CompletableFuturede介绍
Java 8 引入了 CompletableFuture 类,这是 Java 异步编程的一个重要进展。
CompletableFuture 提供了一种基于未来结果的异步编程模型,允许你以更加直观和易于理解的方式编写非阻塞代码。
CompletableFuturede使用场景
CompletableFuture 主要用于:
- 异步计算:如果你有一些计算任务可以异步执行,并且不想阻塞主线程,可以使用 CompletableFuture。
- 多个并行任务组合:当你有多个独立的异步任务,并且想要在它们都完成后执行某些操作时,可以用 CompletableFuture 来组合它们。
- 异步回调:当异步计算完成后,你需要执行某些后续操作(如更新 UI、保存结果等),可以通过 thenApply(), thenAccept(), thenRun() 等方法指定回调。
- 超时控制:可以为异步任务设置超时限制,防止任务执行时间过长,导致线程被长时间占用。
- 错误处理:在异步任务中,如果有异常发生,可以通过 handle() 或 exceptionally() 方法进行错误处理。
- 多任务的组合与合成:可以将多个异步任务的结果进行合成,产生新的任务。
常用异步编程实现方案
- Thread
特点:
- Thread是 Java 中最基本的并发执行单位,代表一个独立的执行路径。
- Thread可以通过继承 Thread 类或实现 Runnable 接口来创建和启动。
- 线程会从 run() 方法开始执行,run() 方法可以包含任何逻辑。
- 适合处理简单的并发任务,但不适合复杂的并发场景,因为线程管理较为麻烦。
使用示例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running..."); }); thread.start(); } |
- ExecutorService
特点:
- ExecutorService 是一个用于执行异步任务的接口,通常与线程池一起使用。
- 它提供了方法来提交任务、关闭线程池、获取任务结果等。
- ExecutorService 包括多种实现,如 ThreadPoolExecutor,并且支持任务的异步执行。
- 支持有返回值的任务(通过 submit() 方法)和无返回值的任务(通过 execute() 方法)。
使用示例:
有返回值:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); // 创建线程池
Callable<Integer> task = () -> { Thread.sleep(1000); return 42; };
Future<Integer> result = executor.submit(task); // 提交任务并获得 Future 对象 System.out.println("Task result: " + result.get()); // 获取结果
executor.shutdown(); // 关闭线程池 } |
无返回值:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); // 创建线程池
Runnable task = () -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running..."); };
executor.execute(task); // 提交任务
executor.shutdown(); // 关闭线程池 } |
- CountDownLatch
特点:
- CountDownLatch 是一个同步辅助类,允许一个或多个线程等待直到其他线程完成某个操作。
- 使用一个计数器(count)来表示待完成的任务数量,每个任务完成后调用 countDown() 方法,计数器减一。
- 当计数器为零时,所有等待的线程会继续执行。
- CountDownLatch 不能重用,它适合用于多个线程并行执行后,等待所有线程完成的场景。
使用示例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { int totalThreads = 3; CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(totalThreads); // 初始化计数器为3
Runnable task = () -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " finished."); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { latch.countDown(); // 每个线程完成后减少计数器 } };
// 启动多个线程 for (int i = 0; i < totalThreads; i++) { new Thread(task).start(); }
latch.await(); // 等待计数器归零 System.out.println("All tasks are finished."); } |
- CyclicBarrier
特点:
- CyclicBarrier 允许一组线程互相等待,直到所有线程都到达一个公共屏障点,然后所有线程再一起继续执行。
- 它的计数器每次归零后会重置,适合用来处理多轮同步任务。
- 每当所有线程到达屏障点时,都会执行一个可选的动作(如回调函数)。
使用示例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { int totalThreads = 3; CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(totalThreads, () -> { System.out.println("All threads reached the barrier point, proceeding..."); });
Runnable task = () -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " reached the barrier."); barrier.await(); // 等待其他线程到达屏障点 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } };
// 启动多个线程 for (int i = 0; i < totalThreads; i++) { new Thread(task).start(); } } |
- ForkJoinPool
特点:
- ForkJoinPool 是专门用于执行递归任务的线程池,特别适合大规模并行计算。
- 它将任务分割成多个子任务并通过递归的方式处理(“fork”),然后合并子任务的结果(“join”)。
- 在 ForkJoinPool 中,任务拆分采用工作窃取算法,尽量平衡工作负载,提升性能。
使用示例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ForkJoinPoolExample { public static void main(String[] args) { ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); // 创建 ForkJoinPool int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}; RecursiveTask<Integer> task = new SumTask(array, 0, array.length); int result = pool.invoke(task); // 执行任务并获取结果 System.out.println("Sum is: " + result); } }
class SumTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer> { private int[] array; private int start, end;
public SumTask(int[] array, int start, int end) { this.array = array; this.start = start; this.end = end; }
@Override protected Integer compute() { if (end - start <= 2) { // 基础情况 int sum = 0; for (int i = start; i < end; i++) { sum += array[i]; } return sum; } else { int mid = (start + end) / 2; SumTask task1 = new SumTask(array, start, mid); SumTask task2 = new SumTask(array, mid, end); task1.fork(); // 异步执行 task2.fork(); return task1.join() + task2.join(); // 合并结果 } } } |
- CompletableFuture
特点:
- CompletableFuture 是 Java 8 引入的异步编程框架,允许你以非阻塞的方式处理任务。
- 它支持任务的组合、回调、异常处理等,适合用于处理复杂的异步任务链。
- 可以通过 supplyAsync()、thenApply() 等方法定义异步任务的执行流程。
使用示例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return 42; });
// 链式调用,处理结果 CompletableFuture<Integer> result = future.thenApplyAsync(value -> value * 2);
System.out.println("Result: " + result.get()); // 输出结果 } |
各种实现方案总结
| 并发方式 | 特点 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thread | - 最基本的线程创建方式- 通过继承Thread 或实现Runnable 接口创建任务 | - 简单直观 | - 需要手动管理线程,容易资源浪费或死锁- 无法直接返回任务结果- 对复杂任务协调不便 |
| ExecutorService | - 通过线程池管理线程- 提供任务的调度、执行、生命周期管理 | - 提供线程池避免手动创建和销毁线程,减少资源浪费- 支持任务的结果返回 | - 任务间依赖和组合较复杂-get() 方法阻塞线程,难以实现非阻塞 |
| CountDownLatch | - 用于等待多个任务完成后执行后续操作- 使用计数器控制任务执行 | - 可以控制任务同步,确保多个任务完成后继续执行 | - 只适用于等待任务完成,无法处理任务的依赖关系- 只能使用一次 |
| CyclicBarrier | - 用于多个线程在某一点上等待- 可重复使用,适合同步多任务 | - 可重复使用,适合多次任务同步 | - 不如CompletableFuture 灵活- 仅适合特定的同步场景 |
| ForkJoinPool | - 专为递归分治任务设计的线程池- 支持任务拆分和合并 | - 高效利用多核处理器,适合分治算法- 支持任务拆分和合并 | - 对于非递归任务不适合- 异常处理不如CompletableFuture 灵活 |
| CompletableFuture | - 基于Future 设计的异步编程API- 支持非阻塞的任务组合和回调处理 | - 支持链式调用,异步任务组合,避免阻塞- 可以处理异常,支持并行处理和同步等待- 支持thenApply、thenAccept 等多种处理方式,简化代码 | - 复杂任务时调试困难- 异常处理仍较为复杂- 比ExecutorService 稍显复杂 |
- Thread:最基础的并发方式,直接通过线程控制执行,但缺乏高级功能。
- ExecutorService:基于线程池的高层接口,能够有效管理线程资源和任务执行。
- CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier:用于线程间的同步协调。CountDownLatch 等待特定任务完成,而 CyclicBarrier 可重复用于多次任务同步。
- ForkJoinPool:适用于任务拆分和合并的场景,特别是递归分治任务。
- CompletableFuture:提供更灵活的异步任务处理方式,支持链式调用、异步执行及异常处理,适合复杂的并发任务调度。
CompletableFuturede结构
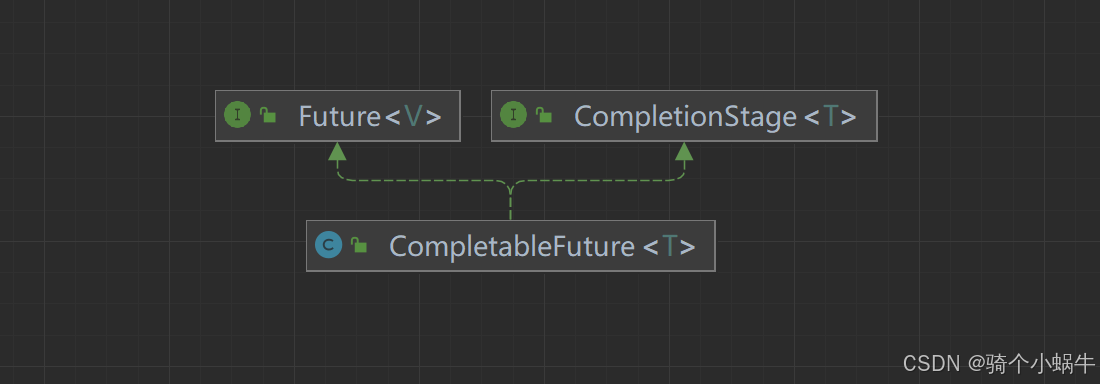
CompletableFuture实现了Future接口和CompletionStage接口。
结构梳理
| 相关接口 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Future | 是一个表示异步计算结果的接口。它提供了方法来检查异步计算是否完成、获取计算的结果以及取消计算。 |
| CompletionStage | 是一个表示异步计算结果的接口,提供了处理计算结果的非阻塞操作。与 Future 不同,CompletionStage 采用链式调用,可以更灵活地组合多个异步操作。 |
- Future接口
Future接口是JDK 5引入的,该接口属于java.util.concurrent包。
Future接口的目的是表示异步计算的结果,它允许你提交一个任务给一个 Executor(执行器),并在稍后获取任务的结果。
主要方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| get() | 阻塞当前线程,直到异步计算完成,并返回计算结果 |
| get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 阻塞当前线程,直到异步计算完成或超时,并返回计算结果 |
| isDone() | 检查异步计算是否完成 |
| cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) | 尝试取消异步计算 |
| isCancelled() | 检查异步计算是否被取消。 |
- CompletionStage接口
CompletionStage 接口是 Java 8 引入的一个重要接口,用于描述异步计算的生命周期和结果。
CompletionStage 提供了一套方法,用于处理异步计算的结果、组合多个计算、处理异常等。
主要方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| thenApply | 在当前阶段完成后,应用给定的 Function,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenAcceptAsync | 异步地执行指定的 Consumer,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage,该阶段没有结果。 |
