本文介绍的如何使用Pandas来读取各种json格式的数据,以及对json数据的保存

读取json数据
使用的是pd.read_json函数,见官网:pandas.pydata.org/docs/refere…
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
pandas.read_json(
path_or_buf=None, # 文件路径
orient=None, # 取值:split、records、index、columns、values
typ='frame', # 要恢复的对象类型(系列或框架),默认'框架'.
dtype=None, # boolean或dict,默认为True
convert_axes=None,
convert_dates=True,
keep_default_dates=True,
numpy=False,
precise_float=False,
date_unit=None,
encoding=None, # 编码
lines=False, # 布尔值,默认为False,每行读取该文件作为json对象
chunksize=None, # 分块读取大小
compression='infer',
nrows=None,
storage_options=None)
|
模拟数据
模拟了一份数据,vscode打开内容:

可以看到默认情况下的读取效果:
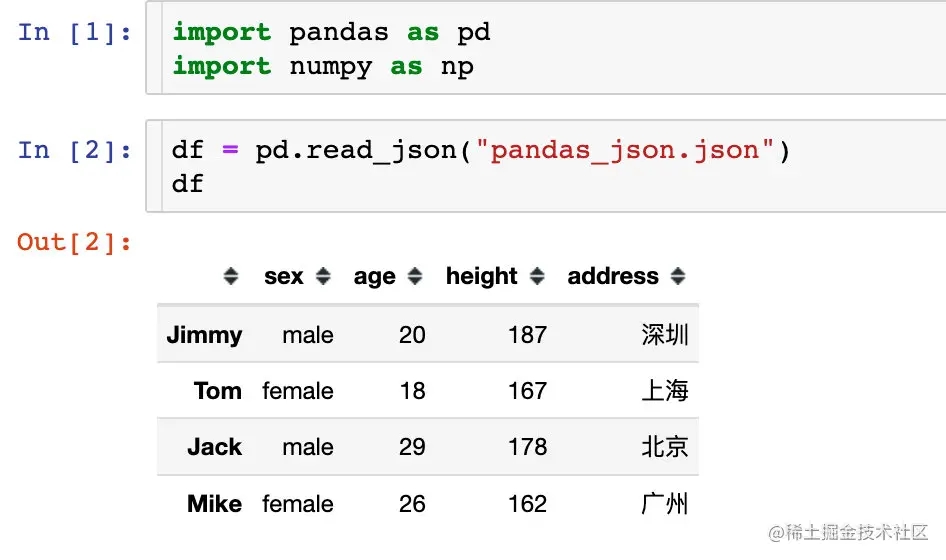
主要有下面几个特点:
- 第一层级字典的键当做了DataFrame的字段
- 第二层级的键默认当做了行索引
下面重点解释下参数orident
参数orident
取值可以是:split、records、index、columns、values
orident="split"
json文件的key的名字只能为index,cloumns,data;不多也不能少。
