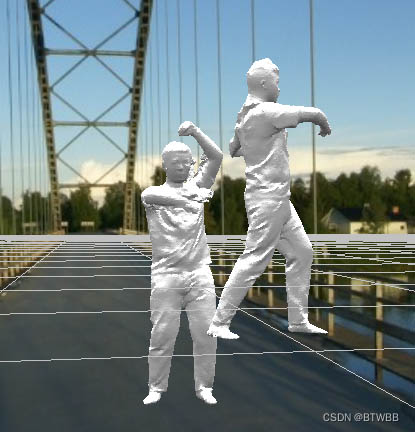
Python将两个三维模型合成一个三维模型
本文主要针对想要将两个obj保存的三维模型合成一个三维模型即obj文件保存。
这样就可以同时观察并对比两个三维模型。
Trimesh是对三维网格模型处理十分好用的库,本次代码即基于此库!
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 |
###################### #同时将两个模型显示在一起,也可以将两个模型拼接成为一个模型 ######################
from cv2 import scaleAdd import trimesh import argparse import numpy as np import os import scipy.io as scio import math
# 根据输入的旋转度数生成相应的旋转矩阵 def make_rotate(rx, ry, rz): sinX = np.sin(rx) sinY = np.sin(ry) sinZ = np.sin(rz)
cosX = np.cos(rx) cosY = np.cos(ry) cosZ = np.cos(rz)
Rx = np.zeros((3, 3)) Rx[0, 0] = 1.0 Rx[1, 1] = cosX Rx[1, 2] = -sinX Rx[2, 1] = sinX Rx[2, 2] = cosX
Ry = np.zeros((3, 3)) Ry[0, 0] = cosY Ry[0, 2] = sinY Ry[1, 1] = 1.0 Ry[2, 0] = -sinY Ry[2, 2] = cosY
Rz = np.zeros((3, 3)) Rz[0, 0] = cosZ Rz[0, 1] = -sinZ Rz[1, 0] = sinZ Rz[1, 1] = cosZ Rz[2, 2] = 1.0
R = np.matmul(np.matmul(Rz, Ry), Rx) return R
if __name__ == "__main__": parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("--obj1_path", type=str, default="对象1路径.obj") parser.add_argument("--obj2_path", type=str, default="对象2路径.obj") parser.add_argument("--out_path", type=str, default="./") parser.add_argument("--save_obj", action="store_true") args = parser.parse_args()
#Load model mesh1 = trimesh.load(args.obj1_path)
#To get vertices and faces for next steps v1 = mesh1.vertices #这样得到的v,f格式是trimesh 内置的格式,不能直接用于其它计算,需要转换为numpy f1 = mesh1.faces v1 = np.array(v1) f1 = np.array(f1)
# #rotate(optional) # R = make_rotate(0, math.radians(-50), 0) # v1 = np.dot(v1, R)
mesh2 = trimesh.load(args.obj2_path) v2 = mesh2.vertices #这样得到的v,f格式是trimesh 内置的格式,不能直接用于其它计算,需要转换为numpy f2 = mesh2.faces v2 = np.array(v2) f2 = np.array(f2)
# ################other steps################# # #registration(optional) # mesh2t= trimesh.Trimesh(vertices = v2, faces = f2) # mesh_to_other = trimesh.registration.mesh_other(mesh1, mesh2t, samples=500, scale=False, icp_first=10, icp_final=50)
#matching f2 = np.array(f2)+np.shape(v1)[0] v=np.concatenate((v1,v2),axis=0) f=np.concatenate((f1,f2),axis=0)
# ############################################ #Transfer result to mesh obj = trimesh.Trimesh(vertices = v, faces = f) #To imshow # obj.show() if args.save_obj: #To save base=os.path.basename(args.out_path) name=os.path.splitext(base)[0] obj.export(f"{args.out_path}/{name}.obj") #保存为obj |
运行
|
1 |
python show_two_model.py --save_obj (optional) |
示例展示
可以通过给顶点统一增加偏移量使模型散开!

|
1 |
v2 = np.array(v2)+0.5 |