1.概述
C++容器属于STL(标准模板库)中的一部分(六大组件之一),从字面意思理解,生活中的容器用来存放(容纳)水或者食物,东西,而C++中的容器用来存放各种各样的数据,不同的容器具有不同的特性,下图(思维导图)中列举除了常见的几种C++容器,而这部分C++的容器与python中的序列有很多相似之处,也许这也很好地印证了江湖上“C生万物”的说法。因本人是学完python后才学C++的,突然有种:“山重水复疑无路,柳暗花明又一村”的感觉。因为python是偏向于顶层的语言,那时候什么迭代器,生成器之类的东西都不是非常清楚,然后在C++中又遇到了类似内容,便有了更好的理解,也许这就是很多人不建议初学者学习python的原因吧。
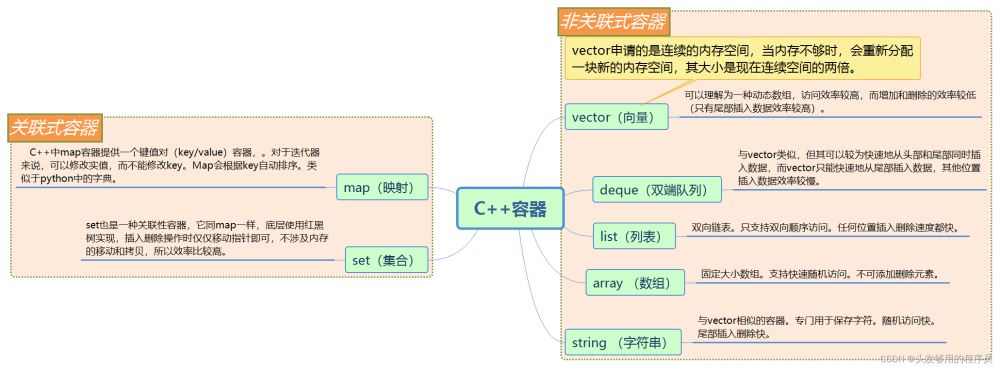
2.容器详解
2.1vector(向量)
从这个命名就可以很好地理解,在线性代数中,向量是一维的结构,而在容器中,向量也是看似一维的存储形式。可以理解为长度可变的数组。只不过在尾部增删数据的时候效率最高,其他位置增删数据则效率较低。举个例子(开胃菜):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
vector<int> V;
V.push_back(1);
V.push_back(2);
V.push_back(1);
V.push_back(2);
cout << V[0] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
打印输出:1。
从上面的例子可以看出,向量和数组的用法极其类似。当然,容器还有一个极其好用的功能,就是容器的嵌套使用。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
vector<vector<int>> V;
vector<int> sub_V;
sub_V.push_back(1);
sub_V.push_back(2);
sub_V.push_back(1);
V.push_back(sub_V);
cout << V[0][1] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
打印输出2这个时候的向量可以看作是一个二维数组,当然比二维数组更加灵活、强大。
当然向量容器还有其他更加丰富的操作。比如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int size = vec1.size(); //元素个数
bool isEmpty = vec1.empty(); //判断是否为空
vec1.insert(vec1.end(),5,3); //从vec1.back位置插入5个值为3的元素
vec1.pop_back(); //删除末尾元素
vec1.erase(vec1.begin(),vec1.end());//删除之间的元素,其他元素前移
cout<<(vec1==vec2)?true:false; //判断是否相等==、!=、>=、<=...