| thenComposeAsync | 异步地将当前阶段的结果应用于一个返回 CompletionStage 的函数,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenCombine | 在两个 CompletionStage 都完成后,使用给定的 BiFunction 合并它们的结果,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| runAfterEitherAsync | 在任意一个给定的两个 CompletionStage 完成后,异步地执行指定的 Runnable。 |
| thenAccept | 在当前阶段完成后,执行指定的 Consumer,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage,该阶段没有结果。 |
| runAfterEither | 在任意一个给定的两个 CompletionStage 完成后,执行指定的 Runnable。 |
| thenCombineAsync | 在两个 CompletionStage 都完成后,异步地使用给定的 BiFunction 合并它们的结果,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenAcceptBothAsync | 在两个 CompletionStage 都完成后,异步地执行指定的 BiConsumer,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| applyToEither | 在两个 CompletionStage 中任意一个完成后,应用给定的 Function,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| applyToEitherAsync | 在两个 CompletionStage 中任意一个完成后,异步地应用给定的 Function,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| runAfterBothAsync | 在两个 CompletionStage 都完成后,异步地执行指定的 Runnable,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenAcceptBothAsync | 在两个 CompletionStage 都完成后,异步地执行指定的 BiConsumer。 |
| acceptEitherAsync | 在两个 CompletionStage 中任意一个完成后,异步地执行指定的 Consumer,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| handleAsync | 异步地处理当前阶段的结果或异常,应用给定的 BiFunction,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenComposeAsync | 同 thenCompose,但异步地应用给定的函数,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenCombineAsync | 同 thenCombine,但异步地使用给定的 BiFunction 合并两个 CompletionStage 的结果。 |
| exceptionally | 如果当前阶段以异常完成,则应用指定的 Function 处理该异常,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| acceptEither | 在两个 CompletionStage 中任意一个完成后,执行指定的 Consumer。 |
| thenCompose | 将当前阶段的结果应用于一个返回 CompletionStage 的函数,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| handle | 处理当前阶段的结果或异常,应用给定的 BiFunction,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenAcceptBoth | 在两个 CompletionStage 都完成后,执行指定的 BiConsumer。 |
| thenApplyAsync | 异步地应用给定的 Function,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| whenCompleteAsync | 异步地执行指定的 BiConsumer,无论结果如何,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| applyToEitherAsync | 同 applyToEither,但异步地应用给定的 Function,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| acceptEitherAsync | 同 acceptEither,但异步地执行指定的 Consumer,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| runAfterEitherAsync | 同 runAfterEither,但异步地执行指定的 Runnable,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenRunAsync | 异步地执行指定的 Runnable,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage,该阶段没有结果。 |
| runAfterBoth | 在两个 CompletionStage 都完成后,执行指定的 Runnable。 |
| whenComplete | 在当前阶段完成后,无论结果如何,执行指定的 BiConsumer,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage。 |
| thenRunAsync | 异步地执行指定的 Runnable,并返回一个新的 CompletionStage,该阶段没有结果。 |
常用方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| supplyAsync() | 异步地运行一个带返回值的任务。 |
| runAsync() | 异步地运行一个无返回值的任务。 |
| thenApply() | 当 CompletableFuture 任务完成时执行某个操作,并返回新的结果。 |
| thenAccept() | 当任务完成时执行某个操作,但不返回结果。 |
| thenRun() | 当任务完成时执行某个操作,无需返回结果。 |
| exceptionally() | 用于处理任务执行中发生的异常。 |
| handle() | 处理任务执行中的正常结果或异常结果。 |
| allOf() | 等待多个 CompletableFuture 全部完成,返回一个新的 CompletableFuture。 |
| anyOf() | 等待多个 CompletableFuture 中的任意一个完成。 |
CompletableFuture使用示例
1. 基本异步操作
