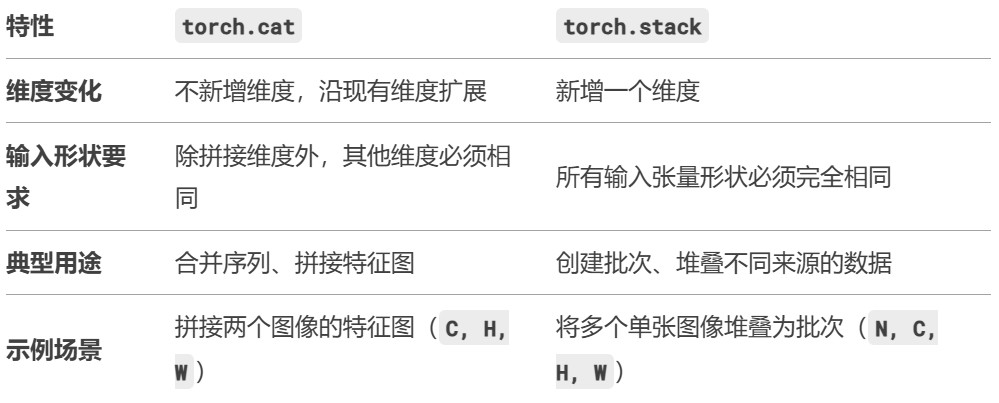
拼接张量:torch.cat() 、torch.stack()
- torch.cat(inputs, dimension=0) → Tensor
在给定维度上对输入的张量序列 seq 进行连接操作
举个例子:
>>> import torch
>>> x = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> x
tensor([[-0.1997, -0.6900, 0.7039],
[ 0.0268, -1.0140, -2.9764]])
>>> torch.cat((x, x, x), 0) # 在 0 维(纵向)进行拼接
tensor([[-0.1997, -0.6900, 0.7039],
[ 0.0268, -1.0140, -2.9764],
[-0.1997, -0.6900, 0.7039],
[ 0.0268, -1.0140, -2.9764],
[-0.1997, -0.6900, 0.7039],
[ 0.0268, -1.0140, -2.9764]])
>>> torch.cat((x, x, x), 1) # 在 1 维(横向)进行拼接
tensor([[-0.1997, -0.6900, 0.7039, -0.1997, -0.6900, 0.7039, -0.1997, -0.6900,
0.7039],
[ 0.0268, -1.0140, -2.9764, 0.0268, -1.0140, -2.9764, 0.0268, -1.0140,
-2.9764]])
>>> y1 = torch.randn(5, 3, 6)
>>> y2 = torch.randn(5, 3, 6)
>>> torch.cat([y1, y2], 2).size()
torch.Size([5, 3, 12])
>>> torch.cat([y1, y2], 1).size()
torch.Size([5, 6, 6])
|
对于需要拼接的张量,维度数量必须相同,进行拼接的维度的尺寸可以不同,但是其它维度的尺寸必须相同。
- torch.stack(sequence, dim=0)
沿着一个新维度对输入张量序列进行连接。 序列中所有的张量都应该为相同形状
举个例子:
>>> x1 = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> x2 = torch.randn(2, 3)
>>> torch.stack((x1, x2), 0).size() # 在 0 维插入一个维度,进行区分拼接
torch.Size([2, 2, 3])
>>> torch.stack((x1, x2), 1).size() # 在 1 维插入一个维度,进行组合拼接
torch.Size([2, 2, 3])
>>> torch.stack((x1, x2), 2).size()
torch.Size([2, 3, 2])
>>> torch.stack((x1, x2), 0)
tensor([[[-0.3499, -0.6124, 1.4332],
[ 0.1516, -1.5439, -0.1758]],
[[-0.4678, -1.1430, -0.5279],
[-0.4917, -0.6504, 2.2512]]])
>>> torch.stack((x1, x2), 1)
tensor([[[-0.3499, -0.6124, 1.4332],
[-0.4678, -1.1430, -0.5279]],
[[ 0.1516, -1.5439, -0.1758],
[-0.4917, -0.6504, 2.2512]]])
>>> torch.stack((x1, x2), 2)
tensor([[[-0.3499, -0.4678],
[-0.6124, -1.1430],
[ 1.4332, -0.5279]],
[[ 0.1516, -0.4917],
[-1.5439, -0.6504],
[-0.1758, 2.2512]]])
|
把相同形状的张量合并,并根据提供的维度序列在相应位置插入维度,方法会根据位置来排列数据。代码中,根据第 0 维和第 1 维来进行合并时,虽然合并后的张量维度和尺寸相等,但是数据的位置并不是相同的。
拆分张量:torch.split()、torch.chunk()
- torch.split(tensor, split_size, dim=0)
将输入张量分割成相等形状的 chunks(如果可分)。 如果沿指定维的张量形状大小不能被 split_size 整分, 则最后一个分块会小于其它分块。
举个例子:
>>> x = torch.randn(3, 10, 6) >>> a, b, c = x.split(1, 0) # 在 0 维进行间隔维 1 的拆分 >>> a.size(), b.size(), c.size() (torch.Size([1, 10, 6]), torch.Size([1, 10, 6]), torch.Size([1, 10, 6])) >>> d, e = x.split(2, 0) # 在 0 维进行间隔维 2 的拆分 >>> d.size(), e.size() (torch.Size([2, 10, 6]), torch.Size([1, 10, 6])) |
把张量在 0 维度上以间隔 1 来拆分时,其中 x 在 0 维度上的尺寸为 3,就可以分成 3 份。
把张量在 0 维度上以间隔 2 来拆分时,只能分成 2 份,且只能把前面部分先以间隔 2 来拆分,后面不足 2 的部分就直接作为一个分块。
- torch.chunk(tensor, chunks, dim=0)
在给定维度(轴)上将输入张量进行分块儿
直接用上面的数据来举个例子:
>>> l, m, n = x.chunk(3, 0) # 在 0 维上拆分成 3 份 >>> l.size(), m.size(), n.size() (torch.Size([1, 10, 6]), torch.Size([1, 10, 6]), torch.Size([1, 10, 6])) >>> u, v = x.chunk(2, 0) # 在 0 维上拆分成 2 份 >>> u.size(), v.size() (torch.Size([2, 10, 6]), torch.Size([1, 10, 6])) |
把张量在 0 维度上拆分成 3 部分时,因为尺寸正好为 3,所以每个分块的间隔相等,都为 1。
把张量在 0 维度上拆分成 2 部分时,无法平均分配,以上面的结果来看,可以看成是,用 0 维度的尺寸除以需要拆分的份数,把余数作为最后一个分块的间隔大小,再把前面的分块以相同的间隔拆分。
在某一维度上拆分的份数不能比这一维度的尺寸大。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44613063/article/details/89576810
相关文章