vector<int>::iterator iter = vec1.begin(); //获取迭代器首地址
vector<int>::const_iterator c_iter = vec1.begin(); //获取const类型迭代器
vec1.clear(); //清空元素
|
举个最常见的例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
vector<int> V;
V.push_back(1);
V.push_back(2);
V.push_back(3);
for (vector<int>::iterator it = V.begin(); it != V.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "==========================" << endl;
V.insert(V.begin() + 2,10);
for (vector<int>::iterator it = V.begin(); it != V.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
注意如果不是在其尾部插入数据,要传入插入位置的迭代器。
打印输出:
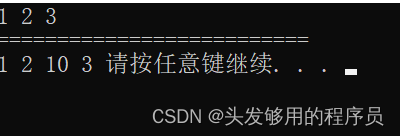
2.2deque(双端队列)
deque,顾名思义,从前后两端都可以进行数据的插入和删除操作,同时支持数据的快速随机访问。举个例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
deque<int> D;
D.push_back(1);
D.push_back(2);
D.push_back(3);
for (deque<int>::iterator it = D.begin(); it != D.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "============在其索引2的位置插入10:" << endl;
D.insert(D.begin() + 2,10);
for (deque<int>::iterator it = D.begin(); it != D.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "============在其头部插入0:" << endl;
D.push_front(0);
for (deque<int>::iterator it = D.begin(); it != D.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "============在其头部弹出0:" << endl;
D.pop_front();
for (deque<int>::iterator it = D.begin(); it != D.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
打印输出:

2.3list(列表)
列表是用双向链表实现的,所谓的双向链表,指的是既可以从链表的头部开始搜索找到链表的尾部,也可以进行反向搜索,从尾部到头部。这使得list在任何位置插入和删除元素都变得非常高效,但是随机访问速度变得非常慢,因为保存的地址是不连续的,所以list没有重载[]运算符,也就是说,访问list元素的时候,再也不像向量和双端队列那么方便,不可以像我们以前在C语言的时候,访问数组那样对其元素进行访问。
一起来看个例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
//list的创建和初始化
list<int> lst1; //创建空list
list<int> lst2(3); //创建含有三个元素的list
list<int> lst3(3, 2); //创建含有三个元素的值为2的list
list<int> lst4(lst3); //使用lst3初始化lst4
list<int> lst5(lst3.begin(), lst3.end()); //同lst4
cout << "lst4中的元素有:" << endl;
for (list<int>::iterator it = lst4.begin(); it != lst4.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "lst5中的元素有:" << endl;
for (list<int>::iterator it = lst5.begin(); it != lst5.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
运行,打印输出:

然后再来看一个元素的添加,排序的例子。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
//list的创建和初始化
list<int> lst1; //创建空list
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
lst1.push_back(9-i); //添加值
cout << "lst1中的元素有:" << endl;
for (list<int>::iterator it = lst1.begin(); it != lst1.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "对lst1中的元素进行排序:" << endl;
lst1.sort();
for (list<int>::iterator it = lst1.begin(); it != lst1.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "在索引为5的地方插入999:" << endl;
list<int>::iterator insert_it = lst1.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
insert_it++;
lst1.insert(insert_it, 3, 999);
for (list<int>::iterator it = lst1.begin(); it != lst1.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "删除相邻重复元素后:" << endl;
lst1.unique(); //删除相邻重复元素
for (list<int>::iterator it = lst1.begin(); it != lst1.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
