Python中的魔术方法__new__介绍
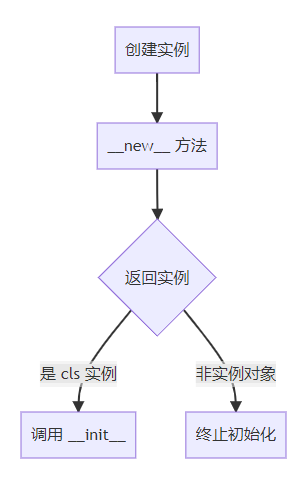
一、核心意义与机制 1.1 构造过程原理 1.2 与 __init__ 对比 特性 __new__ __init__ 方法类型 静态方法 实例方法 返回值 必须返回实例对象 无返回值 调用时机 创建实例时首先调用 在 __new__ 之后调用
一、核心意义与机制1.1 构造过程原理
1.2 与 __init__ 对比
二、核心功能解析2.1 核心能力
2.2 方法签名元类中的 __new__ 参数(示例 4.1)
调用逻辑
不可变类型子类的 __new__(示例 3.2) 样例
调用逻辑
可变类型普通类的 __new__(示例 3.1) 样例
调用逻辑
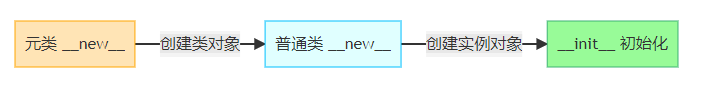
2.3 参数传递关系图示
2.4 核心记忆要点??元类 __new__ 的四个参数是固定结构??
??普通类 __new__ 第一个参数必为 cls??
??super().__new__ 的参数必须与父类一致??
三、典型应用场景3.1 单例模式实现
3.2 不可变类型扩展
3.3 对象池技术
四、高级应用技巧4.1 元类协作
4.2 参数预处理
五、继承体系中的使用5.1 继承链处理
5.2 多继承处理
六、注意事项与调试6.1 常见错误
6.2 调试技巧
七、性能优化建议7.1 对象缓存策略
最佳实践总结??
|
您可能感兴趣的文章 :
-
Python虚拟环境终极(含PyCharm的使用教程)
一、为什么需要虚拟环境? 场景 问题表现 虚拟环境解决方案 多项目依赖冲突 项目A需要Django 3.2,项目B需要Django 4.1 隔离不同项目的依赖版 -
Python中的魔术方法__new__介绍
一、核心意义与机制 1.1 构造过程原理 1.2 与 __init__ 对比 特性 __new__ __init__ 方法类型 静态方法 实例方法 返回值 必须返回实例对象 无返回值 -
宝塔安装的MySQL无法连接的情况及解决方案
一、错误 1130:Host xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is not allowed to connect to this MySQL server 错误原因 此错误表示您的 IP 地址没有被授权访问宝塔服务器上的 MySQL。 -
MySQL中drop、truncate和delete的区别
对于drop、truncate和delete,虽然简单,但是真要使用或者面试时候问到还是需要有一定的总结,今天来简单讲讲他们直接的区别。在此之前先 -
Linux搭建单机MySQL8.0.26版本的操作方法
环境信息 IP 系统 规格 10.0.0.10 Ubuntu22.04 2c4g 数据库服务安装步骤 下载前置依赖 1 2 # 下载libtinfo5、libnuma1依赖 [root@lb ~]# apt update -y apt install -
mysql中的group by高级用法
MySQL中的GROUP BY是数据聚合分析的核心功能,主要用于将结果集按指定列分组,并结合聚合函数进行统计计算。以下从基本语法到高级用法进 -
MySQL双主搭建+keepalived高可用的实现
一、测试环境准备 节点1 节点2 IP地址 192.168.101.77 192.168.101.79 MySQL版本 8.0.32 8.0.32 二、主从搭建 1.创建复制用户 节点1执行: 1 2 3 4 mysql CREA -
MySQL使用SHOW PROCESSLIST的实现
1、SHOW PROCESSLIST 显示进程列表 SHOW [FULL] PROCESSLIST 用于查看当前MySQL服务器上的所有运行中的进程列表信息。这个命令可以帮助我们了解哪些
-
zabbix监控mysql的实例方法
2021-06-02
-
MySQL时间类型的选择
2021-06-05
-
MySQL数据库基本SQL语句教程之高级操作
2022-06-27
-
MySQL文件权限存在的安全问题和解决方
2024-07-31
-
利用Mysql定时+存储过程创建临时表统
2024-02-19