作用
- 反向代理
- 负载均衡
- web缓存
配置
nginx 的配置主要可以划分为main、events、http、server、location 块。
- main:置影响nginx全局的指令。一般有运行nginx服务器的用户组,nginx进程pid存放路径,日志存放路径,配置文件引入,允许生成worker process数等。
- events:配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。有每个进程的最大连接数,选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求,是否允许同时接受多个网路连接,开启多个网络连接序列化等。
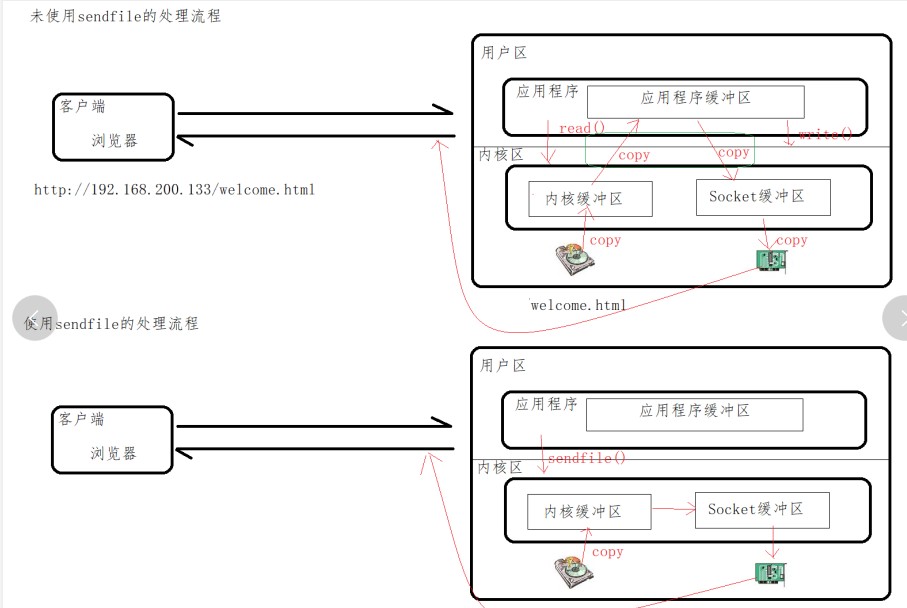
- http:可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。如文件引入,mime-type定义,日志自定义,是否使用sendfile传输文件,连接超时时间,单连接请求数等
- server:配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。
- location:配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。
下面就以配置文件作为参考
每个指令必须以分号结束
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 |
# main块 user nobody nobody; # 配置nginx运行的用户或者组,如果只配置了一个,说明用户跟组都是同一个名称 worker_processes 1; # 允许生成的进程数,默认为1;可以设置为auto,一般设置为cpu的核心数 #pid logs/nginx.pid; # nginx 进程pid的存放地址 # 制定日志路径,级别。这个设置可以放入全局块,http块,server块, # 级别以此为:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; # events块 events { accept_mutex on; #设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on multi_accept on; #设置一个进程是否同时接受多个网络连接,默认为off #use epoll; #事件驱动模型,select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数,默认为512 } # http块 http { # http 全局块 include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表 default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型,默认为text/plain #access_log off; #取消服务日志 # 自定义日志模板 main 为自定义日志模板的名称 #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; # 日志类型 日志输出路径 使用的日志模板 #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #允许sendfile方式传输文件,默认为off,可以在http块,server块,location块 sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #每个进程每次调用传输数量不能大于设定的值,默认为0,即不设上限。 keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间,默认为75s,可以在http,server,location块。 # 启用了sendfile 才会生效,作用是等数据包累积到一定大小才发送 #tcp_nopush on; # 开启gzip压缩,对于文本文件,在服务端发送响应之前进行 GZip 压缩,压缩后的文本大小会减小到原来的 1/4 - 1/3 gzip on; # 负载均衡配置 upstream mysvr { server 127.0.0.1:7878; server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备(其它所有的非backup机器down或者忙的时候,请求backup机器)) } upstream mysvr2 { #weigth参数表示权值,权值越高被分配到的几率越大 server 192.168.1.11:80 weight=5; server 192.168.1.12:80 weight=1; server 192.168.1.13:80 weight=6; } # server 块 server { # server 全局块 listen 80; # 监听端口 server_name localhost; # 监听地址 keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数 # http请求强制跳转https rewrite ^(.*)$ https://$host$1 permanent; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; # location 块 location / { #请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写 root html; #根目录设置 index index.html index.htm; #设置默认页,html/index.html proxy_pass http://mysvr; #请求转向mysvr 定义的服务器列表 deny 127.0.0.1; #拒绝的ip allow 172.18.5.54; #允许的ip } # HTTPS配置,此配置需要ssl模块的支持 server { listen 443 ssl; server_name localhost; # https 证书地址 ssl_certificate cert.pem; ssl_certificate_key cert.key; ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; ssl_session_timeout 5m; #缓存有效期 ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; #安全链接可选的加密协议 ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; #使用服务器端的首选算法 location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } } } |
main