运行后,打印输出:
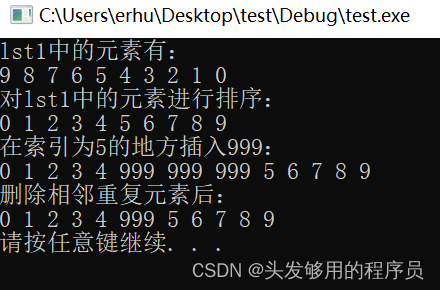
特别注意,由于list的底层是双向链表,因此insert操作无法直接像向量和双端队列一样直接插入数据,只能通过迭代器的自加移动到相应位置,再插入数据。
2.4 array(数组)
array和C语言中的数组没有太大的区别,建立后只能存储一种类型的数据,且不能改变大小。比较简单,举个例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
array<int, 4> arr = {1, 3, 2};
cout << "arr values:" << std::endl;
for (array<int, 4>::iterator it = arr.begin(); it != arr.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "sizeof(arr) = " << sizeof(arr) << endl;
cout << "size of arr = " << arr.size() << endl;
cout << "max size arr = " << arr.max_size() << endl;
cout << "empty = " << (arr.empty() ? "no" : "yes") << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
当然,最常见的,array也支持嵌套,可以采用这样的方式来构建二维(多维)数组,由于比较简单,就不举例了。
2.5 string(字符串)
与vector相似的容器。专门用于保存字符。随机访问快。尾部插入删除快。在部分说法中,string不算是STL容器,但是为了内容的完整性,我们还是将其一并学习。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
string s1 = "Bob:";
string s2("hellow world!");
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i];
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
cout << s2[i];
}
cout << endl;
cout << s1 + s2 << endl;
s1.insert(s1.size(),"you say ");
cout << s1 + s2 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
运行,打印输出如下:

通过以上例子可以发现,与我们在C语言中学习的string并没有多少区别,其实本身区别也不是很大,只是在创建了之后还可以添加元素(盲猜是新创建了一个同名的string,仅此而已),且添加元素的方式也很简单,直接通过insert(插入位置,需要添加的字符串)这样的格式添加即可。上面一个例子是从末尾添加的,所以索引肯定是s1.size()。当然还有字符串的相加,字符串的比较等,都是属于更为基础的内容,没有添加到例子当中去,感兴趣的同学可以自己找资料去学习。
2.6 map(映射)
map容器和python中的字典非常类似,或者说一模一样。都是通过键值对的方式来存储和访问数据的,底层是通过红黑树来实现的。先来看个map的创建以及初始化的例子。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
//map的创建和初始化
//第一种:用insert函数插入pair数据:
map<int, string> my_map;
my_map.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "first"));
my_map.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "second"));
//第二种:用insert函数插入value_type数据:
my_map.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(3, "first"));
my_map.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(4, "second"));
//第三种:用数组的方式直接赋值:
my_map[5] = "first";
my_map[6] = "second";
map<int, string>::iterator it; //迭代器遍历
for (it = my_map.begin(); it != my_map.end(); it++)
cout << it->first << "->" <<it->second << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
运行,打印输出如下结果:

从以上结果可以看出,其中数组直接赋值的方法最简单直接,最容易理解。当然map保存的是键值对,所以前面的int类型数据(key)并不代表其位置。比方说,我们将其中的int修改为float也是可以的。代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
//map的创建和初始化
//第一种:用insert函数插入pair数据:
map<float, string> my_map;
my_map.insert(pair<float, string>(1, "first"));
my_map.insert(pair<float, string>(2, "second"));
//第二种:用insert函数插入value_type数据:
my_map.insert(map<float, string>::value_type(3, "first"));
my_map.insert(map<float, string>::value_type(4, "second"));
//第三种:用数组的方式直接赋值:
my_map[5.3] = "first";
my_map[6.6] = "second";
map<float, string>::iterator it; //迭代器遍历
for (it = my_map.begin(); it != my_map.end(); it++)
cout << it->first << "->" <<it->second << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
当然,同其他的容器类型一样,map同样支持嵌套,比如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