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync() 和 CompletableFuture.runAsync() 是最常用的启动异步任务的方法。
- supplyAsync() 用于执行带返回值的异步任务。
- runAsync() 用于执行不带返回值的异步任务。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { // 带返回值的异步任务 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟耗时任务 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return 42; // 返回结果 });
// 获取异步任务的结果 Integer result = future.get(); // 阻塞,直到任务完成 System.out.println("Result: " + result); } |
2. 任务链式调用
通过 thenApply(), thenAccept(), thenRun() 等方法,可以将多个异步任务串联在一起。
- thenApply() 用于处理任务的返回值。
- thenAccept() 用于消费返回值,但不返回结果。
- thenRun() 用于执行没有返回值的操作。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return 42; // 返回结果 });
// 链式调用,先处理结果,再转换 CompletableFuture<Integer> resultFuture = future .thenApply(value -> value * 2) // 将值乘以2 .thenApply(value -> value + 10); // 再加10
Integer result = resultFuture.get(); // 获取最终结果 System.out.println("Final Result: " + result); // 输出 94 } |
3. 多个异步任务组合
使用 thenCombine()、thenCompose()、allOf() 和 anyOf() 等方法可以组合多个异步任务,执行复杂的操作。
- thenCombine() 用于将两个独立的异步任务的结果合并。
- thenCompose() 用于将第一个异步任务的结果作为参数传递给下一个异步任务。
- allOf() 用于等待多个异步任务完成,并且不关心每个任务的结果。
- anyOf() 用于等待多个异步任务中的任意一个完成。
示例1:组合两个异步任务
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return 10; });
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return 20; });
// 合并两个任务的结果 CompletableFuture<Integer> combinedFuture = future1 .thenCombine(future2, (result1, result2) -> result1 + result2); // 将两个结果相加
Integer result = combinedFuture.get(); // 获取最终结果 System.out.println("Combined Result: " + result); // 输出 30 } |
示例2:使用 allOf() 等待多个任务完成
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("Task 1 completed"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } });
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1500); System.out.println("Task 2 completed"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } });
// 等待多个任务全部完成 CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2).join();
System.out.println("All tasks are completed."); } |
4. 异常处理
在异步任务中,异常可能会发生。CompletableFuture 提供了 exceptionally() 和 handle() 方法来处理异常。
- exceptionally() 用于捕获异常并提供替代值。
- handle() 可以处理正常结果和异常。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { if (true) { throw new RuntimeException("Something went wrong!"); } return 42; });
// 使用 exceptionally 处理异常并提供默认值 CompletableFuture<Integer> resultFuture = future.exceptionally(ex -> { System.out.println("Exception occurred: " + ex.getMessage()); return -1; // 返回默认值 });
Integer result = resultFuture.get(); // 获取结果 System.out.println("Result: " + result); // 输出 -1 } |
5. 并行执行多个任务
使用 CompletableFuture.supplyAsync() 或 runAsync() 来并行执行多个任务,然后使用 allOf() 或 anyOf() 等方法等待这些任务的完成。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); return 1; } catch (InterruptedException e) { return 0; } });
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(500); return 2; } catch (InterruptedException e) { return 0; } });
// 等待所有任务完成并合并结果 CompletableFuture<Integer> result = future1 .thenCombine(future2, (res1, res2) -> res1 + res2); // 将两个结果相加
System.out.println("Combined result: " + result.get()); // 输出 3 } |
6. 处理返回值的转换
通过 thenApply() 等方法可以对异步任务的结果进行转换处理。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 10);
// 转换结果:将值乘以2 CompletableFuture<Integer> transformedFuture = future.thenApply(value -> value * 2);
System.out.println("Transformed Result: " + transformedFuture.get()); // 输出 20 } |