python的random库,提供了很多随机抽样方法。

1. 设置随机数种子 seed()
在适当的情形下,为例保证抽样的结果固定,不因多次运行而改变,可以设置随机数种子。
如果不设置则是以当前系统时间作为随机数种子。
设置随机数种子使用的是random.seed()方法。代码示例如下。
|
1 2 |
import random random.seed(100) |
在jupyternotebook中,seed的影响范围只限于每个代码格子内。
2. random() 与 randint()
random库的random()函数,作为该模块中其他随机方法的基础。
可以在区间 [0.0, 1.0) 内随机生成一个浮点数。
如果想要产生其他范围内的浮点数,则可以使用random.uniform(a,b)方法,
以产生[a,b]范围内一个随机浮点数。
具体示例如下:
|
1 |
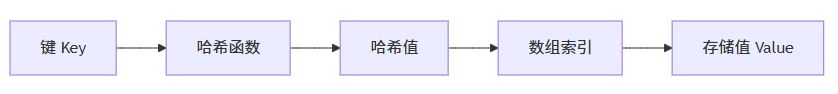
random.random() |
random库的randint()方法则可以在给定区间内随机生一个整数。(左右边界值都可以取)
|
1 |
random.randint(1,2) |
输出效果如下图所示:
此外,如果使用random.randrange(a,b,step)方法,则还可以在原有基础上,限制range的步长,再取整数。
3. sample()方法 无放回抽样
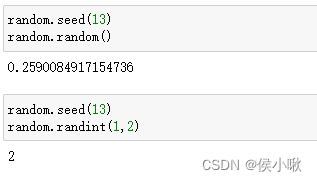
sample()方法可以从给定序列中随机抽取n个元素(无放回抽样。)
该方法语法如下:
random.sample(population,k)
|
1 2 3 |
random.seed(13) listA = ["a", "b", "c"] random.sample(listA,2) |
4. choice() 与 choices() 有放回抽样
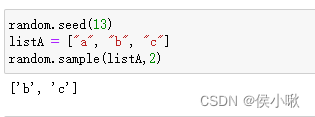
choice() 与 choices()可以实现从给定的序列中进行有放回地随机抽样。
其中chioce()只抽一次,而choices() 表示抽取多次。
random.choices()方法的语法如下:
random.choices(population,weights=None,*,cum_weights=None,k=1)
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
import random
listA = ["a", "b", "c"] print(random.choice(listA)) print(random.choices(listA, k=2)) |
5. shuffle()方法
shuffle()方法可以实现,对序列的随机排序,即打乱原有序列。
|
1 2 3 4 |
random.seed(13) listA = ["a", "b", "c"] random.shuffle(listA) listA |

6. 猜拳小案例
看似简单朴实的案例,往往蕴含着许多值得参考和借鉴的细节。
以猜拳小游戏案例为例,要求是玩家对电脑,电脑随机出,玩家以输入的方式。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
import random while 1: s = int(random.randint(1, 3)) if s == 1: ind = "石头" elif s == 2: ind = "剪子" elif s == 3: ind = "布" m = input('【猜拳游戏】输入 石头、剪子、布猜拳,输入"end"结束游戏:\n') blist = ["石头", "剪子", "布"] if (m not in blist) and (m != 'end'): print ("输入错误,请重新输入!") elif (m not in blist) and (m == 'end'): print ("\n游戏退出中...") print("已退出") break elif m == ind : print ("电脑出了: " + ind + ",平局!") elif (m == '石头' and ind =='剪子') or (m == '剪子' and ind =='布') or (m == '布' and ind =='石头'): print ("电脑出了: " + ind +",你赢了!") elif (m == '石头' and ind =='布') or (m == '剪子' and ind =='石头') or (m == '布' and ind =='剪子'): print ("电脑出了: " + ind +",你输了!") |