生效(写回主存)。

验证如下:
运行结果如下,在写操作执行之前,读操作已完成
运行结果如下,volatile无法保证a++操作的原子性。
1. volatile关键字的作用:
保证了变量的可见性(visibility)。被volatile关键字修饰的变量,如果值发生了变更,其他线程立马可见,避免出现脏读的现象。如以下代码片段,isShutDown被置为true后,doWork方法仍有执行。如用volatile修饰isShutDown变量,可避免此问题。
public class VolatileTest3 {
static class Work {
boolean isShutDown = false;
void shutdown() {
isShutDown = true;
System.out.println("shutdown!");
}
void doWork() {
while (!isShutDown) {
System.out.println("doWork");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Work work = new Work();
new Thread(work::doWork).start();
new Thread(work::doWork).start();
new Thread(work::doWork).start();
new Thread(work::shutdown).start();
new Thread(work::doWork).start();
new Thread(work::doWork).start();
new Thread(work::doWork).start();
}
}
|
出现脏读时,运行结果如下:

2. 为什么会出现脏读?
Java内存模型规定所有的变量都是存在主存当中,每个线程都有自己的工作内存。线程对变量的所有操作都必须在工作内存中进行,而不能直接对主存进行操作。并且每个线程不能访问其他线程的工作内存。变量的值何时从线程的工作内存写回主存,无法确定。
3. happens-before规则的理解与勘误
在网上查volatile关键字相关信息时,多篇博客提到了happens-before原则,个人对此原则的理解是:当操作该volatile变量时,所有前序对该变量的操作都已完成(如不存在已变更,但未写回主存的情况),所有后续对该变量的操作,都未开始。仅此而已。
这里,我认为网上很常见的一个理论对此理解有误,如下图。此观点认为,由于volatile变量flag的happens-before原则,所以A线程2处对其的写操作一定先于B线程3处对其的读操作。其实这种观点是有逻辑缺陷的,如果存在一个C线程,先读取flag的值,后写入flag的值,那C线程的执行时机是什么呢?如果还有其他D、E线程呢。。。对于这段代码的正确理解是,只要3处拿到的flag是true,那么a的值一定是1,而不是0.因为volition修饰的变量,处理器不会对其进行重排序,所以1处对a的赋值,一定发生在2处对flag的赋值之前。
如果flag不是volatile变量,那么1处和2处代码的执行顺序是无法保证的(处理器的指令重排序),虽然大部分情况1会先于2执行。happens-before原则约束的并不是多线程对同一变量的读和写操作之间的顺序,而是保证读操作时,前序所有对该变量的写操作已生效(写回主存)。

验证如下:
public class VolatileTest {
static class A {
int a = 0;
volatile boolean flag = false;
void writer() {
a = 1; //1
flag = true; //2
System.out.println("write");
}
void reader() {
if (flag) { //3
int i = a; //4
System.out.println("read true");
System.out.println("i is :" + i);
} else {
int i = a;
System.out.println("read false");
System.out.println("i is :" + i);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A aaa = new A();
new Thread(() -> aaa.reader()).start();
new Thread(() -> aaa.writer()).start();
}
}
|
运行结果如下,在写操作执行之前,读操作已完成

4. volatile关键字使用场景
注意:volatile只能保证变量的可见性,不能保证对volatile变量操作的原子性,见如下代码:
public class VolatileTest2 {
static class A {
volatile int a = 0;
void increase() {
a++;
}
int getA(){
return a;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0;i < 1000;i++) {
a.increase();
}
System.out.println(a.getA());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0;i < 2000;i++) {
a.increase();
}
System.out.println(a.getA());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0;i < 3000;i++) {
a.increase();
}
System.out.println(a.getA());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0;i < 4000;i++) {
a.increase();
}
System.out.println(a.getA());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0;i < 5000;i++) {
a.increase();
}
System.out.println(a.getA());
}).start();
}
}
|
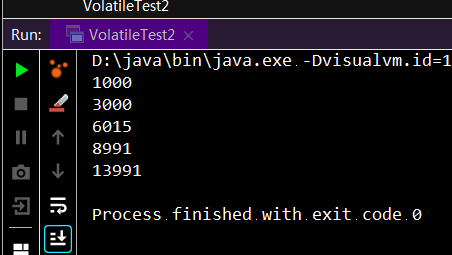
运行结果如下,volatile无法保证a++操作的原子性。

原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/YLsY/p/11295732.html
相关文章