//map的嵌套用法
map<int,map<int,string>> my_map;
my_map[1][1] = "张三";
my_map[1][2] = "李四";
my_map[1][3] = "王五";
for (map<int, map<int, string>>::iterator it = my_map.begin(); it != my_map.end(); it++)
{
for (map<int, string>::iterator in_it = it->second.begin(); in_it != it->second.end(); in_it++)
{
cout << it->first << "年级" << in_it->first << "号同学:" << in_it->second << endl;
}
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
运行,打印输出如下:

还有一个很重要的问题,就是map元素的删除。map元素的删除有好多种方法,下面仅仅列举 常见几种。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void printMap(const map<string, int>& students)
{
for (auto ii = students.begin(); ii != students.end(); ii++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << ii->first
<< " \t诗作: " << ii->second << "篇"
<< endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
map<string, int> students;
students["李白"] = 346;
students["杜甫"] = 300;
students["王维"] = 200;
students["李商隐"] = 113;
students["杜牧"] = 156;
cout << "原map:" << endl;
printMap(students);
students.erase("李白");
cout << "删除 李白 后:" << endl;
printMap(students);
students.erase(std::begin(students));
cout << "删除第一个元素后:" << endl;
printMap(students);
map<string, int>::iterator iter = students.find("杜牧");
students.erase(iter);
cout << "删除杜牧后:" << endl;
printMap(students);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
运行后,打印输出:
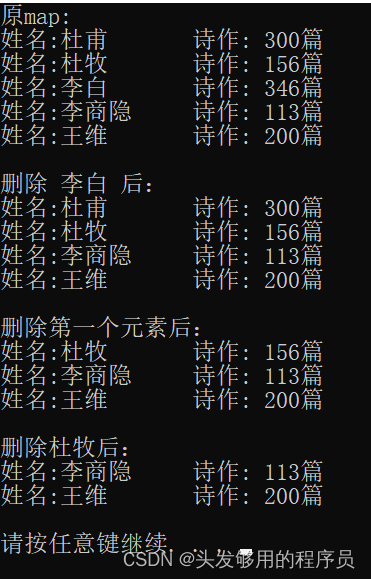
从上面的例子也可以看出,map中的键值对不一定是按照我们创建的顺序保存数据,map会按照key的值内部进行排序,但是保持其键值对的对应关系不变。
2.7 set(集合)
set也是一种关联性容器,它同map一样,底层使用红黑树实现,插入删除操作时仅仅移动指针即可,不涉及内存的移动和拷贝,所以效率比较高。从中文名就可以明显地看出,在set中不会存在重复的元素,若是保存相同的元素,将直接视为无效,我们先来看个简单的例子(关于set的创建和元素的添加等):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec;
for (vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i != 10; i++) {
ivec.push_back(i);
ivec.push_back(i);
}
set<int> iset(ivec.begin(), ivec.end());
cout << "向量中的元素为:" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = ivec.begin(); it != ivec.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "集合中的元素为:" << endl;
for (set<int>::iterator it = iset.begin(); it != iset.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "向量的大小为:" << endl;
cout << ivec.size() << endl;
cout << "集合的大小为:" << endl;
cout << iset.size() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
打印输出:
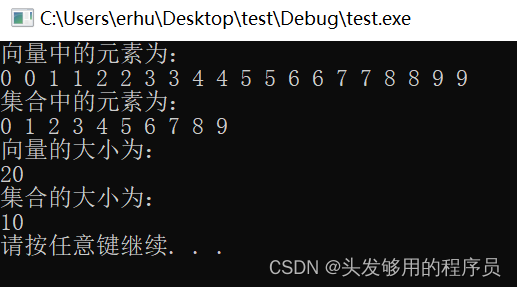
上面例子的方法,相当于直接将向量的值赋给了集合,从而顺便创建了集合,那么如果想通过逐一赋值的方式创建集合,又该如何编写代码呢?如何清除集合中的元素呢?以及是否知道某元素在集合中呢?同样我们通过一段代码来看一下。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 程序的主函数
int main()
{
set<string> set1;
set1.insert("the");
//删除集合
while (!set1.empty())
{
//获取头部
set<string>::iterator it = set1.begin();
//打印头部元素
cout << *it << endl;
//从头部删除元素
set1.erase(set1.begin());
}
set<int>set2;
for (int i = 100; i < 110; i++)
set2.insert(i);
cout << "set2中5出现的次数为:";
cout << set2.count(5) << endl;
set2.clear();
cout << "set2清除之后的大小为:";
cout << set2.size() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
|
运行,打印输出:

通过以上的例子可以发现,set可以直接通过insert()方法添加数据,而数据内部是自动排序的,所以不用担心数据的顺序问题,当然也可以像map那样,通过迭代器添加到指定位置,查询set中有无该数据可以直接使用count()方法,有则返回1,无则返回0。