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
user nobody nobody; worker_processes 1; pid logs/nginx.pid; daemon off; error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; worker_rlimit_nofile 65535; |
- user:配置nginx运行的用户以及组,如果只配置了一个,说明用户跟组都是同一个名称,window下不用配置。
- worker_processes:工作进程数,根据硬件配置调整,通常等于CPU核心数或者2倍,也可以设置为auto,默认为1
- pid:pid(进程标识符)存放路径,windows 放在 logs/nginx.pid
- daemon:设置nginx是否以守护进程运行,off否,on是
- error_log:指定日志路径、级别,这个配置可以放到main块,http块,server块
- worker_rlimit_nofile: 一个进程能打开的文件描述符最大值,理论上该值应该是最多能打开的文件数除以进程数,但是由于 nginx 负载并不是完全均衡的,所以这个值最好等于最多能打开的文件数。
可以通过·getconf PAGESIZE· 来查看LINUX的分页大小
- open_file_cache:配置缓存,为打开的文件指定缓存,默认是没有启用的。max 参数指定缓存最大数量,建议和打开文件数一致。inactive 参数指经过多长时间文件没有被请求(或没有被使用)后删除缓存。打开文件最大数量为我们在 main 配置的 worker_rlimit_nofile 参数(该参数用来为工作进程设置文件描述符的限制)。
- open_file_cache_valid:多久检查一次缓存的有效性,如果一个文件在inactive时间内没有被使用到,它将从缓存中移除。
- open_file_cache_min_uses:配置缓存中的文件在 open_file_cache 指令中的 inactive 参数(open_file_cache max=2000 inactive=60s;)指定的时间内文件的最少使用次数。如果超过这个数字,文件描述符一直是在缓存中打开的。如果有一个文件在 inactive 时间内未达到最少使用次数,它将被从缓存移除。
events
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
events { #use epoll; accept_mutex on; multi_accept on; worker_connections 20000; client_header_buffer_size 4k; open_file_cache max=2000 inactive=60s; open_file_cache_valid 60s; open_file_cache_min_uses 1; } |
- use:指令用来指定要使用的连接处理方法。通常不需要显式指定它,因为 nginx 默认会使用最有效的方法;select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
- accept_mutex:用来设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on;
惊群现象:指多进程(多线程)在同时阻塞等待同一个事件的时候(休眠状态),如果等待的这个事件发生,那么他就会唤醒等待的所有进程(或者线程),但是最终却只能有一个进程(线程)获得这个时间的“控制权”,对该事件进行处理,而其他进程(线程)获取“控制权”失败,只能重新进入休眠状态,这种现象和性能浪费就叫做惊群效应
- multi_accept:设置是否允许同时接受多个网络连接,只能在events块设置。默认关闭
nginx服务器每个工作进程可以同时接受多个新的网络连接,但是默认是关闭的,需要在nginx.conf配置文件中设置multi_accept on;
- worker_connections : 设置工作进程最大连接数,理论上每台 Nginx 服务器的最大连接数为 worker_processes*worker_connections。其中,worker_processes 为指定的工作进程数量,该配置在全局块中。
- client_header_buffer_size:客户端请求头部的缓冲区大小,根据系统分页大小来设置,可以设置为系统分页的大小。
Linux查询系统分页大小命令:getconf PAGESIZE
- open_file_cache:配置缓存,为打开的文件指定缓存,默认是没有启用的。max 参数指定缓存最大数量,建议和打开文件数一致。inactive 参数指经过多长时间文件没有被请求(或没有被使用)后删除缓存。打开文件最大数量为我们在 main 配置的 worker_rlimit_nofile 参数(该参数用来为工作进程设置文件描述符的限制)。
- open_file_cache_valid:多久检查一次缓存的有效性,如果一个文件在inactive时间内没有被使用到,它将从缓存中移除。
- open_file_cache_min_uses:配置缓存中的文件在 open_file_cache 指令中的 inactive 参数(open_file_cache max=2000 inactive=60s;)指定的时间内文件的最少使用次数。如果超过这个数字,文件描述符一直是在缓存中打开的。如果有一个文件在 inactive 时间内未达到最少使用次数,它将被从缓存移除。