|
1
|
split' : dict like {index -> [index], columns -> [columns], data -> [values]}
|
In [3]:
|
1
|
data1 = '{"index":[1,2],"columns":["name","age"],"data":[["xiaoming",28], ["zhouhong",20]]}'
|
In [4]:
|
1
2
|
df1 = pd.read_json(data1, orient="split")
df1
|
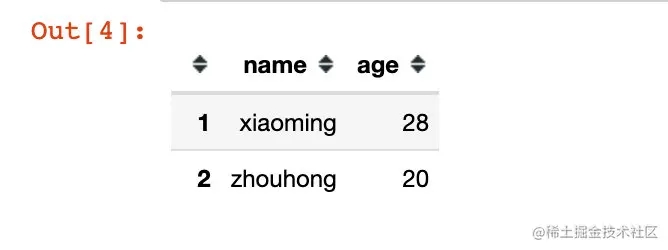
结果表明:
- index:当做行索引
- columns:列名
- data:具体的取值
如果我们改变其中一个key,比如data换成information就报错了:
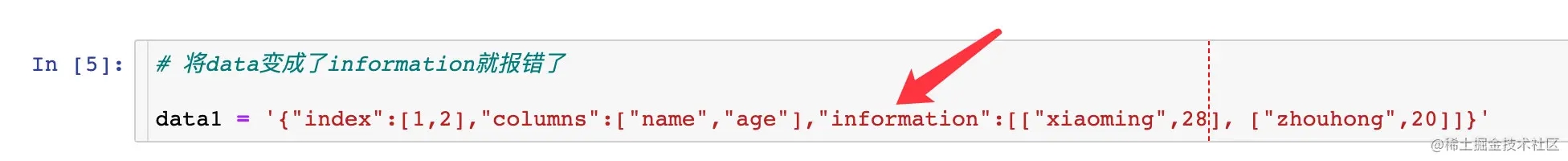
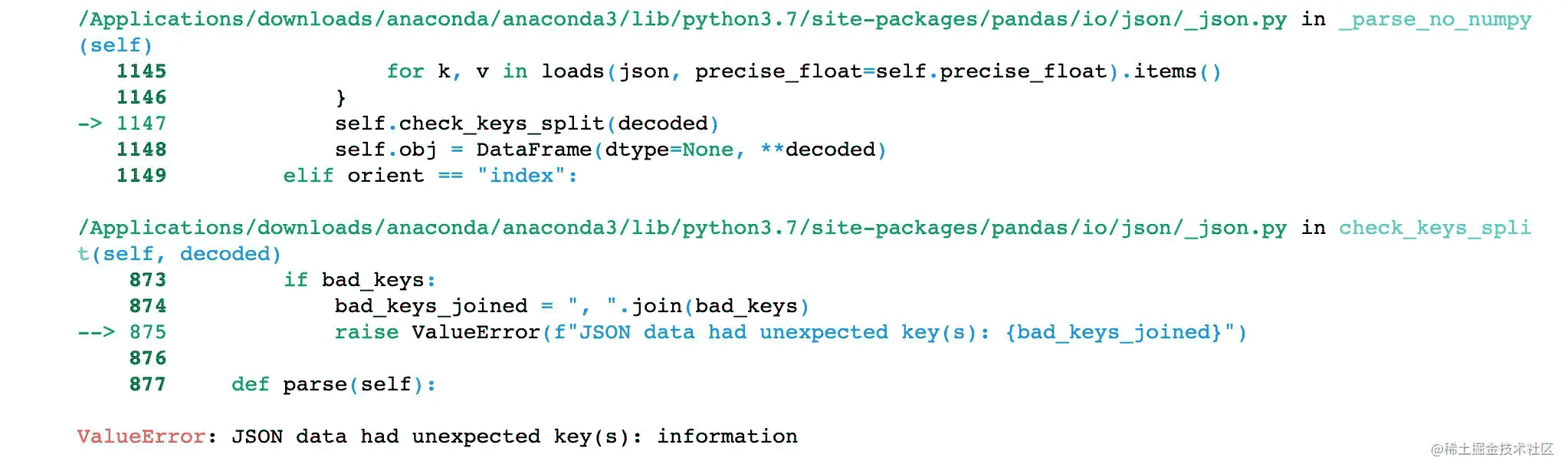
orient="records"
当orient="records"的时候,数据是以字段 + 取值的形式存放的。
|
1
|
‘records' : list like [{column -> value}, … , {column -> value}]
|
In [7]:
|
1
|
data2 = '[{"name":"Peter","sex":"male","age":20},{"name":"Tom","age":27},{"sex":"male"}]'
|
In [8]:
|
1
2
|
df2 = pd.read_json(data2, orient="records")
df2
|
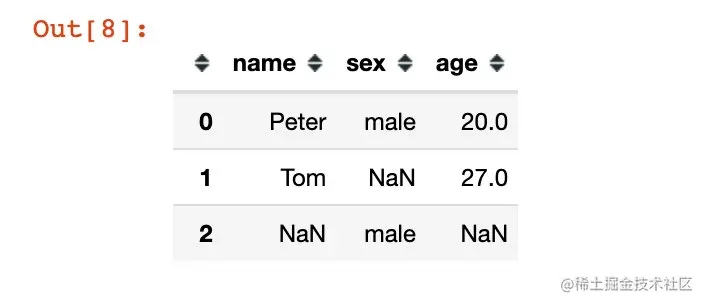
生成数据的特点:
- 列表中元素是以字典的形式存放
- 列表中每个元素(字典)的key,如果没有出现则取值为NaN
orient="index"
当orient="index"的时候,数据是以行的形式来存储。
|
1
|
dict like {index -> {column -> value}}
|
In [9]:
|
1
|
data3 = '{"id1":{"name":"Mike","age":20,"sex":"male","score":80},"id2":{"name":"Jack","sex":"female","score":90}}'
|
In [10]:
|
1
2
|
df3 = pd.read_json(data3, orient="index")
df3
|
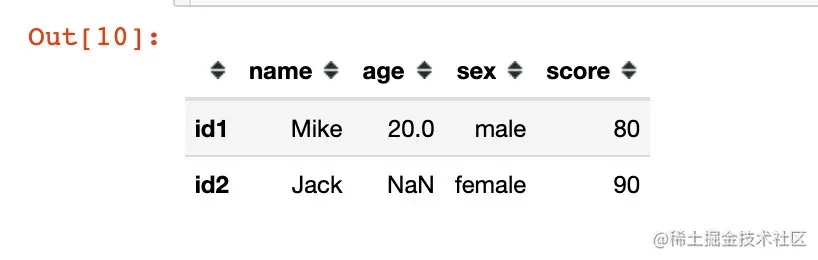
orient="columns"
在这种情况下数据是以列的形式来存储的。
|
1
|
dict like {column -> {index -> value}}
|
In [11]:
|
1
|
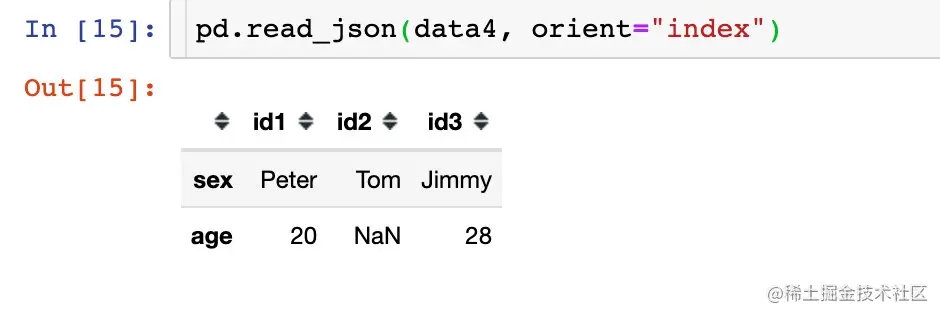
data4 = '{"sex":{"id1":"Peter","id2":"Tom","id3":"Jimmy"},"age":{"id1": 20,"id3":28}}'
|
In [12]:
|
1
2
|
df4 = pd.read_json(data4, orient="columns")
df4
|
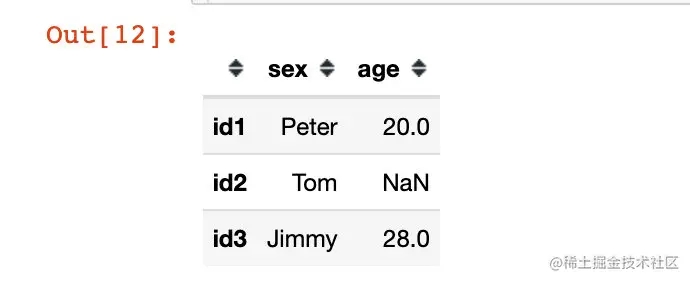
如果我们对上面的结果实施转置(两种方法):
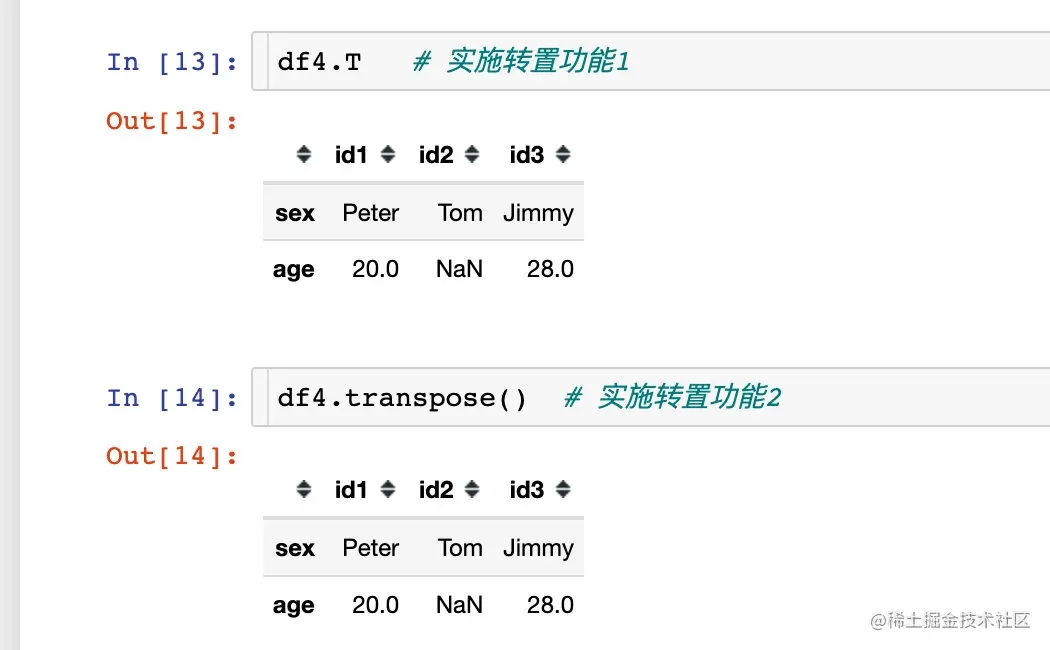
我们会发现这个结果和orient="index"的读取结果是相同的:
orient="values"
在这种情况下,数据是以数组的形式存在的:
|
1
|
‘values' : just the values array
|
In [16]:
|
1
|
data5 = '[["深圳",2000],["广州",1900],["北京",2500]]'
|
In [17]:
|
1
2
|
df5 = pd.read_json(data5, orient="values")
df5
|
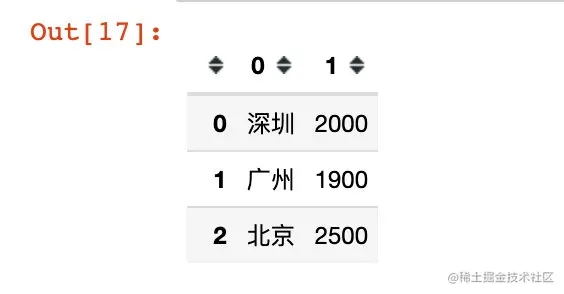
对生成的列名进行重新命名:

to_json
将DataFrame数据保存成json格式的文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
DataFrame.to_json(path_or_buf=None, # 路径
orient=None, # 转换类型
date_format=None, # 日期转换类型
double_precision=10, # 小数保留精度
force_ascii=True, # 是否显示中文
date_unit='ms', # 日期显示最小单位
default_handler=None,
lines=False,
compression='infer',
index=True, # 是否保留行索引
indent=None, # 空格数
storage_options=None)
|
官网学习地址:
pandas.pydata.org/docs/refere…
1、默认保存
|
1
|
df.to_json("df_to_json_1.json", force_ascii=True) # 不显示中文
|
显示结果为一行数据,且存在unicode编码,中文无法显示:
{"sex":{"Jimmy":"male","Tom":"female","Jack":"male","Mike":"female"},"age":{"Jimmy":20,"Tom":18,"Jack":29,"Mike":26},"height":{"Jimmy":187,"Tom":167,"Jack":178,"Mike":162},"address":{"Jimmy":"\u6df1\u5733","Tom":"\u4e0a\u6d77","Jack":"\u5317\u4eac","Mike":"\u5e7f\u5dde"}}
2、显示中文
|
1
|
df.to_json("df_to_json_2.json", force_ascii=False) # 显示中文
|
中文能够正常显示:
{"sex":{"Jimmy":"male","Tom":"female","Jack":"male","Mike":"female"},"age":{"Jimmy":20,"Tom":18,"Jack":29,"Mike":26},"height":{"Jimmy":187,"Tom":167,"Jack":178,"Mike":162},"address":{"Jimmy":"深圳","Tom":"上海","Jack":"北京","Mike":"广州"}}
3、不同的orient显示 + 换行(indent参数)
|
1
2
|
df.to_json("df_to_json_3.json", force_ascii=False, orient="index",indent=4)
# index + 换行
|
显示结果中键为name信息:
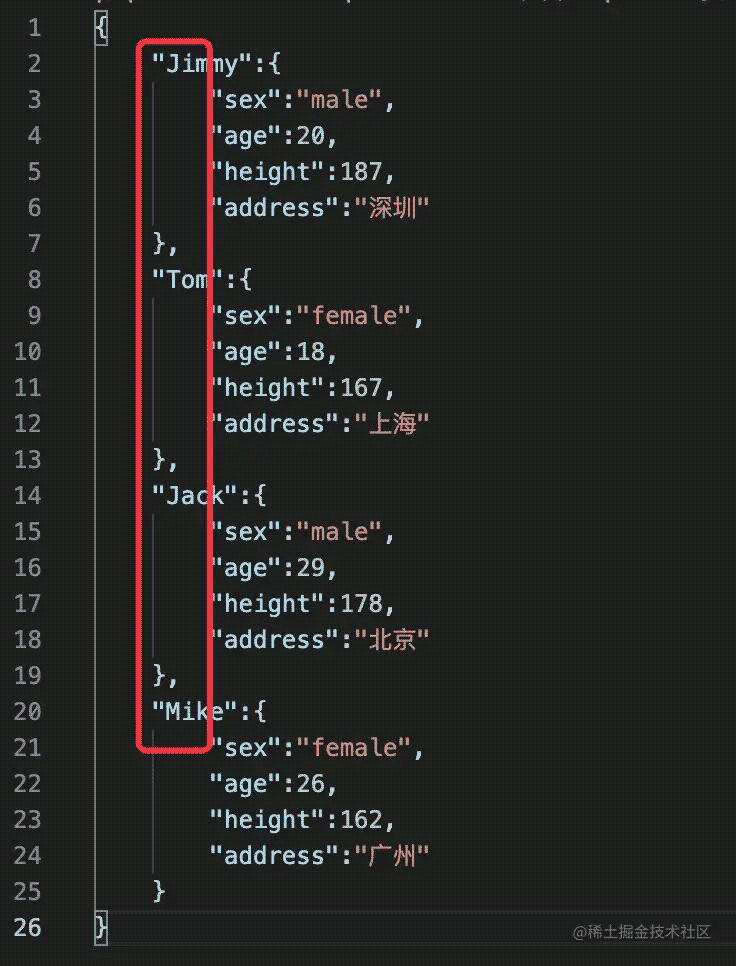
4、改变index
|
1
|
df.to_json("df_to_json_4.json", force_ascii=False, orient="columns",indent=4) # columns + 换行
|
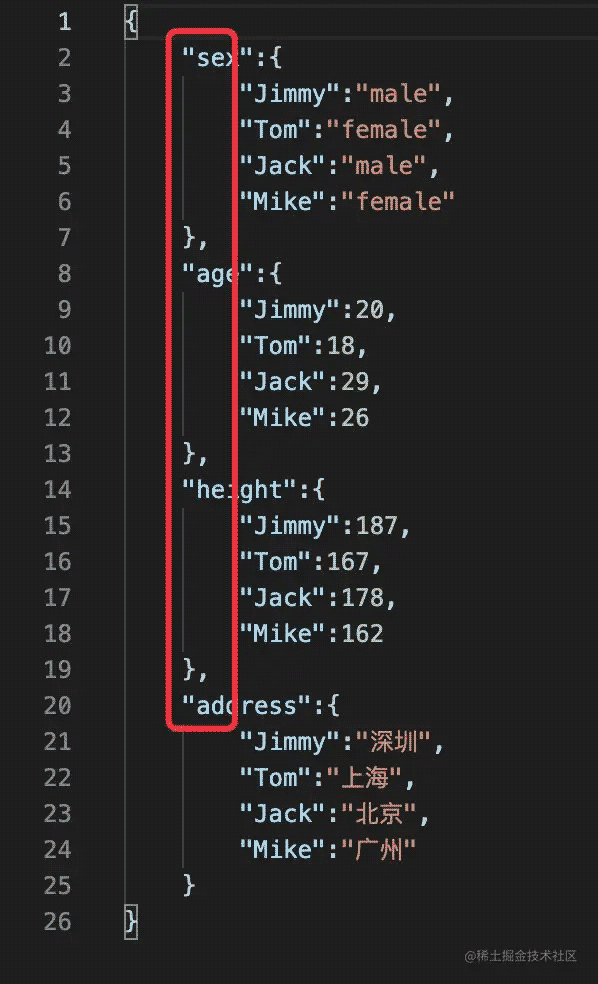
|